Disadvantages of Self-Pollination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Self-Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss self-pollination. Can anyone tell me what self-pollination means?

Is it where a flower's pollen fertilizes its own stigma?

Exactly! Self-pollination happens when pollen from the same flower reaches its own stigma. This ensures that the plant can reproduce without needing a partner. However, what do you think could be a downside to this?

Maybe it won’t create much diversity among the plants?

Correct! Reducing genetic variation is a significant disadvantage. Can anyone explain why having less genetic diversity is problematic for plants?

Plants might not adapt well to diseases or changes in the environment?

That's right! Without genetic variation, if a disease strikes, all plants might be susceptible. This leads us to the next point about offspring.

So, the offspring might inherit weak traits?

Exactly! Self-pollination might produce weaker offspring due to a lack of diverse genes. Can anyone think of examples of plants that self-pollinate?
Implications of Reduced Genetic Variation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore how reduced genetic variation affects plant populations. What is genetic variation?

It’s the differences in genes within a species that can lead to different traits.

Exactly! When plants self-pollinate, they lose that variation over time. How might that impact their long-term survival?

They might not survive if the environment changes, like if there’s a new disease.

Correct! This can lead to some plant species becoming endangered or extinct. Why do you think cross-pollination helps prevent this?

Because it introduces new genes, right? So plants can adapt better?

Exactly! Cross-pollination boosts diversity and the health of the species. Let’s summarize these points. Reducing genetic variation can lead to weakened offspring and potential extinction risks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Self-pollination can limit genetic diversity and may result in weaker offspring over successive generations. This section explores these disadvantages and their implications for plant species.
Detailed
Disadvantages of Self-Pollination
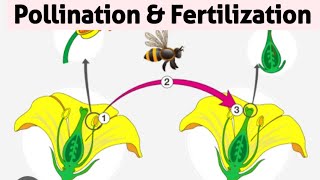
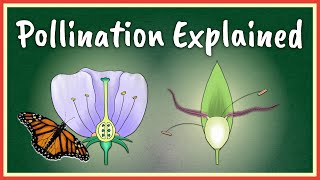
Self-pollination refers to the process where pollen from the anther of a flower fertilizes the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant. While this method of pollination ensures reproduction, it brings along certain disadvantages that may compromise the long-term health of the plant species.
Key Disadvantages:
- Reduces Genetic Variation: Self-pollination leads to a decrease in genetic diversity since the genetic material is derived from a single plant. Lack of genetic variation can hinder a plant's ability to adapt to changing environments.
- May Lead to Weaker Offspring: Over generations, the resulting offspring might inherit negative traits or genetic weaknesses, making them less resilient to diseases and environmental challenges. Without the introduction of diverse genes, the plant population can become stagnant and more susceptible to extinction.
These disadvantages emphasize the importance of cross-pollination, which enhances genetic variation, creates healthier offspring, and allows for better adaptability to the environment.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Reduced Genetic Variation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Reduces genetic variation
Detailed Explanation
Self-pollination occurs when pollen from a flower fertilizes the ovules of the same flower or another flower on the same plant. This process limits genetic mixing since the genetic material is being inherited from the same parental plant. As a result, the offspring are very similar to the parent, leading to less genetic diversity. Reduced genetic variation means that plants may be less adaptable to changing environmental conditions or diseases, which can negatively impact their survival.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a family where all kids look very similar to their parents. If a new trend requires some change in features (like hairstyles or clothing), it might be hard for them to adapt or stand out. Similarly, plants that self-pollinate may struggle to survive when conditions change, as they lack the variety that could help them cope with new challenges.
Weaker Offspring
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● May lead to weaker offspring
Detailed Explanation
Since self-pollination reduces mixing of genetic material, it can result in inbreeding. Inbreeding often causes a decrease in the vigor and health of offspring, known as inbreeding depression. Weak offspring may be more susceptible to diseases and less able to thrive in different environmental conditions. This can ultimately lead to a decline in plant populations over generations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sports team that only recruits players from one local school. They may all have similar skills and play styles, but they lack the diverse talents and strategies that players from a variety of schools would bring. Without that diversity, the team may struggle to compete effectively, just as self-pollinating plants may struggle to survive and thrive in a changing world.
Key Concepts
-
Self-Pollination: A process where a flower fertilizes itself.
-
Genetic Variation: Essential for adaptability and resilience in plant species.
-
Weaker Offspring: Can result from a lack of genetic diversity.
Examples & Applications
Pea plants and mustard plants often self-pollinate, leading to reduced genetic diversity.
Over generations, continuous self-pollination may produce plants vulnerable to diseases.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If a plant's alone and can't take flight, self-pollination is its only sight.
Stories
Once there was a flower that never met another. It thought, 'I’m safe to stay alone,' but soon its children were weak, and they could not even grow.
Memory Tools
For self-pollination think 'Limited Genes, Weak Future'.
Acronyms
SGW - Self-pollination = Stagnant Genes, Weaker Offspring.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SelfPollination
The process where pollen from the same flower fertilizes its own stigma.
- Genetic Variation
The diversity in gene frequencies within a plant species.
- Offspring
The young produced by a plant after fertilization.
- CrossPollination
The transfer of pollen from one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
