Summary of Key Concepts
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Instrumentation Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will talk about instrumentation amplifiers, commonly used for amplifying low-level differential signals. Can anyone tell me why high input impedance is important for these amplifiers?

Is it to prevent drawing current from the source?

Exactly! High input impedance ensures the signal source remains unaffected. High input impedance also yields accurate readings. Let's remember it as H.I.P: High input for Precision! What applications do you think utilize instrumentation amplifiers?

Medical instruments like ECGs!

Right! They are vital in medical instruments, industrial sensors, and for precision measurements. Remember, these amplifiers help amplify low signals while rejecting noise. Any questions?
Precision Rectifiers and Peak Detectors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift gears to precision rectifiers and peak detectors. What do you think a precision rectifier does?

Does it convert AC to DC signals?

Yes! It rectifies AC signals accurately, even at low levels where diodes fail. Remember 'P.R.A.D' – Precision Rectifying AC's Discrepancies! Can someone give an application of peak detectors?

Audio systems use them to detect peak levels!

Exactly! They are essential in various monitoring applications, including audio systems and oscilloscopes. Excellent participation, everyone!
Low-Noise Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s cover low-noise amplifiers. Why do you think reducing noise is critical in measurements?

It ensures the clarity of weak signals like in radio or medical instruments!

Correct! LNAs amplify weak signals while introducing minimal noise, which is vital for applications in RF systems and medical instrumentation. Remember: 'Less Noise, Clarity Close.' What do you think would happen without them?

We would get inaccurate readings?

Precisely! Always consider signal-to-noise ratios when assessing amplifier performance. Great job, everyone!
Differential Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss differential amplifiers. What is their main function?

They amplify the difference between two input signals.

Exactly! They also reject common-mode noise effectively. Think of it as the ‘Two Minus One’ rule to remember their operation. Can anyone point out where they might be applied?

In sensor applications!

Right on! They are fundamental in ensuring accurate readings by suppressing noise. Fantastic work discussing these essential amplifiers!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines essential elements of various types of amplifiers used in instrumentation circuits, emphasizing their roles in accurately amplifying low-level signals, signal rectification, and noise reduction. Key applications in medical instrumentation, industrial sensors, and precision measurements are highlighted.
Detailed
Summary of Key Concepts
This section summarizes the pivotal concepts introduced throughout the chapter concerning instrumentation circuits involving operational amplifiers (Op-Amps).
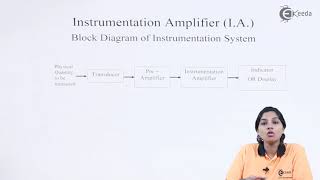
- Instrumentation Amplifiers: These amplifiers excel in the precise amplification of low-level differential signals, making them indispensable in medical instruments, industrial sensors, and high-accuracy measurement systems. Their high input impedance and excellent common-mode rejection are key characteristics.
- Precision Rectifiers and Peak Detectors: These circuits enable accurate signal rectification and peak value detection, crucial for reliable signal processing in various monitoring applications.
- Low-Noise Amplifiers: LNAs are designed to amplify weak signals while minimizing additional noise. Their importance is underscored in fields such as radio communication and medical instrumentation, where integrity of weak signals is crucial.
- Differential Amplifiers: They amplify the difference between two input signals and effectively reject common-mode noise, making them essential for precision measurement applications and signal conditioning.
Through understanding these amplifiers’ configurations and functions, one can appreciate their significance in enhancing accuracy and performance in measurement systems.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Instrumentation Amplifiers
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Used for precise amplification of low-level differential signals.
- Essential for medical instrumentation, industrial sensors, and high-accuracy measurement systems.
Detailed Explanation
Instrumentation amplifiers are specialized amplifiers that are critical in amplifying small signals that are found in many sensing applications. They are particularly effective when measuring the difference between two signals while rejecting any noise that may be present. This makes them extremely useful in medical devices like ECG machines, which need to detect weak heart signals while ignoring interference.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an instrumentation amplifier like a highly focused microphone designed to hear a subtle conversation in a noisy café. While the background noise (like people chatting or coffee machines) can obscure the conversation, the focused microphone captures only the relevant signals clearly, allowing accurate interpretation.
Precision Rectifiers and Peak Detectors
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Used for accurate signal rectification and peak value detection.
- Critical in signal processing and monitoring applications.
Detailed Explanation
Precision rectifiers are circuits designed to accurately convert AC signals to DC without the inaccuracies that can arise from traditional diode rectifiers. Peak detectors, on the other hand, track and hold the peak values of a signal, which is crucial in systems that need to monitor for maximum signal levels, such as audio equipment or signal processing systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are trying to keep track of the highest wave while surfing. A peak detector would be like your friend who marks the tallest wave you ride, allowing you to remember your best waves even while more waves come crashing down around you.
Low-Noise Amplifiers
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Amplify weak signals with minimal additional noise.
- Key in radio, medical, and sensor applications.
Detailed Explanation
Low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) serve a significant role in many applications that require the detection of very faint signals, such as in radio communications and medical instrumentation. LNAs are specially designed to introduce very little noise into the system while boosting the signal strength, which is essential for achieving clear and accurate measurements.
Examples & Analogies
Consider LNAs like a super-efficient sound amplifier at a concert that only captures the singer's voice without amplifying the crowd noise, ensuring that the performance comes across crystal clear even in a bustling venue.
Differential Amplifiers
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting common-mode noise.
- Commonly used in instrumentation and precision measurement applications.
Detailed Explanation
Differential amplifiers can amplify the difference between two voltages while ignoring any voltage component that is common to both. This feature makes them exceptionally useful in noisy environments, ensuring that only the intended signal is amplified, which is critical for instrumentation tasks such as measuring temperature with thermocouples or pressuring sensors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a differential amplifier as a trained translator at a busy government office. While many people might be speaking at once (the noise), the translator focuses only on the specific conversation between two clients, ensuring that the meaning of their dialogue is conveyed clearly.
Key Concepts
-
Instrumentation Amplifiers: Used for precise amplification of low-level differential signals important for measurement systems.
-
Precision Rectifiers: Enable accurate signal rectification even at low levels where diodes fail.
-
Low-Noise Amplifiers: Amplify weak signals while minimizing additional noise crucial for accurate measurements.
-
Differential Amplifiers: Amplify the difference between signals and reject common-mode noise for precision.
Examples & Applications
An instrumentation amplifier is used in an EEG machine to amplify brain signal activity without interference from noise.
A precision rectifier converts small AC audio signal for further processing in audio equipment.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For signals faint, don't you fear, Low noise amplifiers help you hear.
Stories
Imagine a doctor using a precise instrument to listen to a faint heartbeat, amplified by an instrumentation amplifier ensuring clarity, free from noise.
Memory Tools
Remember 'PRIME' - Precision Rectifiers Improve Measurement Efficiency.
Acronyms
H.I.P for High input for Precision related to instrumentation amplifiers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Instrumentation Amplifier
An amplifier designed for precise amplification of low-level differential signals, offering high input impedance.
- Precision Rectifier
An Op-Amp-based circuit that rectifies an AC signal accurately, especially at low levels.
- Low Noise Amplifier (LNA)
Circuits designed to amplify weak signals while minimizing noise.
- Differential Amplifier
An amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input signals and rejects common-mode noise.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
