Biodiversity and Conservation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're discussing biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life on Earth. Can anyone tell me why biodiversity is important?

I think it's important because having different species helps ecosystems stay stable.

Exactly! The more diverse an ecosystem, the more resilient it is to changes and stressors. We can remember this with the acronym 'SAFE' – Stability, Adaptability, Functionality, and Ecosystem services. Can anyone share examples of how biodiversity contributes to these?

Maybe through pollination? Different plants need various species to help them reproduce.

Right! Pollination is one excellent example. Also, higher biodiversity often means better nutrient cycling within ecosystems. Great insights, everyone!
Conservation Strategies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into conservation strategies. What are some ways we protect biodiversity?

Creating national parks and wildlife reserves?

Yes! Protected areas are crucial for safeguarding habitats. Remember the phrase 'PARE!' - Protected Areas Restore Ecosystems. Can anyone think of other strategies?

Regulating hunting and poaching can help maintain animal populations!

Great point! Regulating activities like hunting is vital for species survival. Conservation efforts also include restoring damaged areas. Why do you think international cooperation, like the CBD, is important?

Because wildlife doesn't care about borders; species migrate and need protection everywhere!

Exactly! Biodiversity conservation is a global issue that requires collaboration. Let’s conclude this session with a summary of these strategies and why they matter.
International Conservation Efforts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s discuss international efforts in biodiversity conservation. Who knows what the Convention on Biological Diversity is?

Isn’t it an agreement between countries to protect biodiversity?

Correct! The CBD aims to develop national strategies for the conservation of biological diversity. Remember the term 'GLOBAL' - Global Objectives for Biodiversity Legislation and Actions. What other global initiatives do you think exist?

The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?

Yes! The SDGs include targets for conserving and sustainable use of biodiversity. Why is it crucial for us, as individuals, to support these initiatives?

Because our actions affect biodiversity locally and globally!

Absolutely! Every effort counts. Let’s summarize our key points about global biodiversity conservation. Collaboration leads to effective solutions!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including various species and ecosystems. The section discusses the importance of biodiversity for ecosystem resilience and the strategies for its conservation, including protected areas and international efforts, highlighting the necessity of preserving life forms and their habitats.
Detailed
Biodiversity and Conservation
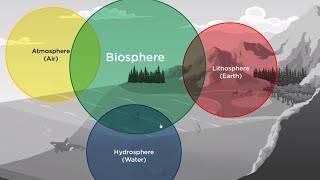
Biodiversity is the comprehensive term that describes the variety and variability of life forms on Earth, ranging from species of plants and animals to fungi and microorganisms. It includes the ecosystems they inhabit and plays a fundamental role in the stability and resilience of these ecosystems. The greater the biodiversity, the stronger the ecosystem's ability to withstand changes and stresses.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Conservation of biodiversity involves proactive measures taken to protect species, habitats, and entire ecosystems in order to prevent extinction and maintain the health of the planet. Various strategies are implemented for this purpose, such as:
- Creating protected areas like national parks and wildlife reserves.
- Regulating activities such as hunting and poaching.
- Restoring damaged ecosystems that have been degraded by human activity.
International efforts are also critical in biodiversity conservation. Initiatives such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to protect biodiversity on a global scale.
By conserving biodiversity, we can ensure the survival of countless species, maintain ecosystem services that benefit humanity, and promote a balanced environment that sustains life.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is Biodiversity?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of life forms on Earth, including different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form.
The higher the biodiversity, the more stable and resilient an ecosystem is.
Detailed Explanation
Biodiversity is a term that describes the incredible variety of life on our planet. This includes all the different species of plants, animals, fungi, and tiny microorganisms. Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem health; greater biodiversity often means that ecosystems can better withstand changes such as climate shifts or the introduction of new diseases. When an ecosystem has a rich variety of life, it can recover more easily from disturbances and is generally more stable.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sports team. A team with a variety of players with different skills (like forwards, defenders, and goalkeepers) is more versatile and can adapt to different challenges compared to a team with only one type of player. Similarly, ecosystems with high biodiversity can handle challenges more effectively.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Biodiversity conservation involves protecting species, habitats, and ecosystems to prevent extinction and preserve the health of the planet.
Conservation Strategies: These include creating protected areas such as national parks and wildlife reserves, regulating hunting and poaching, and restoring damaged ecosystems.
International Efforts: Global initiatives such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the establishment of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) focus on preserving biodiversity.
Detailed Explanation
Conserving biodiversity means taking action to protect not just individual species, but the habitats and ecosystems they depend on. Conservation strategies can include setting up protected areas like national parks where human activity is limited to allow nature to thrive. Additionally, there are laws to regulate hunting and prevent poaching, aiming to protect endangered species from over-exploitation. Efforts are not just local; international organizations work to create agreements, like the Convention on Biological Diversity, to foster global cooperation in these efforts.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library that has a wide range of books. If someone started taking books away and no one replaced them, soon the library would have fewer resources and less value. Protecting biodiversity is like ensuring that a library keeps all its books — each species plays a unique role within its ecosystem, much like how every book contributes to the knowledge in the library.
Key Concepts
-
Biodiversity: Refers to the variety of life forms on Earth, essential for ecosystem stability.
-
Conservation: Protective measures taken to preserve species and their habitats.
-
Ecosystem Services: Benefits provided by healthy ecosystems to humans.
-
Convention on Biological Diversity: An international treaty aimed at biodiversity protection.
Examples & Applications
The Amazon rainforest is an example of a biodiversity hotspot, home to diverse species.
National parks, like Yellowstone in the U.S., serve as protected areas to conserve wildlife and ecosystems.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Biodiversity is the key, for ecosystems to thrive freely.
Stories
Once in a lush forest, every plant and creature played a part. The tiny ants helped trees grow tall by spreading seeds, while the songbirds sang their melodies, showing how each life form is connected in nature's heart.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CROPS' for conservation: Create reserves, Regulate activities, Outreach education, Protect endangered species, Support restoration.
Acronyms
B.E.S.T – Biodiversity Ensures Stability and Thriving ecosystems.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Biodiversity
The variety and variability of life forms on Earth, including species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
- Conservation
The act of protecting and preserving natural resources, species, and ecosystems.
- Ecosystem Services
The benefits that humans derive from healthy ecosystems, such as clean air, water, pollination, and climate regulation.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
An international treaty aimed at conserving biodiversity, promoting sustainable use of its components, and ensuring fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
