Interdependence of Life Forms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Connections between Plants and Animals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore how plants and animals are interconnected. For example, plants produce oxygen and food through photosynthesis. Who can tell me why this is important for animals?

Animals need oxygen to breathe!

And they eat plants as food!

Exactly! So, we can remember this connection with the acronym ‘FOOD’—that stands for 'Fruits, Oxygen, Other, and Dependence.' What happens when animals breathe out?

They release carbon dioxide, which plants need!

Right! This is a perfect example of interdependence. Who can summarize what we discussed?

Plants give us oxygen and food, and in return, we give them carbon dioxide.

Great summary! Let’s remember: LIFE depends on these interconnections.
Nutrient and Energy Cycles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll discuss nutrient and energy cycles. Why do you think these cycles are crucial in ecosystems?

They provide the resources for plants and animals to survive!

And if one part of the cycle breaks down, it affects everything!

Exactly! That's why we call it a cycle; it never ends. Can anyone give me an example of a nutrient that cycles in an ecosystem?

Water! The water cycle helps distribute water!

Perfect! We can use the memory aid ‘E-WATER’—every organism needs water to thrive and expand resources. Let's summarize what we learned today.

Nutrients and energy cycle through life forms, supporting all ecosystems!

Great job summarizing!
Impact on Ecosystem Health
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss how interdependence affects ecosystem health. Why is it important to maintain these relationships?

If one species goes extinct, it can affect others too!

Yes! It can cause an imbalance in the ecosystem!

Very good! That's why we should remember the phrase 'EVERYTHING CONNECTS,' as every species plays a role. How can protecting one species help others?

If we protect predators, herbivore populations stay balanced!

Exactly! Who can summarize the importance of interdependence in maintaining healthy ecosystems?

Interdependence means that all species rely on each other, so protecting each is vital for the health of ecosystems.

Fantastic summary!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
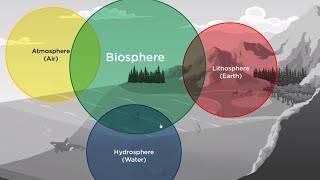
The interdependence of life forms in the biosphere highlights how plants and animals collaborate within ecosystems, emphasizing the significance of nutrient cycles, energy flow, and water for life. This interconnectedness is essential for maintaining balance and sustenance of ecosystems on Earth.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Interdependence of Life Forms
The interdependence of life forms within the biosphere is fundamental to the existence and sustainability of ecosystems. Life is characterized by a network of relationships between organisms, where each species plays a specific role. For example, plants produce oxygen and food through photosynthesis, consumed by herbivores, while the respiration of animals releases carbon dioxide necessary for plant growth. This cycle demonstrates how organisms are not isolated but are instead interconnected through processes vital for survival.
Moreover, the flow of nutrients, energy, and water across different organisms illustrates the complexity of these relationships, which are pivotal for ecosystem health. These interdependencies ensure that resources are recycled efficiently, allowing various species to thrive in their habitats. The balance maintained in these cycles is crucial for the survival of all organisms within the biosphere.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Interconnected Life
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Life in the biosphere is highly interconnected. Plants produce oxygen and food through photosynthesis, which is consumed by animals and other organisms, while animals release carbon dioxide that plants need for photosynthesis.
Detailed Explanation
This point highlights the interdependence of different life forms in the biosphere. Plants take in carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, which they convert into food, while releasing oxygen as a byproduct. Animals, in turn, consume plants (and other animals), using the oxygen produced by plants for their respiratory processes. The waste products of animals return to the environment, where they can be used by plants. This cycle illustrates how life is interconnected; each organism relies on others for survival.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a community where everyone has a specific role that relies on others. For example, in a family, parents provide food and shelter, while children contribute by helping with chores and learning skills. Just like in this family, where everyone depends on one another, in nature, plants and animals depend on each other to survive.
Nutrient, Energy, and Water Cycling
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The cycle of nutrients, energy, and water is essential for the survival and growth of living organisms.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we discuss the vital cycles that sustain life within the biosphere. Nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are recycled through the food chain, moving from one organism to another. Energy flows from the sun, to plants (the primary producers), and then through various levels of consumers, before being released back into the environment as waste. Water also cycles through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, supporting all living processes. Each of these cycles maintains the balance necessary for ecosystems to thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how water is recycled in nature. When it rains, water soaks into the ground or flows into rivers, eventually evaporating back into the atmosphere. Just like how we reuse materials in recycling, in nature, these cycles ensure that everything is reused and nothing goes to waste, allowing life to persist.
Key Concepts
-
Interdependence: Organisms rely on each other for resources and survival.
-
Nutrient Cycles: Nutrients recycle through the ecosystem, sustaining all life forms.
-
Energy Flow: Energy is transferred from producers to consumers, and then to decomposers.
Examples & Applications
The relationship between bees and flowering plants highlights how pollinators support plant reproduction.
Predators play a critical role in controlling herbivore populations, maintaining ecological balance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Plants breathe in CO2, while we breathe out for you; together we thrive, in cycle we drive.
Stories
Once upon a time in a thriving forest, there lived a tree and a rabbit. The tree provided shelter and food for the rabbit, and in turn, the rabbit helped to aerate the soil around the tree, helping it grow strong. This tale shows how their lives are intertwined.
Memory Tools
LIFE—Plants give Light, Inspiration, Food, and Energy!
Acronyms
R-P-C—**R**elationships among **P**lants and **C**reatures.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Biosphere
The layer of Earth where life exists, including land, water, and atmosphere.
- Interdependence
The mutual reliance between different species and their environment for survival.
- Photosynthesis
The process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, producing oxygen.
- Nutrient Cycle
The movement of nutrients between organisms and the environment.
- Energy Flow
The transfer of energy through food chains and webs in an ecosystem.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
