Types of Pollination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Types of Pollination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will learn about types of pollination. Can anyone tell me what pollination is?

Isn't it when pollen is transferred from the male part to the female part of the flower?

Exactly right! Pollination occurs when pollen grains are moved from the anther to the stigma. Now, can you name the two main types of pollination?

Is it self-pollination and cross-pollination?

Correct! Self-pollination happens when pollen comes from the same flower or another flower on the same plant. Can you think of a plant that does this? Remember: **P**ea and **M**ustard.

Oh, Pea and Mustard! I’ll remember those as PM plants!

Great memory aid! Now, cross-pollination occurs between different plants. Can anyone provide an example?

How about Hibiscus and Apple trees?

Exactly! Cross-pollinated plants often have increased genetic diversity, which is vital for adaptation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pollination Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now dive into the advantages and disadvantages of self-pollination and cross-pollination. Why might cross-pollination be beneficial?

It increases genetic variation which is good for survival!

Exactly! Genetic variation helps plants adapt to their environments. What about self-pollination? What could be a drawback?

It might reduce genetic variation and lead to weaker plants?

Precisely! Low genetic variation can make populations more susceptible to diseases. Remember: **S**elf-pollination leads to **S**impler genetics!

So self-pollination has its downsides even if it's easier?

Right! Each method has its place in nature.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Pollination can be classified into two main types: self-pollination, where pollen from the same flower fertilizes itself or another flower on the same plant, and cross-pollination, where pollen is transferred between different plants of the same species. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages affecting genetic variation and offspring health.
Detailed
Types of Pollination
Overview
Pollination is the critical process by which pollen grains transfer from the anther to the stigma of flowers. Understanding the types of pollination provides insights into plant reproduction.
Types of Pollination
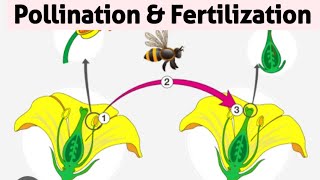
1. Self-Pollination
In self-pollination, pollen from the anther of a flower reaches the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
- Examples: Pea plants, Mustard plants.
2. Cross-Pollination
Cross-pollination involves the transfer of pollen to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species.
- Examples: Hibiscus, Apple trees.
Advantages of Cross-Pollination
- Increased Genetic Variation: Cross-pollination promotes diversity in plant traits, leading to healthier populations.
- Healthier Offspring: Offspring may be more robust and adaptable to environmental changes.
Disadvantages of Self-Pollination
- Reduced Genetic Variation: Self-pollination limits genetic diversity which can lead to a population that is more susceptible to diseases.
- Weaker Offspring: May produce weaker plants over generations due to lack of genetic diversity.
Significance
Understanding these types of pollination and their implications is essential for studies in ecology, agriculture, and conservation.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Self-Pollination
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Self-Pollination: Pollen from the anther reaches the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
- Example: Pea, mustard.
Detailed Explanation
Self-pollination occurs when pollen grains from the male part (anther) of a flower are transferred to the female part (stigma) of either the same flower or another flower on the same plant. This process ensures that the plant can reproduce without needing pollen from another plant, which can be beneficial when pollinators are scarce or when environmental conditions are not favorable.
Examples & Analogies
Think of self-pollination like a person writing a letter to themselves. They don’t need to send it to anyone else because they can deliver the message themselves. Similarly, plants can reproduce on their own without relying on others.
Cross-Pollination
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Cross-Pollination: Pollen is transferred to the stigma of a different flower on a different plant of the same species.
- Example: Hibiscus, apple.
Detailed Explanation
Cross-pollination occurs when pollen from one flower fertilizes the stigma of a different flower on another plant of the same species. This enhances genetic diversity among plants, which is crucial for healthy populations. Cross-pollination often involves pollinators like insects or wind, helping to spread genetic material across distances.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine two friends sharing ideas on a project to create something better than what they could make alone. Just like the friends combine their thoughts for a beneficial outcome, plants benefit from cross-pollination because it mixes genetic traits, leading to stronger and more resilient offspring.
Advantages of Cross-Pollination
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Advantages of Cross-Pollination:
- Increases genetic variation
- Leads to healthier offspring
- Promotes better adaptability.
Detailed Explanation
Cross-pollination contributes to increased genetic variation among plants. This variety is beneficial because it can produce offspring that may be more resilient to diseases, pests, and environmental changes. Such genetic diversity is vital for the adaptability and survival of plant species in different habitats.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sports team that recruits players with different skills and backgrounds. The team becomes stronger and more adaptable to various gaming strategies. Similarly, plants that undergo cross-pollination can thrive better in changing conditions, leading to healthier populations.
Disadvantages of Self-Pollination
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Disadvantages of Self-Pollination:
- Reduces genetic variation
- May lead to weaker offspring.
Detailed Explanation
While self-pollination can be a quick and reliable method for reproduction, it has significant drawbacks. One of the main issues is the reduced genetic variation, which can make populations more susceptible to diseases and environmental stresses. Over time, this lack of diversity may result in weaker seedlings, making it harder for the species to thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a family where everyone looks very similar and shares the same interests. They might not be good at adapting to new situations compared to a diverse group of friends with different perspectives. Similarly, plants that self-pollinate may struggle to cope with new challenges due to their genetic similarities.
Key Concepts
-
Self-Pollination: The fertilization of a flower by its own pollen.
-
Cross-Pollination: The fertilization process involving pollen from different plants of the same species.
-
Genetic Variation: The diversity in gene frequencies among individuals in a population.
-
Adaptive Advantages of Cross-Pollination: Enhanced survival and adaptability in changing environments.
Examples & Applications
In self-pollinated plants like peas, the flowers can seed without needing other plants.
Cross-pollination in apple trees often leads to a wider range of fruit characteristics and health.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When pollen's close, it's self-pollinating; with a friend, it’s cross-pollinating!
Stories
Once there was a pea plant that loved to bloom alone, producing seeds by itself. But when it met an apple tree, the diversity of fruit made true harmony—wider, healthier seeds, all thanks to the fun of cross-pollinating!
Memory Tools
Think of Self for Same (Self-Pollination) and Cross for Diversity (Cross-Pollination)!
Acronyms
Remember CAMP** for cross-pollination
C**ross
**A**daptation
**M**ore genetic variety
**P**lenary opportunities.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SelfPollination
Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
- CrossPollination
Transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of a different flower of the same species.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
