Protection from Harmful Radiation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is Radiation?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss harmful radiation, especially ultraviolet radiation. Can anyone tell me where UV radiation comes from?

From the Sun, right?

Exactly! The Sun emits various types of radiation, including UV radiation, which can be harmful in excessive amounts. Remember, we often use the acronym UVA, UVB, and UVC to categorize these rays. Can someone tell me the primary concern regarding UV radiation?

It's bad for our skin and can cause cancer.

Correct! That's why understanding how our atmosphere protects us from these harmful rays is critical.
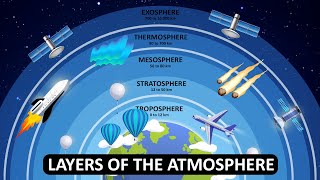
The Ozone Layer
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the key components of our atmosphere that protects us is the ozone layer. Can anyone explain what it does?

It absorbs UV radiation from the Sun.

That's right! The ozone layer is critical because it absorbs the majority of the Sun's harmful UV radiation. This helps prevent skin damage and other health issues. Can anyone remember the specific layer of the atmosphere where the ozone is found?

In the stratosphere!

Excellent! The stratosphere plays a vital role in filtering harmful radiation.
Effects of UV Radiation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss what happens when the ozone layer is damaged. What could be the impact of increased UV radiation on us?

More cases of skin cancer?

That's one major impact. Increased UV exposure can also lead to cataracts and weakened immune systems. Not just humans, but increased UV radiation can also harm ecosystems and wildlife. Can anyone think of how it might affect plant life?

It could damage their growth?

Exactly! Many plants are sensitive to UV radiation, and excessive exposure can hinder their growth and affect food chains.
Protecting the Ozone Layer
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What can we do to help protect our ozone layer?

Stop using products with CFCs?

Exactly! Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) have been a significant contributor to ozone layer depletion. The global agreement known as the Montreal Protocol has led to significant reductions in CFC usage. Why do you think it’s important for us to continue these efforts?

To prevent more damage and protect our health!

Absolutely! Protecting the ozone is a collective global responsibility.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The atmosphere plays a crucial role in filtering harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs and scatters this radiation, safeguarding life on Earth from its damaging effects.
Detailed
Protection from Harmful Radiation
The Earth's atmosphere serves as a vital shield that protects life from harmful radiation. The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, which plays a key role in filtering out much of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This protection is essential, as excessive exposure to UV radiation can cause detrimental effects, including skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues. Additionally, the atmosphere absorbs and scatters other harmful radiation, ensuring that only safe levels of solar energy reach the Earth's surface. The effective functioning of this protective layer is crucial for the sustainability of life and the balance of ecosystems on our planet.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
The Role of the Ozone Layer
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere protects life on Earth by filtering out harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun using the ozone layer in the stratosphere.
Detailed Explanation
The ozone layer is a region of the stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) molecules. This layer plays a critical role in absorbing the majority of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. There are different types of UV radiation, and some of them can cause serious damage to living organisms, including skin cancer in humans and detrimental effects on plants and marine life. By filtering out around 98% of the Sun's UV radiation, the ozone layer protects all life on Earth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ozone layer like a huge, invisible sunscreen for the Earth. Just like how sunscreen protects your skin from harmful rays when you go outside, the ozone layer absorbs the bad rays from the Sun, making it safe for us and other life forms to thrive on our planet.
Absorption and Scattering of Radiation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere also absorbs and scatters other harmful radiation, preventing excessive solar energy from reaching the surface.
Detailed Explanation
In addition to the ozone layer’s role in filtering UV radiation, the entire atmosphere helps to absorb and scatter various types of radiation that come from the Sun. Different gases and particles, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide, absorb some forms of radiation, while they scatter others. This not only prevents excessive solar energy from reaching the Earth's surface but also helps to maintain a balanced climate. If too much solar energy were to reach the Earth, it could lead to higher temperatures and disrupt the climate and ecosystems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine holding a heavy umbrella on a sunny day. The umbrella not only protects you from direct sunlight but also prevents heat from overwhelming you. Similarly, the atmosphere acts like that umbrella, absorbing and deflecting harmful radiation and ensuring that the Earth remains at a suitable temperature for life.
Key Concepts
-
Ozone Layer: Filters harmful UV radiation from the Sun.
-
Chlorofluorocarbons: Chemicals that have contributed to the depletion of the ozone layer.
-
UV Radiation Effects: Can lead to health concerns such as skin cancer and cataracts.
Examples & Applications
The ozone layer absorbs about 97-99% of the Sun's harmful UV radiation.
Increased UV radiation can lead to a rise in skin cancer rates.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Ozone so high, protects from the sun’s shy, keeping our skin from saying bye!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a land where sunlight shone brightly, there was an invisible shield called the ozone layer that protected all living beings from harmful rays, ensuring they could play outside safely.
Memory Tools
Remember CFC: Chlorine Flavored Chemicals - that’s what harms our ozone!
Acronyms
UVA, UVB, UVC - Understanding Very Aware protection from light's cruelty!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ultraviolet Radiation (UV)
A type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun, which can be harmful to living organisms.
- Ozone Layer
A region of the Earth's stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) and absorbs most of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Chemical compounds previously used in aerosol sprays and refrigerants that contribute to ozone depletion.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
