Code Recommendations and Standards
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Code Recommendations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today we’ll discuss the vital code recommendations that guide pavement design. Can anyone share what they think regulations do for engineering?

They probably ensure safety and quality, right?

Exactly! These regulations help maintain safety and performance standards in construction. One important standard is IRC:37. Who knows what it addresses?

I think it’s for flexible pavements based on CBR values?

Correct! The California Bearing Ratio, or CBR, is especially significant because it determines how thick and sturdy a pavement needs to be. Remember this with the mnemonic 'C-B-R: Count on Base Roads'! It helps us remember that CBR relates to base layers in pavements.
Rigid Pavement Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to rigid pavements, guided by IRC:58. Can someone tell me why we need separate guidelines for rigid pavements?

Different materials and loading conditions affect how they behave?

Exactly! Rigid pavements are made from concrete, which behaves differently than flexible materials. IRC:58 offers detailed design principles to withstand these unique conditions. A good memory aid here is 'I-R-C: In Rigid Concrete', which reminds us that IRC guidelines relate directly to concrete pavement.
Resilient Modulus Testing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next up is AASHTO T 307, which covers resilient modulus testing. Can anyone explain what resilient modulus measures?

I think it measures how well the soil can handle repetitive loads?

Correct! It assesses the elastic response of soil, crucial for mechanistic-empirical design. Remember, 'R-M: Resilience Matters' to help recall its importance!
Field Testing and Quality Control
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's talk about MORTH specifications. Why do you think quality control in field testing is critical?

To ensure the pavements last longer and are safe for use?

Absolutely! MORTH lays out guidelines to ensure each construction phase meets quality standards. Remember 'M-O-R-T-H: Maintain Our Roads To Help' to emphasize the goal of these standards.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses critical standards such as IRC:37 for flexible pavements and IRC:58 for rigid pavements, as well as AASHTO T 307 for resilience modulus testing and MORTH specifications focusing on quality control and field testing.
Detailed
Code Recommendations and Standards
This section details essential code recommendations and standards pivotal for pavement design, which helps ensure the reliability and integrity of pavement structures. The major standards highlighted include:
- IRC:37 - This document provides design guidelines specifically for flexible pavements based on the California Bearing Ratio (CBR) values, which are vital in determining the thickness and load-bearing capacity of road surfaces.
- IRC:58 - This guideline focuses on the design of rigid pavements, incorporating principles that account for different loading and stress conditions.
- AASHTO T 307 - This standard is critical for resilient modulus testing, which assesses the elastic behavior of soils when subjected to repetitive loads, a key factor in mechanistic-empirical pavement design.
- MORTH Specifications - These are comprehensive regulations governing field testing and quality control, ensuring that construction practices align with the highest standards of material and workmanship.
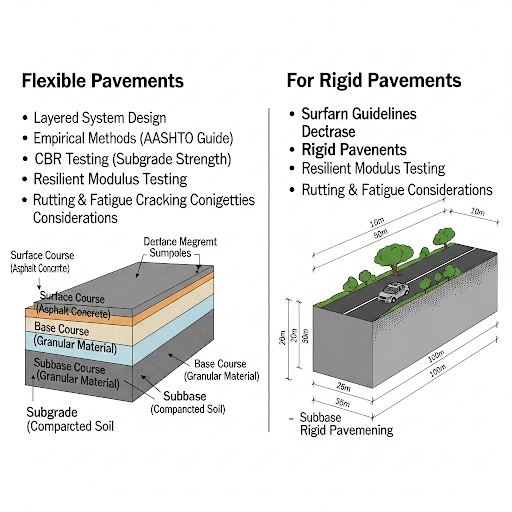
Understanding and applying these standards facilitates effective pavement design, enhances structural durability, and ensures safety across varying environmental conditions.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
IRC:37 - Flexible Pavements
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- IRC:37 – Design guidelines for flexible pavements based on CBR.
Detailed Explanation
IRC:37 refers to the Indian Road Congress guidelines for designing flexible pavements. These guidelines utilize the California Bearing Ratio (CBR) as a key parameter. CBR is a measure of the strength of the subgrade soil, helping engineers determine how thick the pavement needs to be to withstand traffic loads. The guidelines provide standardized methods for evaluating soil strength and recommend structural designs that ensure durability under expected traffic conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are building a road to withstand heavy trucks versus light cars. If the ground is weak, like pudding, the heavier trucks might sink, causing damage. IRC:37 helps ensure the road is strong enough to support the heavier vehicles, just like building a stronger bridge for larger trucks.
IRC:58 - Rigid Pavements
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- IRC:58 – Guidelines for rigid pavement design.
Detailed Explanation
IRC:58 provides specific guidelines for designing rigid pavements, which are typically made of concrete. Unlike flexible pavements, rigid pavements distribute loads over a larger area, making them suitable for high-load vehicles such as buses. The guidelines consider factors like material properties, traffic loads, and environmental conditions to ensure a long-lasting pavement solution.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a rigid pavement like a sturdy table that can hold a heavy load without bending. Just as you would choose a thick, sturdy wood for a heavy tabletop, IRC:58 helps engineers select the right materials and design principles to ensure concrete roads can endure heavy traffic without cracking.
AASHTO T 307 - Resilient Modulus Testing
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- AASHTO T 307 – For resilient modulus testing.
Detailed Explanation
AASHTO T 307 is a standard procedure for testing the resilient modulus of subgrade soils. Resilient modulus represents the elastic response of soil under repeated loading, which occurs when vehicles travel over pavements. This test is crucial for predicting how pavement will behave under actual traffic conditions and helps in making informed design decisions that ensure longevity and functionality.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a sponge reacts when you press down on it and then let go. The resilient modulus test helps engineers understand how soil behaves similarly under the weight of multiple vehicles over time, ensuring the pavement can recover from deformation without permanent damage.
MORTH Specifications - Field Testing Standards
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- MORTH Specifications – Field testing and quality control standards.
Detailed Explanation
MORTH (Ministry of Road Transport and Highways) specifications outline procedures for field testing and quality control during pavement construction. Adhering to these standards ensures all materials and methods meet required safety and performance thresholds, minimizing the risk of future pavement failures. These guidelines also facilitate consistency in construction practices across different projects.
Examples & Analogies
Building a road without following MORTH standards is like cooking without a recipe; you might end up with something that doesn’t taste good or is unsafe to eat. Just as a recipe guides you to use the right ingredients and cooking time, MORTH standards ensure all the right materials and methods are used to create a safe and durable road.
Key Concepts
-
IRC:37: Guidelines for designing flexible pavements based on CBR values.
-
IRC:58: Specifications tailored for the design of rigid pavements.
-
AASHTO T 307: Standard for measuring resilient modulus in soils.
-
MORTH: Regulations ensuring quality control in pavement construction.
Examples & Applications
Application of IRC:37 in the design of a new urban road based on CBR test results.
Use of AASHTO T 307 in assessing the elasticity of subgrade in a highway reconstruction project.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
IRC sets the pace, for roads to embrace, whether flexible or rigid, it keeps quality in place.
Stories
Imagine a town planning a new highway. They carefully follow IRC:37 for flexible designs and IRC:58 when using concrete, ensuring safe travels for all.
Memory Tools
R-M: Remember Modulus for AASHTO, it's key for soil testing.
Acronyms
M-O-R-T-H
Maintain Our Roads To Help!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- IRC:37
Design guidelines for flexible pavements based on the California Bearing Ratio.
- IRC:58
Guidelines for rigid pavement design.
- AASHTO T 307
Standard for resilient modulus testing in soils.
- MORTH Specifications
Specifications governing field testing and quality control in construction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
