Global Warming
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Human Activities and Greenhouse Gases
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss how certain human activities contribute to global warming by increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Can anyone tell me what greenhouse gases are?

Greenhouse gases are gases that trap heat in the atmosphere.

Exactly! The key ones are carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Remember this acronym: CMN for Carbon, Methane, and Nitrous oxide. What are some activities that release these gases?

Burning fossil fuels for energy and deforestation.

Right! Burning fossil fuels is the major contributor to CO2 emissions. What effects do these increased gases have on the planet?

They lead to climate change and extreme weather.

Correct! In summary, human activities release greenhouse gases that trap heat, resulting in global warming.
Impacts of Global Warming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into the impacts of global warming. What are some of the noticeable changes we have observed?

Rising sea levels and more frequent natural disasters.

Yes! Sea levels are rising due to melting polar ice and thermal expansion of water. Remember, MRS: Melting, Rising Sea levels. What about ecosystems?

Ecosystems are being affected, resulting in habitat loss for many species.

Exactly! And it also leads to loss of biodiversity. As we summarize, global warming has vast implications, including environmental, economic, and social challenges.
Solutions to Mitigate Global Warming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about solutions. What can we do to combat global warming?

Switching to renewable energy sources like solar and wind.

Correct! This transition is critical. Remember the acronym: R.E.S.T. for Renewable Energy Solutions Together. How about individual actions?

We can reduce our carbon footprint by using public transport or cycling.

Great point! Individual actions combined with international cooperation are vital to making a significant impact. In summary, both collective and personal efforts are essential to combatting global warming.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Global warming refers to the increase in Earth's average surface temperature due to human-induced greenhouse gas emissions. The section discusses the sources of these emissions, their impact on the environment, and the necessity for international collaboration to mitigate this issue through renewable energy and sustainability.
Detailed
Global Warming
Global warming refers to the long-term rise in Earth's average surface temperature due to human activities, mainly through the emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide (CO2). These emissions are largely a result of burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. This increase in greenhouse gases enhances the natural greenhouse effect, which leads to a rise in global temperatures, impacting weather patterns, melting polar ice, and rising sea levels.
Key Points Covered:
- Causes: Human activities, specifically fossil fuel consumption, deforestation, and agricultural practices, significantly increase atmospheric concentrations of GHGs.
- Impacts: Consequences of global warming include extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels, which pose significant threats to ecosystems and human livelihoods.
- Solutions: Addressing global warming requires collective action, including the reduction of emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and promoting sustainable practices worldwide.
Youtube Videos


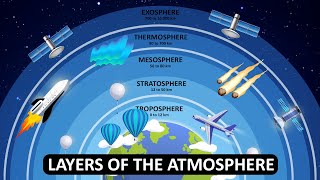




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Increase in Greenhouse Gases
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The increase in greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, due to human activities, is contributing to global warming, which is causing rising global temperatures, melting polar ice, and changing weather patterns.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses how human activities, such as burning fossil fuels for energy and transportation, lead to an increase in greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun, creating a 'greenhouse effect' that warms the Earth's surface. As a result of this increased warming, we notice global temperatures rising, polar ice caps melting, and shifts in regular weather patterns that can lead to more extreme weather events.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the atmosphere like a blanket around the Earth. When we add more greenhouse gases to the blanket by burning coal, oil, and gas, we are thickening it. This means more heat gets trapped underneath, making the Earth warmer. Just like on a cold day when you pull up a thicker blanket to feel warmer, the Earth's 'blanket' is getting thicker as we add more greenhouse gases.
Consequences of Global Warming
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Addressing global warming requires international cooperation to reduce emissions, transition to renewable energy sources, and promote environmental sustainability.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk highlights that addressing the issue of global warming is not something any single country can achieve alone; it requires collaboration among nations. Countries need to work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using cleaner, renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, rather than relying heavily on fossil fuels. Promotion of sustainability also means adopting practices that protect our environment and conserve resources for future generations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider global warming like a global puzzle. Each country has a piece, and to complete the puzzle, they must work together. If one country doesn’t do its part, the picture won’t be complete; this is similar to how we need all nations to contribute by cutting down emissions and switching to renewable energy to effectively combat global warming.
Key Concepts
-
Human activities including burning fossil fuels and deforestation contribute significantly to global warming.
-
The increase in greenhouse gases leads to rising global temperatures and climate change.
-
Global warming impacts ecosystems, weather patterns, and sea levels.
-
International cooperation and renewable energy are crucial for addressing global warming.
Examples & Applications
The use of coal and oil for energy increases CO2 emissions, worsening global warming.
Melting ice caps in Greenland are direct evidence of global warming's impact.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Greenhouse gases in the air, trap the heat, that's our care!
Stories
Once there was Earth, so warm and bright, but humans burned fuels, and caused a fright. Ice caps wept as the oceans sighed, global warming spread wide, so we must decide to save our planet, oh pride!
Memory Tools
Remember CMN: Carbon, Methane, Nitrous for GHGs that cause global warming.
Acronyms
R.E.S.T. for Renewable Energy Solutions Together is key to battle global warming.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Greenhouse Gases
Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
A greenhouse gas produced by burning fossil fuels and deforestation, known for its significant role in global warming.
- Global Warming
The long-term increase in Earth's average surface temperature due to human-induced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Energy
Energy derived from natural processes that are continually replenished, such as solar, wind, and hydro power.
- Climate Change
Long-term changes in temperature and typical weather patterns in a place.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
