Significance of Pollination and Fertilization
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the significance of pollination and fertilization. Let's start with what you know about pollination. Can anyone explain what it is?

Pollination is when pollen moves from the male part of the flower to the female part.

Exactly, Student_1! And is there just one way this can happen?

No, there are different types like self-pollination and cross-pollination.

Correct! Self-pollination occurs within the same flower or plant, while cross-pollination happens between different plants. Let’s remember this with the acronym 'SCC' for Self and Cross. Can anyone tell me one advantage of cross-pollination?

It increases genetic variation!

Great job! Genetic variation is crucial for the adaptability of species. So, to summarize, pollination is vital as it ensures sexual reproduction and leads to genetic diversity.
Fertilization Process
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered pollination, let’s discuss fertilization. What happens right after a pollen grain lands on the stigma?

The pollen grain starts to grow a pollen tube!

Right! The pollen tube grows through the style to the ovary where the ovules are. What happens next?

The male gamete travels through the pollen tube to meet the egg cell!

Perfect! This fusion creates the zygote. This whole process is called syngamy. Can anyone tell me what double fertilization is?

That’s when one gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with polar nuclei to form endosperm.

Exactly! The endosperm provides nourishment to the developing embryo. So, we see that fertilization not only allows for new life but also supports it!
Significance of Pollination and Fertilization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s wrap this up by discussing why pollination and fertilization are vital for plants. Why do you think these processes are important for a plant species?

They ensure reproduction!

Yes, reproduction allows for the continuation of species. What about genetic variation?

Genetic variation helps plants adapt to changing environments!

Exactly! It leads to healthier offspring that can thrive. Lastly, how do these processes lead to the dispersal of plants?

Seeds and fruits are formed, which can be spread by wind, animals, or water.

Great explanation! So, in summary, pollination and fertilization are essential not just for producing new plants but also for ensuring they are diverse and can thrive in their environments.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The chapter underscores the importance of pollination and fertilization in flowering plants, highlighting how these processes promote sexual reproduction, genetic variation, and the formation of seeds and fruits, which are essential for the proliferation of plant species.
Detailed
Significance of Pollination and Fertilization
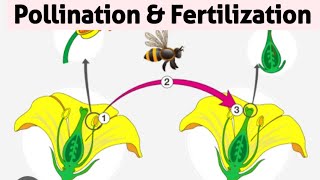
Pollination and fertilization are two essential processes that facilitate sexual reproduction in flowering plants (angiosperms). Pollination refers to the transfer of pollen grains from the male part (anther) to the female part (stigma) of a flower, which can occur via self-pollination or cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs within the same plant or flower, while cross-pollination involves pollen from different plants, contributing to greater genetic diversity. The advantages of cross-pollination include increased genetic variation, healthier offspring, and improved adaptability to environmental changes.
Fertilization follows pollination, as it is the fusion of male and female gametes, leading to the formation of a zygote, which ultimately develops into an embryo. In angiosperms, double fertilization occurs, resulting not only in a zygote but also in the formation of endosperm, providing nourishment to the developing embryo. The significance of these processes is profound, as they ensure the continuity of plant species through the formation of seeds and fruits, enabling further dispersal and propagation.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Ensures Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Ensures sexual reproduction in plants
Detailed Explanation
Pollination and fertilization are fundamental processes for sexual reproduction in flowering plants. Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parent plants, which leads to the production of offspring. In plants, this is achieved through pollination—the transfer of pollen grains from the male part of a flower to the female part. Once pollination occurs, fertilization can take place, leading to the formation of seeds. This is essential for producing the next generation of plants.
Examples & Analogies
Think of sexual reproduction in plants like a dance between two partners. Just as a dance couple moves together to create a beautiful performance, male and female gametes come together during fertilization to create a new life—a seed that will grow into a new plant.
Leads to Genetic Variation
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Leads to genetic variation (in cross-pollination)
Detailed Explanation
Cross-pollination, which occurs when pollen from one plant fertilizes the ovule of another plant, results in greater genetic diversity among the offspring. This variation is vital for the survival and adaptation of plant populations, as it increases the likelihood that some individuals will possess traits suited to survive changing environmental conditions or diseases. In contrast, self-pollination produces genetically similar offspring, which can make the population more vulnerable over time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a fruit salad made from various fruits. Each fruit adds its unique flavor and texture, creating a delicious mix. In the same way, genetically diverse plants from cross-pollination have varied traits that contribute to a stronger and more resilient plant population.
Results in Formation of Seeds and Fruits
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Results in formation of seeds and fruits
Detailed Explanation
The processes of pollination and fertilization culminate in the formation of seeds and fruits. After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary matures into a fruit. Fruits serve not only as protection for seeds but also as a means of dispersal. When animals eat fruits, they help distribute the seeds across different areas, aiding in the propagation of the plant species.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a fruit as a protective pod for a surprise gift (the seed) inside. When you eat the fruit, the seeds are sometimes spread out into new places, just like sharing gifts with friends ensures that they will enjoy the surprise too!
Enables Dispersal and Propagation of Plant Species
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Enables dispersal and propagation of plant species
Detailed Explanation
Dispersal of seeds is a critical aspect of a plant's life cycle. By having fruits that can be carried away by the wind, water, or animals, plants can spread their offspring far and wide, which is important for finding new locations to grow and develop. This capability to propagate themselves supports biodiversity and helps plant populations thrive across different environments.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a dandelion puff. When the wind blows, it carries the seeds away to new places where they can grow into new dandelions. Similarly, plants use various methods to ensure their seeds are spread out, giving new life a chance to grow in fresh soil.
Key Concepts
-
Pollination is essential for sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
-
Cross-pollination increases genetic diversity and adaptability.
-
Fertilization leads to the formation of a zygote and ultimately develops into an embryo.
-
Double fertilization occurs in angiosperms, involving both zygote and endosperm development.
Examples & Applications
In apple trees, cross-pollination occurs when pollen from one tree fertilizes the ovules of another tree, leading to greater fruit production.
In pea plants, self-pollination happens when pollen from the anther of one flower fertilizes the stigma of the same or another flower of the same plant.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Pollination brings the seed, crossing flowers is the need!
Stories
Once upon a time, a bee named Buzz traveled from one flower to another, sharing pollen to help them grow seeds and fruits, ensuring that more flowers could bloom in the sunny meadows.
Memory Tools
Remember 'E-G-E' for Egg (ovum), Gamete, Endosperm - crucial parts involved in fertilization.
Acronyms
Use 'PFS' for Pollination, Fertilization, Seeds to remember the process flow.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
- Fertilization
The fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- SelfPollination
Pollination that occurs within the same flower or plant.
- CrossPollination
Pollination that involves different plants or flowers of the same species.
- Genetic Variation
Differences in DNA among individuals, important for population adaptability.
- Endosperm
A nutritive tissue that nourishes the developing embryo in plants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
