Applications of Instrumentation Amplifiers
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Role in Medical Instruments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the application of instrumentation amplifiers, starting with their role in medical instruments, like ECGs and EEGs. Can anyone tell me what these devices measure?

ECGs measure electrical activity in the heart, and EEGs track brain activity.

Exactly! Instrumentation amplifiers are crucial here because they can amplify those tiny electrical signals without interfering with the measurements. Why is that important?

If the amplifier adds noise or loads the signal, it could affect the readings.

Correct! The high input impedance of instrumentation amplifiers ensures minimal loading and high accuracy. Let's remember it as 'HI-AI'—High Input, Accurate Instrumentation.

Got it! HI-AI helps me remember the importance of accurate readings in medical devices.

Great! In summary, instrumentation amplifiers allow for accurate measurements in medical applications.
Use in Industrial Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's move on to industrial applications. How do instrumentation amplifiers assist in industrial sensors, like temperature sensors or strain gauges?

They amplify the weak signals coming from these sensors so that they can be processed or displayed.

Exactly! Instrumentation amplifiers enhance those signals, but they also reject any noise present. What might be the consequence of not using them in these cases?

If we don’t use them, noise could corrupt the data, leading to incorrect readings.

Yes! Remember the abc—'Amplify, Boost, Clean.' It helps remind us that they amplify the signal while cleaning up noise. What are some real-world applications we can think of?

In factories, they help monitor processes, ensuring equipment operates at the right temperatures.

Spot on! Instrumentation amplifiers are essential for maintaining optimal conditions in industrial environments.
Importance of Precision Measurement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss precision measurement systems. Why do you think instrumentation amplifiers are preferred in high-accuracy measurement systems?

Because they need to amplify low-level signals without introducing distortion or error.

Right! They help ensure that the data collected is as reliable as possible. How does this relate to research or lab settings?

In labs, we rely on accurate measurements to draw correct conclusions from experiments.

Exactly! Let's condense that into a phrase: 'Precision is in the Amplification'—it shows that good amplifiers lead to precise outcomes.

I like that phrase! It’s easy to remember.

Fantastic! Remember, without precise amplification, much of our understanding in technology and science could be compromised.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the significant applications of instrumentation amplifiers in fields such as medical instruments (e.g., ECG, EEG) and industrial sensors for temperature, strain, and pressure measurement. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of precision measurement in systems requiring accurate signal conditioning.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Instrumentation amplifiers play a crucial role in amplifying low-level signals while maintaining high precision and low noise. This section specifically highlights the practical applications of instrumentation amplifiers in various domains:
- Medical Instruments: Instrumentation amplifiers are integral in medical diagnostics, utilized in devices such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electroencephalograms (EEGs) for monitoring bio-potential measurements. Their high input impedance and low output impedance are vital for ensuring accurate readings without loading the sensor outputs.
- Industrial Sensors: These amplifiers are essential for amplifying signals from industrial sensors like temperature sensors, strain gauges, and pressure sensors. Their ability to reject noise and enhance weak signals makes them ideal for real-world applications in manufacturing, process control, and automation.
- Precision Measurement Systems: Instrumentation amplifiers are favored in high-accuracy measurement setups where precise low-level signal amplification is mandatory. This is particularly significant in laboratory settings and research applications where measurement accuracy is paramount. By ensuring that weak signals are faithfully amplified without distortion, instrumentation amplifiers facilitate reliable data acquisition and analysis.
Youtube Videos
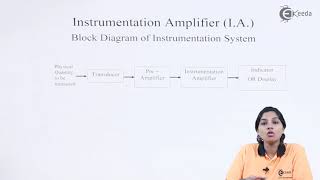



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Medical Instruments
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used in electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalogram (EEG), and other bio-potential measurements.
Detailed Explanation
Instrumentation amplifiers are essential in medical instruments like ECG and EEG machines. They are used to amplify the tiny electrical signals generated by the heart and brain. These signals are very low-level, so the high gain and precision provided by instrumentation amplifiers allow for accurate readings. This is crucial for diagnosing health conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the instrumentation amplifier like a microphone that picks up a whisper in a noisy room. Just as the microphone amplifies that quiet sound so you can hear it clearly, the instrumentation amplifier raises the weak electrical signals from your body so doctors can see what’s happening inside.
Industrial Sensors
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Amplifies signals from temperature sensors, strain gauges, and pressure sensors.
Detailed Explanation
Instrumentation amplifiers play a key role in industrial settings by amplifying signals from various sensors used to monitor temperature, pressure, and other critical parameters. These sensors often generate small voltage changes that need to be reliably processed and transmitted for monitoring and control purposes. The high input impedance and low noise attributes of these amplifiers ensure that the readings are accurate and not influenced by external factors.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a weather station that measures temperature and pressure. If the sensors detect a slight change in temperature, the instrumentation amplifier acts like a reliable translator, converting that small change into a loud, clear signal that can be read and recorded. This ensures that even the slightest fluctuations in weather are captured and analyzed.
Precision Measurement
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used in high-accuracy measurement systems where low-level signal amplification is required.
Detailed Explanation
In applications that demand extreme accuracy, such as laboratory experiments and high-tech manufacturing, instrumentation amplifiers are indispensable. They provide the necessary low-level signal amplification to ensure that measurements are precise and reliable. The ability to accurately amplify small signals without introducing noise is crucial to obtaining valid results in these high-stakes environments.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a scientist measuring the minute changes in a solution's properties in a lab. The instrumentation amplifier functions like a powerful magnifying glass, making tiny details visible so the scientist can feel confident in their measurements. Just as a magnifying glass helps see fine print that would otherwise be missed, the instrumentation amplifier clarifies small electrical signals for precise analysis.
Key Concepts
-
Instrumentation Amplifiers: Essential for amplifying low-level signals with high accuracy.
-
Medical Applications: Used in devices like ECGs and EEGs for monitoring vital signs.
-
Industrial Sensors: Amplify sensor outputs in various industrial applications for better data accuracy.
Examples & Applications
In medical devices, such as ECGs, instrumentation amplifiers capture weak heart signals for accurate health monitoring.
In temperature control systems, instrumentation amplifiers enhance data from thermocouples to ensure safe operational conditions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To amplify with precision and gain, instrumentation's what you should retain.
Stories
Imagine a doctor listening to a heartbeat. Without instrumentation amplifiers, the delicate signals would be drowned in noise, just like a faint whisper in a loud crowd. These amplifiers help clarify that whisper.
Memory Tools
H.I.A—High Input, Accurate Amplification, helps remember that instrumentation amplifiers enhance signal precision.
Acronyms
R.E.A.C.T—Rejects noise, Enhances signal, Accurate measurements, Crucial for measurement, Tests reliability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Instrumentation Amplifier
A type of differential amplifier specifically designed for low-level signal amplification with high input impedance.
- CommonMode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)
A measure of an amplifier's ability to reject common-mode signals, thus enhancing the accuracy of the desired output.
- BioPotential Measurements
Electrical signals produced by biological systems, crucial for medical diagnostics.
- Signal Conditioning
The process of manipulating a signal to prepare it for the next stage of processing.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
