Diversity of Life
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life forms on Earth, including all plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Can anyone tell me why biodiversity is important?

It’s important for ecosystems, right? Like, if one species goes extinct, it can affect others.

Exactly! Biodiversity ensures the health and stability of ecosystems. We can remember this with the acronym 'B.E.E.S.' — Balance, Education, Energy, Sustainability. It emphasizes those key benefits of biodiversity.

Balance helps ecosystems stay stable. What about education?

Education about biodiversity helps us understand and appreciate the interconnectedness of all life. Great question! Now, what do you think energy refers to in this context?

Energy must be the energy flow through food chains and webs!

That's right! Biodiversity supports energy flow. To sum up, biodiversity is crucial for ecological balance, energy transfer, and sustainability.
Components of Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into the components of biodiversity. We often break it down into species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Can anyone share what each of these means?

Species diversity is about the number of different species in an area.

Correct! And genetic diversity refers to the variation within species, crucial for resilience. Remember 'G.E.S.' for Genetic, Ecosystem, Species. Now what about ecosystem diversity?

That must be the different habitats and ecological roles!

Exactly! Each ecosystem supports unique species and provides different services. In summary, remember these components as G.E.S. They play a key role in our planet's health.
Threats to Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss threats to biodiversity. Humans have caused significant harm to ecosystems. What are some threats we can think of?

Pollution and habitat destruction like deforestation.

Great! Let's remember them with 'P.A.C.K.' for Pollution, Agriculture, Climate change, and Killing species. Can anyone expand on how each of these threats impacts biodiversity?

Pollution can poison habitats, while agriculture can destroy them!

Exactly! Climate change also alters habitats, and over-exploitation threatens species. In summary, these P.A.C.K. threats significantly reduce biodiversity and disrupt ecosystem functions.
Conservation Efforts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s talk about conservation. What are some ways we can protect biodiversity?

Creating protected areas like national parks!

Absolutely! Remember 'S.P.A.C.E.' for Sustainability, Protected areas, Awareness, Conservation measures, and Education. Why do you think awareness is important?

Because if people understand the importance of biodiversity, they’ll want to help!

Exactly! Conservation efforts rely on public involvement. In conclusion, these S.P.A.C.E. strategies are vital to sustaining our planet's biodiversity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Diversity of Life emphasizes the vast array of organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, and their interactions within various ecosystems. This biodiversity is crucial for the stability and resilience of the planet's ecosystems.
Detailed
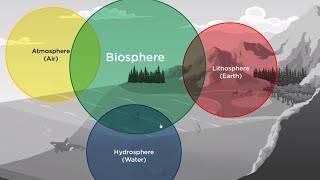
Diversity of Life
The biosphere encompasses a multitude of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to large mammals and trees. This variety of life, known as biodiversity, includes different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Biodiversity is not simply the number of species present; it also refers to the genetic variation within these species and the ecological complexes they form.
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and is essential for the functioning of the planet. Diverse ecosystems can better withstand environmental changes, provide resources for humans, and ensure ecological stability. The intricate relationships between different life forms facilitate processes such as pollination, nutrient recycling, and water purification, further showcasing the significance of biodiversity in sustaining life on Earth.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Variety of Life Forms
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The biosphere supports a vast array of life forms, ranging from microscopic organisms like bacteria and algae to large mammals and trees.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the concept that the biosphere is home to a huge diversity of living organisms. This diversity includes both very small life forms, such as bacteria that are only visible under a microscope, as well as much larger life forms like elephants and giant sequoia trees. Each of these organisms plays a specific role in the ecosystem, and they together create a rich tapestry of life on Earth.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large city. Just like a city has different types of people—builders, teachers, artists, and doctors—each contributing to the community, the biosphere has many different types of organisms fulfilling various roles. Some tiny bacteria help decompose organic matter, while larger trees provide homes for birds and shade for smaller plants.
Understanding Biodiversity
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This diversity of life is termed biodiversity, and it includes different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, all interacting within ecosystems.
Detailed Explanation
Here, biodiversity is defined as the variety of life present in an ecosystem. Biodiversity encompasses not only the number of different species but also the genetic diversity within those species and the variety of ecosystems themselves. High levels of biodiversity are critical because they contribute to the resilience of ecosystems, helping them recover from disturbances and maintain functions critical for survival.
Examples & Analogies
Consider biodiversity as a recipe for a cake, where each ingredient adds its unique flavor. If you’re missing a key ingredient (like eggs or flour), the cake won’t turn out well. Similarly, if an ecosystem loses species (like plants or animals), its ability to function effectively and support life diminishes. Biodiversity helps maintain the 'taste' or health of our planet.
Interactions Among Life Forms
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
All different species of organisms interact within ecosystems.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the interconnectedness of various species within an ecosystem. Every organism, from the smallest bacterium to the largest mammal, has a role that can affect other organisms. For example, plants produce oxygen and food that animals rely on, while animals produce carbon dioxide needed by plants. These interactions create a network of relationships that sustain life within ecosystems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a symphony orchestra, where different musicians play various instruments—strings, brass, woodwinds, etc. If one section is out of tune or not playing, the overall sound of the orchestra suffers. Likewise, if one species in an ecosystem struggles to survive, it can affect many others, highlighting the importance of each member in maintaining harmony.
Key Concepts
-
Biodiversity: The variety of life forms on Earth, vital for ecosystem stability.
-
Ecosystem: A community of organisms interacting with their environment, crucial for biodiversity.
-
Species Diversity: Refers to the number of different species present in an ecosystem.
-
Genetic Diversity: Variation within species that contributes to resilience and adaptation.
-
Ecosystem Diversity: The variety of ecosystems in different habitats fostering diverse life.
Examples & Applications
A rainforest with thousands of plant and animal species exemplifies high biodiversity.
Coral reefs represent an ecosystem with rich biodiversity, home to many marine species.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the forest and the sea, biodiversity is key, it helps the world be healthy and free.
Stories
Imagine a lively forest filled with different animals and plants. Each one depends on the others for food, shelter, and survival. This is biodiversity at work!
Memory Tools
G.E.S. for Genetic, Ecosystem, Species - the components of biodiversity.
Acronyms
B.E.E.S. for Balance, Education, Energy, Sustainability - key benefits of biodiversity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Biodiversity
The variety of life forms in an environment, including the different species and their genetic differences.
- Ecosystem
A community of living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment.
- Species Diversity
The number of different species in a given area.
- Genetic Diversity
The variety of genetic information within a species.
- Ecosystem Diversity
The variety of ecosystems in a given area, including different habitats and their species.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
