Identity Matrix
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Identity Matrix
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll be focusing on the identity matrix. Can anyone tell me what an identity matrix is?

Is it like the number 1 for matrices? It keeps things the same when you multiply.

Exactly! The identity matrix is a square matrix with ones on the diagonal and zeros everywhere else. For example, for a 3x3 matrix, it looks like this: [1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0 1]. We denote it as I_n, where n is the order.

So what happens if we multiply any matrix by it?

Great question! Multiplying any matrix A by the identity matrix I will yield A. This property confirms its role as a multiplicative identity in matrix algebra.
Rank of the Identity Matrix
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the rank of the identity matrix. Who can tell me what the rank of I_n is?

Isn't it n because all rows and columns are independent?

Correct! The rank of an identity matrix is n, indicating full linear independence. This quality is significant in applications such as linear transformations and solving systems of equations.

So the identity matrix always has a complete rank, right?

Exactly! Rank measures the maximum number of linearly independent rows or columns. An identity matrix maximizes this value by having all rows and columns linearly independent.
Applications of the Identity Matrix
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone think of applications where identity matrices are utilized?

They must be used in computer graphics for transformations!

That's right! Identity matrices are pivotal in computer graphics to transform shapes without changing their size or orientation. They are also crucial in algorithm designs and matrix inversion.

What about in solving equations? Do they play a role there too?

Absolutely! The identity matrix is used in linear algebra to find solutions to equations and to confirm the maintainability of systems. This will become clearer as we advance in our studies.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
An identity matrix of order n is defined as a square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. It holds significant importance in various linear algebra applications, as it serves as the multiplicative identity in matrix multiplication, and its rank, equating to n, reflects its complete linear independence.
Detailed
Identity Matrix
The identity matrix of order n, denoted as I_n, is a square matrix where the diagonal elements are all equal to 1 and all off-diagonal elements are 0. This structure gives the identity matrix unique properties in linear algebra. The rank of an identity matrix is n, indicating that all its rows (or columns) are linearly independent. This characteristic signifies that the identity matrix can be employed in solving linear systems and developing the concept of matrix inverses, since the multiplication of any matrix A by the identity matrix I results in A itself (i.e., AI = A). This property confirms the identity matrix's role as the multiplicative identity in the matrix algebra domain.
Youtube Videos





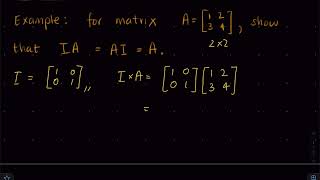
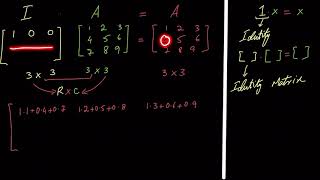


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Identity Matrix
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The identity matrix of order n has rank n because all rows (and columns) are linearly independent.
Detailed Explanation
An identity matrix is a special kind of square matrix where all the elements on the main diagonal (from the top left to the bottom right) are 1, and all other elements are 0. This matrix plays a crucial role in linear algebra, particularly in matrix multiplication, as it acts like the number 1 in regular multiplication. For an identity matrix of order n, which means it has n rows and n columns, the rank is equal to n because each row is linearly independent. Linear independence here means that no row can be written as a combination of the others.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the identity matrix like a set of unique identifiers (like Social Security numbers) where each number is distinct and cannot be derived from others. Just as every individual has a unique identifier that cannot be recreated from others, each row of the identity matrix uniquely contributes to the matrix's structure, making it fully encompassing (i.e., each row and column is independently valuable).
Key Concepts
-
Identity Matrix: A square matrix with ones on the diagonal and zeros everywhere else.
-
Rank: The number of linearly independent rows or columns in a matrix.
Examples & Applications
An example of a 3x3 identity matrix is:
[1 0 0]
[0 1 0]
[0 0 1].
The identity matrix I_2 is:
[1 0]
[0 1].
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a diagonal dance, ones take a chance; zeros by their side hold the identity's pride.
Stories
Imagine a kingdom where the rulers are all the same number, 1, standing tall in their castle (the diagonal), while the rest are mere shadows (0s) reflecting their strength.
Memory Tools
Remember I for Identity, where 'I' stands for Independence in linear rows.
Acronyms
I.M.A. - Identity Matrix Always means independence.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Identity Matrix
A square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere, symbolized as I_n.
- Rank
The maximum number of linearly independent rows or columns in a matrix.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
