Agents of Pollination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Pollination Agents
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the agents of pollination. Can anyone tell me what they think pollination agents are?

Are they the things that help move pollen from one place to another?

Exactly! Pollination agents are organisms or natural elements that assist in transferring pollen grains to facilitate fertilization. Can you give me an example?

I think it’s insects like bees!

Correct! Insects are a primary pollination agent known as entomophiles. They often rely on flowers for nectar and are drawn to colorful petals and fragrances.

What about plants that are pollinated by wind?

Great question! Wind-pollinated plants, referred to as anemophiles, produce light and dry pollen to be easily carried by the wind. Think grass and maize!

How do water-pollinated flowers work?

Water-pollinated plants, or hydrophiles, produce pollen that can float on water. An example is Vallisneria. Well done, everyone! Remember, these agents significantly contribute to genetic diversity in plants.
Insect Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into insects as pollinators. Why do you think flowers attract insects?

Because they want to eat nectar!

Exactly! The nectar serves as a food source for insects. In return, they help in pollination. What features do you think these flowers have to attract insects?

Bright colors and strong smells?

Yes! Bright petals and a pleasant fragrance are key features. This relationship highlights mutualism, benefiting both plants and insects.

Can you name some flowers that attract insects?

Of course! Roses and sunflowers are excellent examples of insect-pollinated plants. Great participation, class!
Wind and Water Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about wind as a pollination agent. What comes to your mind when you think of wind-pollinated plants?

Plants that don’t have bright flowers?

Exactly! Anemophile plants typically have less elaborate flowers. Why do you think that is?

Because they rely on the wind instead of attracting insects?

Correct! They produce light, dry pollen. Flowers like maize and grasses do this. What about waters, how does that work?

Do water plants just float their pollen?

Yes, that’s right! Hydrophilic plants like Vallisneria release pollen that can float on water. Great insights today, everyone!
Bird Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore birds as pollination agents. What do you think attracts birds to flowers?

Bright colors, I guess!

Yes! Birds are attracted to bright-colored flowers with tubular shapes. Can anyone name a flower that’s bird-pollinated?

Hibiscus?

Exactly! Flowers like hibiscus exemplify ornithophily, which helps them achieve effective pollination.

What do birds get from these flowers?

Birds receive nectar, similar to insects. This floral relationship fosters plant reproduction and genetic variation.
Importance of Pollination Agents
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In this last session, let’s discuss why different pollination agents are essential.

They help plants reproduce?

Absolutely! They also contribute to genetic variety in plant species. Can you think of how that might affect ecosystems?

More variety means healthier ecosystems, right?

Exactly! More diversity can improve plant resilience to diseases and environmental changes. Great discussion today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
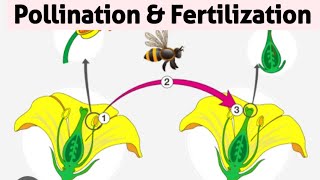
Pollination occurs through various natural agents such as insects, wind, water, and birds. Each agent has unique characteristics that facilitate the transfer of pollen, contributing to the reproductive process in flowering plants.
Detailed
Pollination is a critical step in the reproductive process of flowering plants, ensuring the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma. This section discusses the various agents of pollination, which include insects (entomophily), wind (anemophily), water (hydrophily), and birds (ornithophily). Each agent plays a specific role and exhibits distinct features that aid in effective pollination. For instance, insect-pollinated flowers often have bright petals and fragrances to attract pollinators, while wind-pollinated plants produce light, dry pollen and have exposed stamens. Understanding these agents is essential as they contribute significantly to genetic variation and the proliferation of plant species.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Insects as Pollinators
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Insects (Entomophily): Bright petals, fragrance, nectar. Example: Rose, sunflower.
Detailed Explanation
Insects, such as bees and butterflies, are significant agents of pollination. They are attracted to flowers due to their bright colors and pleasant scents. When insects visit a flower to collect nectar, they inadvertently pick up pollen grains from the anther. As they move from flower to flower, they transfer this pollen to the stigma of other flowers, facilitating cross-pollination and increasing genetic diversity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a bee as a little delivery service. When it goes from flower to flower, it collects pollen just like a postal worker collects letters. Each time it delivers pollen, it helps make new seeds, similar to how delivering mail helps connect people.
Wind Pollination
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Wind (Anemophily): Light, dry pollen; exposed stamens and feathery stigma. Example: Grass, maize.
Detailed Explanation
Wind-pollinated plants produce pollen that is light and dry, making it easy for wind to carry it from one plant to another. These flowers usually have exposed stamens that release pollen into the air and feathery stigmas to catch the airborne pollen. This type of pollination is less selective than insect pollination but is effective for many grasses and certain crops.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a kid throwing confetti into the air during a celebration. If the wind blows, the confetti spreads everywhere. Similarly, wind helps spread tiny pollen grains from one flower to another, assisting in plant reproduction.
Water Pollination
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Water (Hydrophily): Light pollen that floats. Example: Vallisneria, hydrilla.
Detailed Explanation
Some aquatic plants rely on water for pollination. These plants produce lightweight pollen that can float on water surfaces. When the water moves, it carries the pollen to the stigmas of other flowers within the same water body. This is a less common method of pollination but is essential for the reproduction of certain water plants.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like dropping food into a pond. If you throw breadcrumbs, they might float away and reach other parts of the pond. In a similar way, pollen from one flower can drift through the water to reach another flower.
Bird Pollination
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Birds (Ornithophily): Bright-colored flowers, tubular shape. Example: Hibiscus.
Detailed Explanation
Certain bright and tubular flowers attract birds, like hummingbirds, for pollination. Birds feed on the nectar and, while doing so, transfer pollen from one flower to another. This relationship is a beautiful example of mutualism, where both the birds and flowers benefit from each other.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a restaurant attracts customers with colorful signs and tasty smells. Flowers, too, attract birds with vibrant colors and sweet nectar. Just like a diner enjoying their meal helps the restaurant thrive, birds help flowers flourish by carrying pollen from one to another.
Key Concepts
-
Entomophily: Pollination through insects.
-
Anemophily: Pollination through wind.
-
Hydrophily: Pollination through water.
-
Ornithophily: Pollination through birds.
Examples & Applications
Rose and sunflower are examples of flowers pollinated by insects.
Maize and grass are examples of flowers pollinated by wind.
Hibiscus is an example of a bird-pollinated flower.
Vallisneria and hydrilla are examples of water-pollinated plants.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Insects buzz, flowers blossom, together they make nature’s awesome!
Stories
Once upon a time, a bee named Buzz flew from flower to flower, helping them create new life, as they gifted him sweet nectar to thrive. Thus, the cycle of nature spun beautifully!
Memory Tools
The mnemonic 'I WOB' can help you remember: Insects, Wind, Ornithophily, and Birds – all agents of pollination.
Acronyms
Acronym 'WIOH'
Wind
Insects
Ornithophily
Hydrophily – the four main agents.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Entomophily
Pollination that occurs through insects.
- Anemophily
Pollination that occurs through wind.
- Hydrophily
Pollination that occurs through water.
- Ornithophily
Pollination that occurs through birds.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
