Weather and Climate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Weather
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

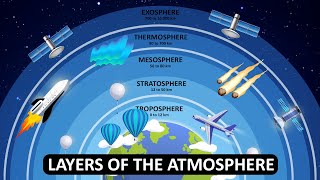
Let's start with weather! Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific location. When we talk about weather, we're looking at variables like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation. Can anyone give me an example of weather conditions?

Today was sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius!

Or it can be rainy, like it was yesterday!

Exactly! Weather can change very quickly. What factors do you think influence these changes?

I think it's due to pressure systems.

And maybe the temperature differences between regions!

Great points! Changes in atmospheric pressure due to the Sun's heating create different weather patterns. Now, let's summarize: weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere, affected by temperature and moisture among other factors.
Exploring Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand weather, let’s discuss climate. Climate is the long-term average of weather patterns in a specific region over periods of 30 years or more. What do you think affects climate?

Latitude probably plays a big role because areas near the equator are usually warmer.

Altitude matters too! Higher elevations can be much cooler.

Absolutely! Distance from seas and prevailing wind systems also influence climate. Climate zones can be categorized as tropical, temperate, polar, and arid based on these long-term weather patterns. Why do you think understanding climate is important?

Because it helps predict future weather patterns!

And we can understand environmental changes like climate change!

Great insights! In summary, climate represents the average weather conditions over a long time and helps us understand broader atmospheric changes.
Climate Change
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss climate change, which refers to long-term changes in climate variables like temperature and precipitation patterns. What do you think causes climate change?

Human activities like burning fossil fuels increase greenhouse gases!

And deforestation reduces the number of trees that can absorb CO2!

Exactly! These activities enhance the greenhouse effect and lead to global warming, melting glaciers, and shifting weather patterns. Why should we care about climate change?

Because it affects all life on Earth!

And we need to make sure future generations can live!

Well said! Climate change impacts our environment, making it crucial to adopt sustainable practices to reduce emissions and conserve resources. Let’s summarize: climate change is primarily influenced by human activities and poses significant threats to our planet.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Weather encompasses the immediate atmospheric conditions such as temperature and precipitation in a specific location, and can change rapidly. In contrast, climate reflects the average weather patterns over an extended period, which are influenced by factors like latitude and altitude. Understanding both weather and climate is essential for analyzing environmental changes, including climate change.
Detailed
Weather and Climate
Weather and climate are fundamental concepts in atmospheric sciences that illustrate the dynamic nature of the atmosphere. Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific location, characterized by phenomena such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation. These variables can change rapidly due to local atmospheric pressure systems and varying geographical factors.
Conversely, climate signifies the long-term patterns of weather observed in a particular region over extended periods, typically defined as 30 years or more. Climate is shaped by numerous influencing factors, including latitude, altitude, proximity to water bodies, and dominant wind systems. As a result, various climate zones are classified, such as tropical, temperate, polar, and arid, based on consistent weather patterns.
A pressing global issue linked to these concepts is climate change, denoting long-term alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns, primarily driven by human activities—like burning fossil fuels—that increase greenhouse gas concentrations. The ramifications of climate change manifest in the form of rising global temperatures, melting glaciers, and shifting weather phenomena, highlighting the necessity for sustainable practices to safeguard the atmosphere for future generations.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Weather
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Weather
○ Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific location, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation.
○ Weather is highly variable and can change quickly due to atmospheric pressure systems and other factors.
Detailed Explanation
Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. It includes elements like temperature, humidity (amount of water vapor in the air), wind speed, and precipitation (like rain or snow). Weather can change rapidly; for example, it might be sunny in the morning and stormy by the afternoon due to shifts in atmospheric pressure. This variability is influenced by various factors and atmospheric systems, like high and low-pressure areas, which can bring different weather conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of weather like a daily mood—just as a person's mood can change from happy to sad quickly, the weather can change from sunny to rainy. For instance, if you've ever experienced sudden rain on a sunny day, you know that weather is quite unpredictable.
Defining Climate
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Climate
○ Climate refers to the long-term average of weather patterns in a particular region over an extended period (typically 30 years or more).
○ It is influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, and prevailing wind systems.
○ Climate zones are classified into categories such as tropical, temperate, polar, and arid based on long-term weather patterns.
Detailed Explanation
Climate is different from weather because it represents the average atmospheric conditions over a long time, usually at least 30 years. It gives us an idea of what the weather is typically like in a region. Factors like how far north or south (latitude) and how high above sea level (altitude) a place is, as well as how close it is to oceans, all influence its climate. For example, areas near the equator tend to have tropical climates, characterized by warm temperatures and lots of rainfall, while polar regions are cold and often have ice.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine climate as the overall flavor of a dish, while weather is like the specific ingredients used on a given day. Just as a dish may regularly be salty or sweet, a region's climate typically has warm, cold, dry, or wet characteristics that define it, but the specific 'taste' on any given day can differ greatly.
Exploring Climate Change
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Climate Change
○ Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and other climate variables. It is often caused by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
○ The impact of climate change includes rising global temperatures, melting glaciers, and shifting weather patterns.
Detailed Explanation
Climate change involves significant and lasting changes in the Earth's climate. These changes can affect not only temperature and precipitation but also the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Many scientists believe that human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels (like coal and gasoline), contribute to climate change by increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. For instance, as temperatures rise, glaciers in polar regions are melting, contributing to higher sea levels and changing ecosystems.
Examples & Analogies
Consider climate change like a car that is getting faster because of a heavy foot on the gas pedal. Normally, cars can change speed gradually, but when someone accelerates too much, they zoom forward quickly. In this analogy, humans are the heavy foot increasing the greenhouse gases and speeding up climate change, leading to notable consequences like flooding in coastal areas due to melting ice.
Key Concepts
-
Weather: Short-term conditions that can change rapidly in a location.
-
Climate: Long-term weather patterns that reflect averages over many years.
-
Climate Change: Long-term shifts in climate primarily caused by human impact.
Examples & Applications
A thunderstorm passing through a city represents a weather condition.
The average temperature of a region over 30 years, showing a trend towards warmer winters represents climate.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Weather is what happens today, Climate's the average, come what may!
Stories
Imagine a farmer checking today's weather for planting, but relying on climate patterns to decide when to harvest.
Memory Tools
W-C-C: Weather is Current, Climate is Consistent, Climate Change is Catastrophic.
Acronyms
W-C-C
Weather
Climate
Climate Change.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Weather
The short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific location, including temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
- Climate
The long-term average of weather patterns in a specific region over an extended period.
- Climate Change
Long-term alterations in climate variables typically caused by human activities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
