Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we start understanding sexual reproduction in flowering plants. Can anyone tell me what pollination is?

Isn’t it when pollen goes from the male part of the flower to the female part?

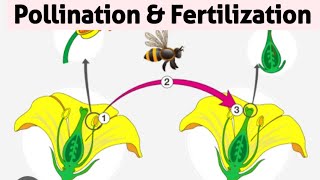
Exactly! Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma. We can remember it as A to S, A for Anther and S for Stigma.

What happens next after pollination?

Great question! Following pollination, fertilization takes place, where male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.

What do you mean by gametes?

Gametes are reproductive cells; in plants, the male gamete comes from pollen. Let’s summarize: Pollination transfers pollen from A to S, and fertilization involves gametes coming together.
Significance of Pollination and Fertilization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, why do you think pollination and fertilization are important? What do they lead to?

They help plants reproduce!

That's right! They ensure continuity of plant species and can also increase genetic variation, especially with cross-pollination.

What is genetic variation?

Genetic variation refers to differences in genes among individuals, which can enhance adaptation to environmental changes. Remember, more variety means more survival chances!

So, without this process, plants wouldn't be as resilient?

Exactly! Pollination and fertilization not only ensure reproduction but also contribute to the health of ecosystems by maintaining diversity.
How Pollination Occurs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss how pollination actually occurs. Can anyone name the methods by which pollen can be transferred?

I think insects and wind are two ways?

Correct! We have different methods like entomophily, which involves insects, and anemophily, which involves wind. Each has unique features that help in pollen transfer. Can you think of examples?

A rose would attract insects, right?

Yes! And grass uses wind for pollination. Remember, different flowers adapt their traits depending on their pollinators. This is an excellent way to associate plants with their pollination agents.

So, most flowering plants rely on these processes to keep thriving?

Yes! Each method of pollination plays a crucial role in sustaining plant diversity and ensuring successful reproduction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In flowering plants, pollination involves transferring pollen grains from the male part to the female part of the flower. Fertilization is the subsequent fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of seeds and fruits, crucial for plant reproduction.
Detailed
Introduction to Pollination and Fertilization in Flowering Plants
Pollination and fertilization are fundamental processes in the sexual reproduction of flowering plants, being essential for the formation of seeds and fruits. This section introduces the concepts of pollination as the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma and fertilization as the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in the zygote formation. Both processes are critical for the continuation of plant species, genetic diversity, and the development of new plant life, ensuring not only survival but also adaptation to changing environments.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Pollination and Fertilization
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pollination and fertilization are crucial steps in sexual reproduction in flowering plants. These processes lead to the formation of seeds and fruits for reproduction and continuity of the plant species.
Detailed Explanation
Pollination and fertilization are fundamental biological processes in the life cycle of flowering plants. Pollination refers to the transfer of pollen grains, which contain male gametes, from the male part of a flower (the anther) to the female part (the stigma). Once pollination occurs, fertilization takes place when the male gamete fuses with the female gamete (egg cell) to form a zygote. This fertilized ovule can then develop into seeds. The ability to produce seeds is essential for the propagation of plant species and ensures their survival and continuation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of pollination and fertilization as essential steps in creating a recipe. Just as combining the right ingredients leads to a delicious dish, pollination (gathering the necessary ingredients) and fertilization (mixing them together) result in the formation of seeds and fruits, which are crucial for the plant's life cycle.
Key Concepts
-
Pollination: The transfer of pollen from the male anther to the female stigma, essential for plant reproduction.
-
Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gametes which leads to the creation of a zygote.
-
Zygote: The initial cell that forms after the fertilization process, which will develop into an embryo.
Examples & Applications
In self-pollination, a pea plant can pollinate itself, while in cross-pollination, an apple tree receives pollen from another apple tree.
A rose flower is bright and fragrant to attract insects, facilitating entomophily.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Pollination, oh what a breeze, From the anther to the stigma it flees!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a colorful garden, there were flowers that needed help from bees to share their pollen. One day, a bee flew from one bloom to the next, helping them create seeds; that’s how they all connected!
Memory Tools
Remember P for Pollen and S for Stigma: PS for Pollination Steps.
Acronyms
F.A.S.T. - Fertilization
Anther
Stigma
Tube (for growing)
Zygote (as a result).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
- Fertilization
The process where male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.
- Gametes
Reproductive cells involved in sexual reproduction.
- Zygote
The cell formed by the fusion of male and female gametes.
- CrossPollination
Pollination occurring between different plants of the same species.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
