Biomes of the Earth
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Tropical Rainforests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're starting with tropical rainforests! These are warm and wet ecosystems located near the equator. Can anyone tell me why they're so important?

They have a lot of plants and animals!

That's correct! They are the most biodiverse ecosystems. Remember the acronym 'OCEAN' for their importance: *O*xgen production, *C*arbon absorption, *E*nvironmental regulation, *A*nimals' habitat, and *N*utrient cycling.

Wow, I didn’t know rainforests were so crucial for oxygen!

Yes, exactly! They significantly affect our global climate. Who can name some plants or animals found in tropical rainforests?

Monkeys and tall trees!

Great examples! Let's remember these for our next discussion on biodiversity.

So, to summarize, tropical rainforests are essential for oxygen and carbon cycles, supporting rich biodiversity. Keep that acronym 'OCEAN' in mind!
Deserts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s switch gears to deserts! What can you tell me about their characteristics?

They are really dry and have big temperature changes!

Absolutely! The extreme minimal rainfall is a key defining feature. Let's create a mnemonic: 'DURTY,' which stands for *D*ry, *U*nique flora, *R*anging temperatures, *T*ough animals, *Y*ellow sands.

What kinds of plants live there?

Great question! Common plants include cacti and other xerophytes. They adapt really well to conserve water. Any animals come to mind?

Camels and snakes?

Exactly! Remember, deserts also contribute to mineral resources. So, who can summarize the mnemonic 'DURTY'?

Deserts are Dry, have Unique flora, Ranging temperatures, Tough animals, and Yellow sands!

Perfect! Deserts play a crucial role in our ecosystem too. Let's continue to the next biome.
Grasslands
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about grasslands. Who knows how they differ from forests?

They have more grass and fewer trees!

Great observation! Grasslands have moderate rainfall and are predominantly covered with grasses. They are critical habitats for many herbivores. Let's use 'GREENS,' standing for *G*rasses, *R*oaming animals, *E*cosystem balance, *E*ssential for agriculture, *N*utrient-rich soil, *S*ustained by fire.

What animals live in grasslands?

You can find animals like bison and zebras! They rely on grass for food. Does anyone have examples of grassland ecosystems?

Savannas and prairies!

Exactly! Grasslands are vital for grazing animals and significant crop production. So remember 'GREENS' for grasslands!
Tundra
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore the tundra biome now. What do you think makes the tundra unique?

It's super cold and has permafrost!

Correct! The presence of permafrost is a key feature, which significantly affects vegetation. Can anyone remember a mnemonic for tundra?

How about 'COLD' for *C*old, *O*nly mosses, *L*ow temperatures, *D*angerous climate changes?

That’s excellent! Tundras host unique flora like mosses and lichens as well as migratory species like polar bears. Can someone explain the impact of climate change on tundra?

It might melt the permafrost and disrupt ecosystems.

Absolutely, well stated! So let's summarize: Tundras are characterized by their cold climate, low vegetation, and the mnemonic 'COLD'.
Temperate Forests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss temperate forests. What seasons do you think they experience?

They have four distinct seasons!

Right! These forests feature deciduous trees, which shed leaves in winter. Can someone summarize their importance?

They help with the carbon cycle and are home to many animals.

Correct! To remember their importance, use 'FOCUS': *F*our seasons, *O*xygen production, *C*arbon cycling, *U*rbans' resource, *S*upport for wildlife.

That’s helpful!

Excellent! To recap, temperate forests are influenced by seasonal changes and support diverse life. Remember 'FOCUS' for their importance in the ecosystem!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The biomes of Earth, including tropical rainforests, deserts, grasslands, tundras, and temperate forests, are characterized by distinct climates and life forms. Each biome plays a crucial role in ecological balance, regulates the environment, and supports biodiversity.
Detailed
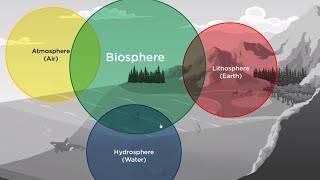
Biomes of the Earth
Biomes are large regional ecosystems characterized by specific climate conditions and distinct flora and fauna. This section primarily discusses five biomes: tropical rainforests, deserts, grasslands, tundras, and temperate forests.
- Tropical Rainforests: Found near the equator, these biomes experience warm temperatures and high rainfall, supporting a rich diversity of species. They are vital for climate regulation, oxygen production, and carbon dioxide absorption.
- Deserts: Defined by extreme dryness and temperature variations, deserts host resilient flora like cacti and fauna adapted to the lack of water. They contribute to mineral resources and temperature regulation.
- Grasslands: Characterized by moderate rainfall, grasslands are ecological savannas for many herbivorous and predatory animals, providing habitats that support agriculture.
- Tundra: Cold and low in precipitation, tundras have permanently frozen soil and host mosses and migratory animals. They are sensitive to climate changes affecting carbon cycles.
- Temperate Forests: These forests experience four distinct seasons and are home to diverse deciduous trees and wildlife. They play a role in the global carbon cycle and provide resources for human habitation. Understanding these biomes is essential for appreciating Earth's biodiversity and the complex interactions within ecosystems.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Tropical Rainforests
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Tropical Rainforests
- Characteristics: Warm temperatures, high rainfall, and dense vegetation. These biomes are located near the equator.
- Flora and Fauna: Home to diverse species of plants and animals, such as tall trees, vines, birds, and monkeys. Tropical rainforests are the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
- Importance: Tropical rainforests regulate the global climate and are critical for oxygen production and carbon dioxide absorption.
Detailed Explanation
Tropical rainforests are located near the equator and are characterized by warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. This environment leads to dense vegetation, making them extremely rich in biodiversity. They host a wide variety of species, including tall trees, various plants, birds, and monkeys. The importance of these ecosystems cannot be overstated—they play a key role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, which is essential for life.
Examples & Analogies
Think of tropical rainforests as the Earth's lungs; they breathe in carbon dioxide and breathe out oxygen, much like we do. Just like a household plant that needs good soil, sunlight, and water to thrive, the diverse life in rainforests flourishes in their warm, wet environment.
Deserts
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Deserts
- Characteristics: Dry, arid regions with minimal rainfall and extreme temperature variations between day and night.
- Flora and Fauna: Cacti, shrubs, and xerophytic plants that can survive with little water. Animals include camels, snakes, and rodents.
- Importance: Deserts play a role in regulating temperature and provide important mineral resources.
Detailed Explanation
Deserts are defined by their extreme dryness and can have significant temperature swings from day to night. The plants that thrive in these environments, like cacti and other drought-resistant species, have adapted to conserve water. The animal life, including camels and various reptiles, has similarly adapted to survive with minimal water. Deserts are critical for regulating temperatures and are sources of valuable minerals, demonstrating that even such harsh environments are vital to our planet.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine living in a house where it’s hot during the day but gets very chilly at night—like wearing a jacket when the sun goes down. Animals and plants in deserts have learned to cope with these harsh conditions, just as you might adjust by changing your clothing.
Grasslands
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Grasslands
- Characteristics: Regions with low rainfall and moderate temperatures, primarily covered by grasses and shrubs.
- Flora and Fauna: Dominated by grasses, with animals such as bison, lions, and zebras in savannas, and prairie dogs, antelope, and various herbivores in temperate grasslands.
- Importance: Grasslands are important for grazing animals and contribute to the production of food crops like wheat, corn, and barley.
Detailed Explanation
Grasslands are characterized by moderate temperatures and lower rainfall, which can support grasses rather than trees. In these regions, herbivores like bison and zebras thrive, forming an important part of the food chain. Grasslands are crucial not only as grazing grounds for animals but also for agriculture, as they are often used to grow crops such as wheat and corn, making them significant for human food production.
Examples & Analogies
Think of grasslands like a giant salad bowl filled with greens. Just as a salad can be both nutritious and delicious, grasslands provide vital resources not just for wildlife, but also for humans looking to grow food.
Tundra
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Tundra
- Characteristics: Cold regions with low precipitation and permafrost (permanently frozen soil).
- Flora and Fauna: Low-growing vegetation such as mosses, lichens, and small shrubs. Animals include polar bears, caribou, and migratory birds.
- Importance: Tundra ecosystems are sensitive to climate change and play a role in regulating global carbon cycles.
Detailed Explanation
Tundra regions are defined by their cold climate, low rainfall, and presence of permafrost, which is soil that stays frozen year-round. The plant life here is limited but includes hardy species like mosses and lichens. Various animals have adapted to the harsh conditions, such as polar bears and caribou. These ecosystems are incredibly sensitive to climate change, highlighting their importance in maintaining the Earth's overall carbon balance by storing carbon in their frozen soils.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine an icebox for food—you can keep items frozen for a long time. The tundra acts like that icebox for carbon, trapping it in permafrost and helping regulate our planet’s climate, which is why any warming affects it so profoundly.
Temperate Forests
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Temperate Forests
- Characteristics: These forests are characterized by four distinct seasons, moderate rainfall, and mild temperatures.
- Flora and Fauna: Deciduous trees (oak, maple, and beech) shed their leaves in winter. Animals include deer, bears, and birds like owls.
- Importance: Temperate forests contribute to the regulation of the global carbon cycle and are important for human habitation.
Detailed Explanation
Temperate forests experience all four seasons and provide a diverse habitat for many species. The trees in these forests lose their leaves in the fall as part of their lifecycle, illustrating adaptations to seasonal changes. This biome is significant not only for its biodiversity but also for its crucial role in regulating the carbon cycle, helping to absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen—essential for maintaining a balanced environment for both wildlife and humans.
Examples & Analogies
Think of temperate forests as nature's playground that changes with the seasons. Just like you might wear different clothes to match each season—like warm coats in winter or light shirts in summer—plants and animals in these forests adapt to the changing weather, creating a vibrant and dynamic ecosystem.
Key Concepts
-
Biomes: Large ecological areas on Earth with distinct climates and life forms.
-
Tropical Rainforests: Biodiverse ecosystems that are crucial for climate regulation.
-
Deserts: Arid environments characterized by low rainfall and unique adaptations.
-
Grasslands: Dominated by grasses and essential for grazing species and agriculture.
-
Tundra: Cold regions with low biodiversity and permafrost, sensitive to climate change.
-
Temperate Forests: Four-season forests with significant contributions to global ecology.
Examples & Applications
The Amazon rainforest is a quintessential example of a tropical rainforest, showcasing high biodiversity.
The Sahara Desert exemplifies a desert biome, featuring extreme temperatures and specialized flora and fauna.
The Great Plains in North America represent grasslands, vital for both wildlife and agriculture.
The Arctic tundra is an example of a tundra biome, with its frozen soil and unique wildlife.
Eastern deciduous forests serve as a classic example of temperate forests, housing diverse species of trees and wildlife.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In ecuador’s tropical trees, where the warm and rain is a breeze, biodiversity thrives with ease.
Stories
In the desert, a curious cactus meets a wandering camel. They share stories of surviving harsh conditions under the blazing sun.
Memory Tools
To remember the importance of temperate forests, think 'FOCUS': Four seasons, Oxygen production, Carbon cycling, Urban habitat, Support wildlife.
Acronyms
Use 'DURTY' for deserts
Dry
Unique flora
Ranging temperatures
Tough animals
Yellow sands.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Biome
Large regions characterized by specific climate and ecological conditions.
- Tropical Rainforest
Warm, high-rainfall ecosystems located near the equator, rich in biodiversity.
- Desert
Arid regions with minimal rainfall and extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Grassland
Regions characterized by low rainfall and dominated by grasses.
- Tundra
Cold regions with low precipitation, often featuring permafrost.
- Temperate Forest
Forests characterized by four seasons and mixed tree species.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
