Lithosphere - 6.3.3
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Components of the Lithosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the lithosphere, which is the solid outer layer of the Earth. Can anyone tell me what the lithosphere consists of?

Is it made of rocks and soil?

Exactly! The lithosphere includes soil, rocks, and various landforms. It's important for supporting life. What do you think the role of soil is in the lithosphere?

Soil helps plants grow because it has nutrients.

Right! The soil is crucial for providing nutrients and anchoring plants. Let's remember: 'Soil Supports Life' to help us keep this in mind.
Importance of Lithosphere in Ecosystems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into why the lithosphere matters for ecosystems. How do you think it connects with the hydrosphere and atmosphere?

Maybe it helps with collecting water and offers a place for animals to live?

Great observation! The lithosphere does help in water retention and provides habitats. Can anyone explain how this interaction might work?

Rainwater seeps into the soil, and that helps plants get water!

Exactly! This relationship is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Don't forget: 'Water Needs Soil to Grow' — that's a good mnemonic for us.
Nutrient Cycling in the Lithosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at nutrient cycling within the lithosphere. How do you think nutrients get from the soil to the plants?

Plants take nutrients up through their roots, right?

Exactly! Those nutrients are crucial for plant growth. And when plants die, they return nutrients back to the soil. Can anyone give an example of this process?

When leaves fall, they decompose and add nutrients back to the soil!

Perfect! Remember, 'Nature's Cycle' helps keep ecosystems balanced.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The lithosphere, comprising soil, rocks, and landforms, is essential for sustaining life on Earth. It plays a significant role in providing habitat and resources necessary for the growth of plants and animals, thereby maintaining ecosystem balance.
Detailed
Lithosphere Overview
The lithosphere is defined as the solid outer layer of the Earth, encompassing soil, rocks, and various landforms. It serves as the foundational component for terrestrial ecosystems by providing habitats for countless organisms. Key points about the lithosphere include:
Key Components of the Lithosphere
- Soil Formation: The lithosphere contains fertile soil, which is critical for plant life, serving as a nutrient reservoir and anchorage for roots.
- Landforms: The various landforms found in the lithosphere, such as mountains, valleys, and plains, create diverse habitats for different organisms.
Importance for Ecosystems
- Nutrient Cycling: Soil in the lithosphere plays a vital role in nutrient cycling, essential for plant growth and the base of food chains in ecosystems.
- Water Retention: The lithosphere also affects water retention and drainage, influencing the availability of water for plants and animals.
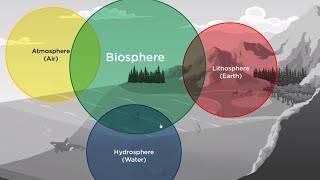
- Interaction with Other Spheres: The lithosphere interacts closely with the hydrosphere and atmosphere to create suitable living conditions. Together, these spheres maintain Earth's balance and support life.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of the Lithosphere
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The lithosphere refers to the solid outer layer of the Earth, where soil, rock formations, and various landforms exist.
Detailed Explanation
The lithosphere is the rigid outer part of the Earth that includes both the crust and the upper mantle. This layer is crucial as it forms the land we walk on and includes various materials like soil and rocks. These materials are vital for creating landscapes, providing solid ground, and facilitating various geological processes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the lithosphere as a giant puzzle laid out on the Earth's surface. Each piece of the puzzle - whether it's a mountain, valley, or flat land - is formed from soil and rocks, creating different environments where various life forms can thrive.
Habitat for Terrestrial Life
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The lithosphere provides habitats for terrestrial life, from forests to mountains to deserts.
Detailed Explanation
The diverse landforms in the lithosphere support a variety of ecosystems. Each type of landform, whether it's a forest, mountain range, or desert, creates specific conditions such as temperature, moisture, and soil type. These conditions are essential for different species of plants and animals to live and thrive in their unique environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine going to different parts of a country. In the mountains, you might find bears and pine trees, while in a desert, you'd find camels and cacti. Each environment is unique because of how the lithosphere is structured and composed.
Importance of Soil in the Lithosphere
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The soil is the most fertile part of the lithosphere, providing nutrients and anchorage for plant life, which is the base of the food chain in most ecosystems.
Detailed Explanation
Soil is crucial for life on Earth. It not only provides the necessary minerals and nutrients that plants need to grow, but it also acts as an anchoring medium, allowing plants to remain stable as they grow. Healthy soil supports a wide range of plant life, which forms the foundation of food webs and ecosystems by serving as primary producers.
Examples & Analogies
Consider soil like a kitchen pantry for plants. Just as you need various ingredients to cook a meal, plants require different nutrients found in the soil to grow healthy and strong. Healthy soil produces bountiful crops, similar to how a well-stocked pantry results in delicious meals.
Key Concepts
-
Lithosphere: The solid outer shell of the Earth, essential for providing habitats for terrestrial life.
-
Soil: A critical component of the lithosphere that supports plant life and nutrient cycling.
-
Nutrient Cycling: The ongoing process by which nutrients are recycled in ecosystems, significantly facilitated by the lithosphere.
Examples & Applications
The presence of fertile soil allows crops to flourish, contributing to agriculture.
Rock formations can create diverse habitats, such as caves, which host unique species.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the lithosphere, soil is grand, it helps the plants grow on land.
Stories
Imagine a forest where trees grow tall. The soil holds them steady, preventing a fall.
Memory Tools
S.P.O.R.T. - Soil Provides Optimal Resources for Trees.
Acronyms
LIFE - Lithosphere Influencing Flora and Ecosystems.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Lithosphere
The solid outer layer of Earth, including soil, rocks, and landforms that provide habitat for organisms.
- Soil
The upper layer of earth where plants grow, composed of organic matter, minerals, and microorganisms.
- Nutrient Cycling
The process where nutrients are continuously recycled in ecosystems, beginning and ending with plants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
