What is Biodiversity?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re delving into biodiversity. Can anyone tell me what biodiversity means?

I think it has something to do with the variety of living things?

Exactly! Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. This includes all species—plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. It's crucial for a stable ecosystem.

Why is it so important for ecosystems?

Great question! Higher biodiversity means a more resilient ecosystem, which can withstand changes and stressors better. You can remember this with the acronym R.E.S.T. — Resilience, Ecosystems, Stability, and Tolerance.

Can you give an example of how biodiversity helps?

Sure! In a forest ecosystem, various plant species provide food and habitat for diverse animal species. If one species declines, others can fill in, ensuring the ecosystem remains stable.

What happens if biodiversity decreases?

If biodiversity decreases, ecosystems become more vulnerable to disturbances like disease or climate change. We need to conserve biodiversity to protect these ecosystems! Let's summarize: biodiversity means variety of life, it's crucial for ecosystem resilience, and we can remember it with R.E.S.T.
Conservation of Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about conserving biodiversity. What are some strategies we can use?

Creating national parks?

Exactly! Protected areas help conserve habitats and species. This strategy can be remembered by the acronym P.A.C.E—Protected Areas for Conservation of Ecosystems.

What other methods are there?

We can regulate hunting and poaching, and restore damaged ecosystems. These actions prevent extinction and promote biodiversity. In conservation, it's all about balance!

What international efforts exist?

Great inquiry! The Convention on Biological Diversity, or CBD, is an important global initiative to conserve biodiversity. Remember it as C.B.D. for Conservation of Biodiversity Development.

If everyone follows these strategies, can we recover biodiversity?

In many cases, yes! Conservation efforts increase the likelihood of species recovery and ecosystem health. Let's summarize: we conserve biodiversity through strategies like protected areas, regulation, and international efforts like the CBD.
Impacts of Biodiversity Loss
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Our next topic is the impact of losing biodiversity. What do you think might happen?

Species might go extinct?

Correct! When species become extinct, it affects the entire ecosystem. You can remember this with the phrase 'The web breaks' to signify interconnectedness.

Does that affect humans too?

Absolutely. Humans rely on biodiversity for food, medicine, and clean air. Less biodiversity means fewer resources and increased vulnerability to changes.

What can individuals do to help?

Individuals can participate in local conservation efforts, reduce waste, and advocate for sustainable practices. Remember, small actions lead to big changes!

So, to conclude, saving biodiversity is crucial for everyone's survival?

Yes! Conserving biodiversity is essential for sustainability. Let's summarize: loss of biodiversity leads to ecosystem risks and impacts human life, so every effort counts!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
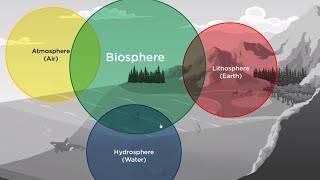
Biodiversity refers to the intricate variety of organisms on our planet, ranging from microscopic entities to larger animals, and is crucial for the stability and health of ecosystems. Conservation of biodiversity is vital to preserve species and environments against extinction and degradation.
Detailed
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, refers to the variety and variability of life forms on Earth, including different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as the ecosystems they form. It is often measured in terms of species richness, genetic diversity, and ecosystem variety. The importance of biodiversity lies in its ability to contribute to ecosystem resilience and stability; ecosystems with higher biodiversity tend to be better at coping with disturbances and stresses. Moreover, the conservation of biodiversity is critical for maintaining the balance of ecosystems and ensuring the survival of species by protecting their habitats and mitigating extinction risks. Conservation strategies include creating protected areas, regulating resource use, and promoting international initiatives like the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Biodiversity
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of life forms on Earth, including different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form.
Detailed Explanation
Biodiversity is essentially the richness of life on our planet. It includes all species of living organisms, from the smallest microbes to the largest mammals. This vast array of life is categorized into various species, and ecosystems are formed by all these species interacting with one another and their environment. Biodiversity also emphasizes the significance of not just the number of species, but their variability and roles within an ecosystem.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a diverse garden full of different types of flowers, plants, and trees. Each plant plays a unique role, contributing to the overall beauty and health of the garden. If all you have is one type of flower, the garden becomes less resilient to pests or diseases, just as an ecosystem is stronger and more sustainable with a variety of species.
Stability and Resilience of Ecosystems
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The higher the biodiversity, the more stable and resilient an ecosystem is.
Detailed Explanation
Ecosystems with higher biodiversity tend to be more stable and resilient because they can better withstand changes and disturbances such as climate change, diseases, and natural disasters. If one species is affected, others can fill in its role. This stability is crucial for maintaining the balance of ecosystems, ensuring that they continue to provide essential services like clean air, water, and food.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a relay race with a team of four runners. If one runner gets injured, the team can still rely on the other three to complete the race. However, if there was only one runner, the team would be unable to finish the race at all. Similarly, in a biodiverse ecosystem, if one species is lost, others help maintain the ecosystem's function.
Key Concepts
-
Biodiversity: Encompasses the variety of life forms on Earth.
-
Ecosystems: Complex networks where organisms interact with each other and their environment.
-
Conservation: Strategies to protect biodiversity and prevent extinction.
-
Resilience: The ability of an ecosystem to recover from disturbances.
-
Sustainability: Practices that meet present needs without compromising future generations.
Examples & Applications
In a coral reef ecosystem, the presence of various fish species ensures food resources, habitat stability, and promotes overall environmental health.
In a rainforest, the diversity of plant species allows for different niches, making it resilient against diseases and pests.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In forests and seas, diversity pleases, a world rich in life, where balance increases.
Stories
Once upon a time in a vibrant meadow, each plant, animal, and bug played a vital role in nurturing each other and keeping the environment thriving, showing us that together, we create a rich tapestry of life.
Memory Tools
R.E.S.T. - Resilience, Ecosystems, Stability, Tolerance to help remember why biodiversity matters.
Acronyms
P.A.C.E. - Protected Areas for Conservation of Ecosystems, our way to save biodiversity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Biodiversity
The variety and variability of life forms on Earth, encompassing different species and their ecosystems.
- Ecosystem
A community of living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment.
- Conservation
The effort to protect species, habitats, and ecosystems to prevent extinction and preserve the health of the planet.
- Extinction
The permanent loss of a species from Earth.
- Genetic Diversity
The variety of genes within a species, which contributes to its resilience and adaptability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
