Advantages of Cross-Pollination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cross-Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today we'll explore the advantages of cross-pollination. Can anyone remind me what cross-pollination is?

It's when pollen from one plant fertilizes another plant's stigma!

Exactly! So, why do you think this process is important for plants?

Maybe it helps them produce better seeds or fruits?

Great point! Cross-pollination increases genetic variation, which is crucial for the health and adaptability of plant offspring.

How does it make them healthier?

When plants cross-pollinate, the mixing of different genes creates stronger plants that are more resilient to diseases and environmental changes. Let's remember this with the mnemonic 'GHA' - Genetic Variation, Healthier Offspring, Adaptability!

GHA! I like that!

Well done! To sum up, cross-pollination enhances genetic diversity, produces healthier offspring, and promotes better adaptability.
Benefits of Genetic Variation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the basics, let's dive deeper. Why is genetic variation important?

I think it helps with survival in different environments!

Correct! Genetic variation allows some plants to adapt better to environmental changes or resist diseases. Can anyone think of an example?

Plants in different climates or soils might have different traits!

Exactly! The more genetic diversity, the better the chances of survival. This interconnectedness helps sustainable ecosystems.

What happens if there's no variation?

Great question! Without variation, plants become vulnerable to diseases, which can endanger entire species. Remember, genetic diversity is key!
Healthier Offspring
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about how cross-pollination leads to healthier offspring. Why do you think that happens?

Maybe it's because there's new genetic material?

Absolutely! New genetic material can provide traits that may help plants resist diseases or withstand unfavorable conditions.

So does that mean self-pollinated plants are weaker?

Yes, they can be! Self-pollination reduces genetic variation, sometimes leading to weaker offspring. Can anyone give an example of such plants?

Maybe peas or mustard? They are often self-pollinated.

Exactly! Keeping track of this helps us appreciate the role of cross-pollination more! Remember, healthier offspring increase survival rates.
Adaptability of Plants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look into how cross-pollination enhances adaptability. Why is adaptability essential for plants?

It helps them survive in changing environments!

Exactly! Plants that can adapt can find resources like water and sunlight more efficiently. How does cross-pollination contribute to this?

By creating diverse traits in the offspring that might be better suited to the environment!

Spot on! Flexible traits allow plants to thrive in various conditions. Remember, adaptability is crucial for the survival of species. Let’s recap: Cross-pollination enhances adaptability, helping plants survive and thrive.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The advantages of cross-pollination include increasing genetic variation, producing healthier offspring, and enhancing adaptability, which play critical roles in the evolution and survival of plant species.
Detailed
Advantages of Cross-Pollination
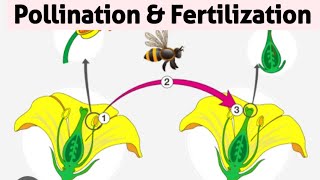
Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen between different plants, leading to greater genetic diversity. This process offers several advantages:
- Increases Genetic Variation: Unlike self-pollination, which limits genetic diversity, cross-pollination opens the gene pool, resulting in offspring with varied traits, which can be beneficial for adaptation.
- Leads to Healthier Offspring: Offspring produced from cross-pollination tend to be stronger and more resilient to diseases and environmental changes due to the increased genetic makeup.
- Promotes Better Adaptability: The combination of diverse genes allows plants to adapt to changing conditions more easily, enhancing their chances of survival.
These points highlight the importance of cross-pollination in the reproductive strategies of flowering plants, ultimately contributing to their success in various ecosystems.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Increases Genetic Variation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Increases genetic variation
Detailed Explanation
Cross-pollination helps in mixing the genetic material from two different plants, which creates new combinations of traits. This genetic variation is important for the long-term survival and adaptability of a species, as it allows the population to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cross-pollination like mixing different colors of paint. When you combine blue and yellow, you get green—a new color. Similarly, when plants cross-pollinate, they create offspring with new genetic combinations, much like creating new colors.
Leads to Healthier Offspring
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Leads to healthier offspring
Detailed Explanation
When plants undergo cross-pollination, the genetic diversity leads to stronger and more vigorous plants. These plants tend to be less susceptible to diseases and pests because they inherit a wider variety of genes that can fight off attacks from various threats.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of athletes from different backgrounds competing together. Their varied training methods and unique skills can lead to a stronger team that performs better overall. In the same way, cross-pollination produces plants that are better equipped to thrive in their environments.
Promotes Better Adaptability
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Promotes better adaptability
Detailed Explanation
Cross-pollination enables the creation of plants that can better adapt to different environmental stresses such as changes in climate, soil types, or the presence of diseases. This adaptability is crucial for the longer-term survival of plant species in a dynamic world.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a family that moves to a new country. The family's children grow up learning to adapt to both their original culture and the new one. This dual exposure helps them navigate various situations effectively. Similarly, plants produced through cross-pollination can mix traits from both parent plants, making them more versatile in adapting to different environments.
Key Concepts
-
Cross-Pollination: The process of transferring pollen across different plants.
-
Genetic Variation: The increase in diversity of the genetic makeup.
-
Healthier Offspring: Offspring that have better chances of survival and overall vigor.
-
Adaptability: The ability of species to adjust and thrive in various environmental conditions.
Examples & Applications
Hibiscus and apple trees, which benefit from cross-pollination, produce stronger and more resilient plants compared to those that self-pollinate.
Pea and mustard plants, which primarily self-pollinate, often lead to reduced genetic diversity resulting in weaker offspring.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Mix it up, watch it grow, cross-pollination makes plants glow!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a garden filled with diverse flowers, cross-pollination created a multitude of vibrant plants, each stronger than before.
Memory Tools
Remember 'GHA' for Genetic Variation, Healthier Offspring, Adaptability.
Acronyms
GHA - Genetic diversity, Health, Adaptability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CrossPollination
Transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another, resulting in genetic variance.
- Genetic Variation
Diversity in genetic makeup among individuals of the same species.
- Healthier Offspring
Offspring that possess strong traits leading to better survival rates.
- Adaptability
The ability of organisms to adjust to changes in their environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
