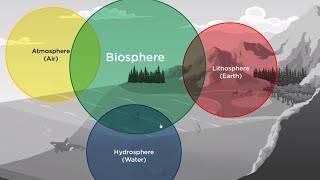
Layers of the Biosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll begin with the atmosphere. Can anyone tell me how the atmosphere supports life?

It gives us oxygen to breathe!

That's correct! The atmosphere provides oxygen and carbon dioxide which are vital for respiration and photosynthesis. Remember the acronym O2 for Oxygen and CO2 for Carbon Dioxide to help you recall their roles.

What else does the atmosphere do?

Great question! The atmosphere also regulates climate and weather patterns. This is critical for maintaining the ecosystems where life exists. Can anyone think of an example of a weather pattern?

Maybe hurricanes or thunderstorms?

Exactly! These weather events are products of the atmosphere and have significant effects on the biosphere.

So, without the atmosphere, life as we know it wouldn’t exist?

Correct! To summarize, the atmosphere is essential for oxygen supply, climate regulation, and sustaining life. Remember that we depend on this layer for our survival.
Hydrosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss the hydrosphere. Who can explain why water is so vital for life?

We need water to drink!

Absolutely! Water is crucial for hydration. Additionally, it helps transport nutrients in our bodies and in ecosystems. There's an acronym we can use: H2O for water. Who can tell me other roles water plays?

Water also helps regulate temperature!

Yes! It serves as a temperature buffer, ensuring living organisms don't experience extreme fluctuations in temperature. What are some examples of bodies of water?

Oceans, rivers, and lakes!

Correct! These bodies allow for diverse habitats for aquatic and even terrestrial life. Remember, the hydrosphere is critical for supporting ecosystems and the overall health of our planet.
Lithosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s explore the lithosphere. Can anyone share what the lithosphere consists of?

I think it’s the solid part of Earth, like rocks and soil!

Exactly! The lithosphere comprises soil, rocks, and landforms. Remember the word 'soil' as it’s the most fertile part, providing nutrients for plants. Why do plants matter to ecosystems?

Plants are the base of the food chain!

Correct! Plants produce energy through photosynthesis and provide food for herbivores. The lithosphere supports various habitats like forests and deserts. Can you think of an example?

Forests have a lot of different plants and animals!

Great observation! The lithosphere is home to diverse ecosystems that greatly affect life on Earth. Remember, this solid layer is crucial for providing habitats and nutrients necessary for life.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the three main layers of the biosphere: the atmosphere, which provides essential gases for life; the hydrosphere, encompassing various water bodies that sustain aquatic and terrestrial organisms; and the lithosphere, the solid outer layer of the Earth that provides habitat and nutrients for terrestrial life.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Layers of the Biosphere
The biosphere is defined by three essential layers that contribute significantly to sustaining life on Earth:
- Atmosphere: This layer includes the troposphere, which is the lowest part of the atmosphere where all weather events occur and where oxygen and carbon dioxide exist in the right proportions to support life. The atmosphere also regulates the Earth’s climate and temperature, enabling survival across various ecosystems.
- Hydrosphere: Incorporating all of Earth’s water bodies, such as oceans, rivers, lakes, and groundwater, the hydrosphere is essential for hydration and nutrient transportation. It also plays a critical role in temperature regulation, ensuring living organisms can thrive in diverse habitats.
- Lithosphere: This is the solid outer shell of the Earth, composed of soil, rocks, and landforms. It provides habitats for terrestrial life, as the soil is rich in nutrients that support plant growth, forming the base of food chains in various ecosystems.
Understanding these layers is fundamental for studying ecological balance, as they interact dynamically to support life and maintain the planet's health.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Atmosphere Overview
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is the thin layer of gases surrounding the Earth, providing oxygen for respiration and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, essential for life.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is the layer of gases that envelops our planet. It is crucial because it supplies the oxygen we breathe, which is vital for respiration in animals, and carbon dioxide, which is necessary for plants to perform photosynthesis. These processes are fundamental for sustaining life on Earth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the atmosphere like a protective blanket around the Earth. Just as a blanket keeps you warm by trapping heat, the atmosphere keeps the Earth warm enough to support life by regulating temperature and providing crucial gases needed for living organisms.
Role of the Atmosphere in Climate Regulation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere also plays a key role in regulating Earth's climate, influencing temperature and weather patterns that sustain various life forms.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is not just a source of essential gases; it also greatly influences the planet's climate. For instance, it helps in maintaining a stable temperature by trapping heat (the greenhouse effect). This stability allows different types of ecosystems to flourish. Weather patterns, such as rain and wind, are also generated in the atmosphere, which directly impacts the distribution and health of life on Earth.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine cooking a meal. Just like how the heat in the oven cooks your food evenly, the atmosphere helps distribute the sun's heat across the Earth. If the atmosphere didn't exist to keep things balanced, we would have areas that are far too hot and others that are too cold, making it hard for life to thrive.
Key Concepts
-
Atmosphere: The layer of gases necessary for life, providing oxygen and regulating climate.
-
Hydrosphere: The water component of the biosphere essential for all living organisms.
-
Lithosphere: The Earth’s solid outer shell that provides nutrients and habitat for terrestrial life.
Examples & Applications
The atmosphere supplies oxygen to humans and carbon dioxide to plants.
Rivers and lakes in the hydrosphere provide essential habitats for aquatic species like fish and amphibians.
Soil in the lithosphere supports the growth of crops, which are vital for food supply.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the air, we find O2, / Life to breathe, it’s true! / Water flows from sea to shore, / Without it, life can't explore.
Stories
Once upon a time, three friends lived in a beautiful realm: Atmo, Hydro, and Lito. Atmo provided the air for everyone to breathe, Hydro kept the rivers flowing, while Lito formed the ground where they could stand. Together, they created a thriving ecosystem where life flourished.
Memory Tools
Think 'AHL' to remember Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Lithosphere.
Acronyms
Use 'AHL' as an acronym to recall the layers of the biosphere
for Atmosphere
for Hydrosphere
and L for Lithosphere.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth, essential for respiration, photosynthesis, and climate regulation.
- Hydrosphere
All the water bodies on Earth, including oceans, rivers, and lakes, crucial for hydration, nutrient transportation, and temperature regulation.
- Lithosphere
The solid outer layer of the Earth, comprising soil, rocks, and landforms that provide habitats for terrestrial life.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
