Introduction to the Atmosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Importance of the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the atmosphere, which is the layer of gases surrounding our planet. Can anyone tell me why the atmosphere is important for us?

It provides oxygen that we breathe!

And it protects us from harmful radiation!

Exactly! The atmosphere is essential for sustaining life. It's held in place by gravity and contains different gases, water vapor, and dust. What do you think might happen if we didn’t have an atmosphere?

We wouldn’t be able to survive since there would be no oxygen.

And it would be much colder!

You're right! Without it, temperatures would vary drastically, making it inhospitable for life. Remember: the atmosphere = life support. Let’s move on to its composition next.
Composition of the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s break down the atmosphere's composition. Can someone tell me what gas is most abundant in the atmosphere?

Nitrogen!

It makes up 78% of the atmosphere!

Correct! Nitrogen is important because it’s inert and doesn't support combustion. Next, what’s the second most abundant gas?

Oxygen! It’s 21%.

Well done! Oxygen is critical for life. And there’s also argon, which doesn’t react much with other elements. Now, can anyone tell me why carbon dioxide is important?

It's vital for photosynthesis!

Exactly! Remember: **N**itrogen, **O**xygen, **A**rgon, and **C**arbon Dioxide (NOAC) to help you recall the main components of the atmosphere.
Role of Water Vapor in the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about water vapor. What do you think is the significance of water vapor in the atmosphere?

It helps form clouds and precipitation!

And it can affect temperature too, right?

Yes! Water vapor is critical for weather patterns. It varies in concentration and can trap heat, contributing to the greenhouse effect. Let’s try to remember its role: **C**louds, **P**recipitation, and **T**emperature — how about the acronym CPT?

That’s a good way to remember it!

So, water vapor really influences our weather!

Correct! To summarize, water vapor is vital in forming clouds, precipitation, and it impacts temperature regulation.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The atmosphere encompasses a mixture of gases that sustain life, primarily nitrogen and oxygen, along with water vapor that influences weather. Its role extends to temperature regulation, protection from harmful solar radiation, and maintaining the balance of gases necessary for life processes. Understanding the atmosphere's composition and function is key to grasping its impact on Earth's environment.
Detailed
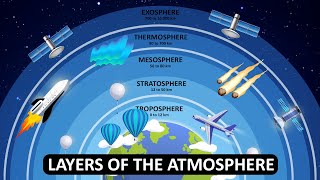
Introduction to the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is defined as the layer of gases surrounding the Earth, retained by gravitational force. It is essential for life as it provides oxygen for respiration, protects against harmful ultraviolet radiation, and stabilizes temperature through the greenhouse effect.
Composition
The atmosphere consists of a mixture of gases:
- Nitrogen (78%): The most abundant and inert gas that does not support combustion.
- Oxygen (21%): Essential for life, enabling respiration and combustion.
- Argon (0.93%): An inert gas with no reactive role.
- Carbon Dioxide (0.04%): Vital for photosynthesis and a significant greenhouse gas.
- Trace Gases: Includes gases like neon and methane which, while present in smaller amounts, have important roles.
Water Vapor
Water vapor is a highly variable component of the atmosphere that plays a critical role in weather patterns, influencing phenomena like clouds and precipitation while contributing to the greenhouse effect,
In summary, the atmosphere is not only life-sustaining through its composition but also plays a fundamental role in Earth's ecosystems and climate regulation.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Atmosphere
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the Earth, held in place by gravity. It is essential for sustaining life, as it provides oxygen, protects us from harmful radiation, and regulates temperature.
The atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases, water vapor, and dust particles that vary in composition at different altitudes.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is essentially a protective layer of gases that envelops the Earth. Think of it like a blanket; it keeps us warm by retaining heat and providing the air we breathe. Gravity plays a crucial role in keeping this layer close to the Earth's surface. It's not just any gas, though—it's a specific mix that includes oxygen for us to breathe, and it serves to filter out harmful radiation from the sun, keeping life on our planet safe. Additionally, the composition of the atmosphere changes with altitude, meaning that the gases we breathe and that contribute to our climate are affected by how high we go in the sky.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the atmosphere as the skin of our planet. Just as your skin protects your body from external threats and helps regulate your temperature, the atmosphere shields the Earth from harmful rays and maintains a stable climate, essential for life. If we didn't have this 'skin', the planet would be exposed to extreme temperatures and cosmic radiation, making it uninhabitable.
Composition of the Atmosphere
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is composed of:
- Nitrogen (78%): The most abundant gas in the atmosphere, which is inert and does not support combustion.
- Oxygen (21%): Essential for respiration and combustion processes, supporting life on Earth.
- Argon (0.93%): An inert gas that does not react with other elements.
- Carbon Dioxide (0.04%): Vital for plant photosynthesis and a key greenhouse gas influencing Earth's climate.
- Other Gases: Trace gases like neon, helium, methane, and ozone exist in small quantities but play important roles in the atmosphere.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is made up primarily of nitrogen and oxygen, which are essential for life. Nitrogen makes up the majority (78%) and is inert, meaning it doesn't react with other substances, while oxygen (21%) is crucial for all aerobic life forms. Argon is present in smaller amounts and is also inert. Carbon dioxide, while only a small fraction of the atmosphere, plays a vital role in natural processes like photosynthesis, where plants convert CO2 into oxygen. Additionally, even trace gases like neon, helium, methane, and ozone, though less abundant, have significant impacts on atmospheric and environmental chemistry.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the atmosphere as a smoothie. The bulk of the drink is made up of a base ingredient—like nitrogen in this case—while other ingredients like fruits and sweeteners—in this case, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and trace gases—are mixed in smaller amounts to create a blend that nourishes us. Just as each fruit has its own unique benefits, every gas in the atmosphere contributes to a balanced environment necessary for life.
Water Vapor
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Water vapor is another crucial component of the atmosphere. It varies in concentration depending on the location and time of day, affecting weather patterns and climate.
Water vapor is responsible for cloud formation, precipitation, and influencing the Earth's temperature through the greenhouse effect.
Detailed Explanation
Water vapor is essentially water in its gas form, and it plays an integral role in weather and climate. Its levels fluctuate based on various factors, including weather and location, leading to varying weather phenomena. For example, when water vapor in the atmosphere cools, it condenses to form clouds, which can lead to rainfall or other precipitation. Additionally, water vapor contributes to the greenhouse effect by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which helps keep the Earth's surface warm enough to support life.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of water vapor like the steam from a pot of boiling water. Just as steam can rise, change shapes, and eventually condense back into water, water vapor behaves similarly in the atmosphere, constantly cycling through different states. This cycle is crucial for all weather, as it helps to create clouds and precipitation that maintain the Earth's ecosystems.
Key Concepts
-
Atmosphere: The layer of gases surrounding Earth.
-
Composition: Major gases include nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.93%), and carbon dioxide (0.04%).
-
Water Vapor: A critical component affecting weather, temperature, and cloud formation.
-
Greenhouse Effect: The process by which specific gases in the atmosphere trap heat.
Examples & Applications
The atmosphere provides the necessary oxygen for humans and animals to breathe, while plants utilize carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis.
Water vapor in the atmosphere can lead to cloud formation and precipitation, which are essential for the water cycle.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The air we breathe is a layer so grand, protects us from rays that are harmful and bland.
Stories
Once upon a time, Earth wore a blanket made of air, where each gas played a role; oxygen helped us care, nitrogen was friendly and stayed so still, while carbon dioxide met plants, giving life a thrill.
Memory Tools
N-O-A-C: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, Carbon Dioxide – remember the gases that help Earth abide.
Acronyms
CPT for Water Vapor – Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth, held by gravity, which is essential for supporting life.
- Nitrogen
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere, making up 78%, which is inert and does not support combustion.
- Oxygen
A gas that makes up 21% of the atmosphere and is essential for respiration and combustion.
- Water Vapor
Water in its gaseous state found in the atmosphere, essential for weather and temperature regulation.
- Greenhouse Effect
The process by which certain gases trap heat in the atmosphere, regulating Earth's temperature.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
