Lithosphere - 6.1.2.1
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Composition of Lithosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the concept of the lithosphere. Can anyone tell me what the lithosphere refers to?

Is it the outer layer of the Earth?

Exactly! It is indeed the solid outer layer of the Earth. To remember that, think of it as the 'rocky outer shell' of our planet. Now, can anyone say what components make up the lithosphere?

I think it includes soil and rocks.

And landforms too, right?

Spot on! The lithosphere consists of soil, rocks, and various landforms. It's essential for providing habitats to numerous organisms. Let's remember this with the acronym 'SRL' for Soil, Rocks, and Landforms.
Importance of the Lithosphere in Ecosystems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think the lithosphere is important for ecosystems?

Because it provides a place for plants to grow.

That's right! Plants grow in the soil, which is the most fertile part of the lithosphere. Why is this important for animals?

Because animals eat the plants for food.

Exactly! The lithosphere supports the food chain. To make it easier to remember, let's think of the lithosphere as the 'foundation of life' on land.
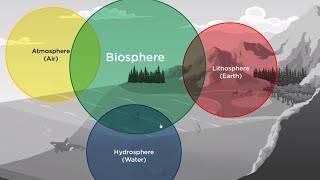
Interactions Between Lithosphere and Other Spheres
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How does the lithosphere interact with other components of the biosphere, like the hydrosphere or atmosphere?

Water from lakes and rivers soaks into the soil, right?

Correct! This interaction is crucial as it helps in nutrient cycling. Now, who can tell me how the atmosphere influences the lithosphere?

The atmosphere provides rain that helps plants grow in the soil.

Well done! Rain from the atmosphere nourishes the lithosphere. Together, they support life. To remember this, think of the phrase 'Life depends on layers' - lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The lithosphere comprises soil, rocks, and landforms that provide habitats for terrestrial life. It plays a significant role in supporting ecosystems and is vital for the food chain, where healthy soil nurtures plants, which, in turn, serve as a foundation for various life forms.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Lithosphere
The lithosphere is defined as the solid outer layer of the Earth, which includes the soil, rocks, and various landforms. It serves as a critical habitat for many organisms, providing them with a stable environment and essential resources. In ecosystems, the lithosphere's soil is especially important as it is typically the most fertile layer, rich in nutrients necessary for plant life.
Key Functions of the Lithosphere:
- Habitat Provider: It supports a diverse range of life forms, serving as their home and source of nutrients.
- Nutrient Source: The soil provides essential minerals and nutrients necessary for the survival and growth of plants, which are the base of the food chain.
- Ecosystem Balance: Interactions between the lithosphere and other components of the biosphere (Hydrosphere and Atmosphere) foster a balanced ecosystem where energy, nutrients, and water circulate efficiently.
Overall, the lithosphere is integral to the biosphere's functioning, aiding in the growth of flora that sustains various animal species and contributes to the Earth’s ecological health.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Lithosphere
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The lithosphere refers to the solid outer layer of the Earth, where soil, rock formations, and various landforms exist.
Detailed Explanation
The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth. It includes everything we can see when we look at the surface, such as mountains, valleys, and plains. This layer is made up of both soil and rocks, which are crucial for many biological processes. Without the lithosphere, there would be no ground for plants to grow, and hence no habitats for animals, making it a fundamental part of the biosphere.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the lithosphere as the 'skin' of the Earth. Just like our skin protects our body and allows us to interact with the world, the lithosphere protects the interior of the Earth and provides a foundation for all terrestrial life.
Habitats and Ecosystems
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The lithosphere provides habitats for terrestrial life, from forests to mountains to deserts.
Detailed Explanation
The lithosphere is diverse and hosts many different types of habitats. Each habitat, such as forests, mountains, or deserts, has its own unique characteristics that support various forms of life. For example, forests are rich in trees and undergrowth that provide food and shelter for animals. In contrast, deserts have very little water, and the organisms that live there have adapted to survive in extreme conditions. This diversity in habitats is essential for maintaining the overall health of ecosystems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the lithosphere as a giant buffet with different cuisines. Each type of environment (like forests, mountains, and deserts) represents a different cuisine, offering unique foods (habitats) appealing to various tastes (species). Just as a buffet needs a variety of dishes to satisfy different preferences, the variety in the lithosphere allows different species to thrive.
Role of Soil
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The soil is the most fertile part of the lithosphere, providing nutrients and anchorage for plant life, which is the base of the food chain in most ecosystems.
Detailed Explanation
Soil is a critical component of the lithosphere, as it contains organic matter, minerals, air, and water, all of which are essential for plant growth. Healthy soil allows plants to extract nutrients that fuel their growth, which in turn supports herbivores and other animals. Therefore, fertile soil is fundamental to food production and the overall health of ecosystems, forming the foundation of the food chain.
Examples & Analogies
Think of soil as a 'garden bed' where plants grow. Just like a gardener needs good soil to grow healthy vegetables, all plants need nutrient-rich soil to thrive. Without rich soil, plants struggle to grow, just as vegetables would not flourish in poor garden conditions.
Key Concepts
-
Lithosphere: The outer solid layer of Earth, crucial for supporting life.
-
Soil: The nutrient-rich upper layer of the lithosphere necessary for plant growth.
-
Ecosystem: An interaction of living organisms with their physical environment.
Examples & Applications
An example of the lithosphere is the soil in a forest, which supports diverse plant and animal species.
Mountain ranges represent a distinct landform within the lithosphere, providing unique habitats.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To grow and thrive, plants must derive, From the earth, the solid lithosphere's strive.
Stories
Once upon a time in a vast forest, trees thrived in the fertile soil, part of the lithosphere. It was the foundation for all life, where every plant and animal played their role in a perfect ecosystem.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SOL' - Soil, Outer layer, Living foundation to recall the importance of the lithosphere.
Acronyms
Use 'SLR' for the components of the lithosphere
Soil
Landforms
Rocks.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Lithosphere
The solid outer layer of the Earth, consisting of soil, rocks, and landforms.
- Soil
The upper layer of earth in which plants grow, containing organic matter, clay, and rock particles.
- Ecosystem
A community of living organisms and their interactions with their physical environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
