Steps in Fertilization
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Fertilization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to talk about fertilization in flowering plants. Can anyone tell me what fertilization is?

Isn't it when the male and female gametes come together?

Exactly! Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes. It's essential for creating new life in plants. Let's remember this with the acronym SYNGAMY, which stands for 'S'exual 'Y'earning of 'N'ature's 'G'ametes 'A't 'M'y 'Y'ard – it emphasizes the importance of this process.

What happens after they come together?

Good question! After the fusion, a zygote is formed, which develops into an embryo. This is just the beginning of our journey through fertilization.
Steps Involved in Fertilization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's break down the steps of fertilization. Firstly, what is the first step?

The pollen grain lands on the stigma, right?

Exactly! So, the first step is when the pollen grain lands on the stigma of a flower. Then, what happens next?

The pollen tube grows through the style!

Yes! The pollen tube grows from the pollen grain down through the style toward the ovary. This is crucial for delivering the male gamete. Can anyone tell me what happens after the pollen tube reaches the ovary?

The male gamete travels through the tube!

Correct! The male gamete then travels through the pollen tube and fuses with the egg cell in the ovule, resulting in the formation of the zygote.
Significance of Fertilization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've learned about the steps, why do you think fertilization is so important for plants?

It helps in making seeds and new plants?

Exactly! It leads to the formation of seeds and fruits, ensuring plant species continue. Remember, without fertilization, there would be no new plants!

Does it affect genetic diversity?

Yes! Fertilization, particularly through cross-pollination, increases genetic variation, making plants more resilient.
Recap and Questions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's recap! What are the main steps of fertilization?

Pollen lands on stigma, pollen tube grows, male gamete travels, and they fuse to form a zygote!

Perfect! Now, why is it critical for the continuation of plant species?

It leads to the formation of seeds and fruits!

Great job, everyone! Always remember how significant fertilization is in plant reproduction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The fertilization process includes the landing of the pollen grain on the stigma, the growth of a pollen tube, and the fusion of the male gamete with the egg cell. This ultimately results in the formation of a zygote, which develops into an embryo.
Detailed
In flowering plants, fertilization refers to the process where male and female gametes unite to form a zygote, a crucial step in sexual reproduction. The fertilization process begins when a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a flower. Subsequently, the pollen tube emerges from the pollen grain and grows down through the style toward the ovary. Inside the ovary, the male gamete travels through the pollen tube and fuses with the egg cell (ovum) present in the ovule. This fusion culminates in the formation of a zygote, which develops into an embryo. This important process is known as syngamy or true fertilization.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
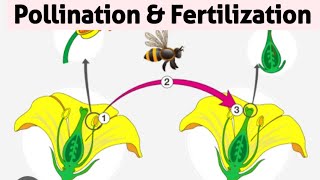
Pollen Grain Lands on Stigma
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Pollen grain lands on stigma (pollination)
Detailed Explanation
The very first step in the fertilization process begins with the pollen grain landing on the stigma of a flower. This step is part of the process known as pollination, where pollen is transferred from the male part of the flower to the female part. The stigma is a sticky structure on top of the pistil where pollen must land for fertilization to begin.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the stigma as a landing pad for a helicopter (the pollen grain). Just like a helicopter needs to land on a specific spot to allow passengers (the male gametes) to board, the pollen needs to land on the stigma before fertilization can happen.
Pollen Tube Growth
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Pollen tube grows through the style toward the ovary
Detailed Explanation
After the pollen grain successfully lands on the stigma, it begins to grow a structure called the pollen tube. This tube forms and extends down through the style, which is the slender part of the pistil, leading toward the ovary. The pollen tube serves as a pathway for the male gamete to travel down to reach the ovule for fertilization.
Examples & Analogies
It's similar to a subway system in a city. The pollen tube acts like a train that travels through a tunnel (the style) to reach a specific station (the ovary) where it can deliver its cargo (the male gamete).
Transport of Male Gamete
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Male gamete travels through the tube
Detailed Explanation
As the pollen tube grows, it facilitates the movement of the male gamete (sperm cell) through its length toward the ovule, which is located in the ovary. This movement is a critical step because this gamete is what will later fuse with the egg cell for fertilization to occur.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the pollen tube as a delivery truck, transporting a crucial item (the male gamete) to a client (the egg cell) waiting in a warehouse (the ovule) to complete a deal (fertilization).
Fusion of Gametes
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Fusion of male gamete with egg cell (ovum) in ovule
Detailed Explanation
Once the male gamete travels through the pollen tube and reaches the ovule, it undergoes fusion with the egg cell (ovum). This union between the male and female gametes is known as syngamy. This critical process results in the formation of a zygote, marking the first step in the development of a new organism.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like two puzzle pieces coming together to form a complete picture. When the male gamete and egg cell fuse, they create a new piece (the zygote) that will grow into a new plant.
Zygote Development
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Zygote is formed → develops into embryo
Detailed Explanation
After the fusion of the gametes, a zygote is formed. This zygote is the very first cell of the new plant and will begin to divide and develop into an embryo. The embryo is the early stage of the plant's development before it eventually becomes a seed.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the zygote as a seedling that starts its journey towards becoming a tree. Just like a small seedling needs time and nourishment to grow into a strong tree, the zygote will go through several stages to eventually develop into a mature plant.
Key Concepts
-
Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gametes.
-
Zygote: The result of the fertilization process, developing into an embryo.
-
Pollen Tube: Carries the male gamete to the ovule for fertilization.
Examples & Applications
When a pollen grain from a sunflower lands on the stigma of another sunflower, it can lead to fertilization.
Cross-pollination between apple trees can enhance the quality of fruits through genetic diversity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When pollen travels far away, fertilization is here to stay.
Stories
Picture a bee delivering pollen to a flower. It lands on the stigma and from there, the pollen tube grows, sending the male gamete to meet the egg, forming a zygote. This new life begins its journey!
Memory Tools
Remember the steps of fertilization with the mnemonic 'P-P-F-Z': Pollen lands, Pollen tube grows, Fusion happens, Zygote forms.
Acronyms
S.P.E.E.D
Stigma (where pollen lands)
Pollen tube (growth)
Egg (where gamete meets)
Embryo (what zygote becomes)
Development (new life).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fertilization
The process of fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- Zygote
The initial cell formed when a male gamete fuses with a female gamete.
- Pollen Tube
A slender tube that develops from a pollen grain and transports male gametes to the ovule.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
