Origin and Composition of Bitumen
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Production of Bitumen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss how bitumen is produced and its importance in construction. Can anyone tell me what the primary source of bitumen is?

Is it derived from crude oil?

Absolutely! Bitumen is produced from the fractional distillation of crude oil. What do you think happens to the lighter fuels during this process?

They are extracted first, right?

Yes, well done! The lighter fractions like gasoline and diesel are removed, leaving behind the heavier bitumen. This heavy material is crucial for road surfaces. Now, why do you think it's important to understand the composition of bitumen?

Because different components affect its properties and performance?

Exactly! Composition impacts its performance as a binder in pavements. Let's remember that using the acronym 'A.R.S.' can help us recall its components: Asphaltenes, Resins, and Saturates. What's our acronym?

A.R.S.!

Great job! In summary, bitumen is produced from crude oil, and understanding its composition is key to ensuring the durability and effectiveness of our roads.
Components of Bitumen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into the different components in bitumen. Who remembers what Asphaltenes contribute to?

They contribute to the stiffness of bitumen!

Correct! And how about Resins? What do we know about them?

They help with adhesion and ductility.

Exactly! Resins enhance adhesion to aggregates in roads. Now, when we talk about Aromatics, what do they influence?

They influence flow characteristics?

That's right! And Saturates affect the aging of bitumen. To help remember these components, let’s create a little rhyme: 'Asphaltenes make it tough, Resins keep it smooth enough, Aromatics aid the flow, Saturates help it not to slow.' Can anyone repeat the rhyme?

Asphaltenes make it tough, Resins keep it smooth enough, Aromatics aid the flow, Saturates help it not to slow!

Perfect! Understanding these components allows us to assess the performance of bitumen in road construction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the origin of bitumen, emphasizing its production through the fractional distillation of crude oil in refineries and its critical role as a binding agent in flexible pavement structures. The composition of bitumen consists of various hydrocarbons that affect its physical and chemical properties.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Bitumen, primarily used in road construction, is produced through the fractional distillation of crude oil. It represents the heaviest fraction left after lighter fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and kerosene are extracted. The composition of bitumen is complex, incorporating different hydrocarbon types, each contributing unique characteristics:
- Asphaltenes contribute to stiffness due to their high molecular weight.
- Resins enhance adhesion and ductility, making the material effective in various environmental conditions.
- Aromatics affect the flow characteristics, essential for the blending and application processes.
- Saturates, which are paraffinic hydrocarbons, play a role in aging, influencing the long-term performance of bitumen in pavement structures.
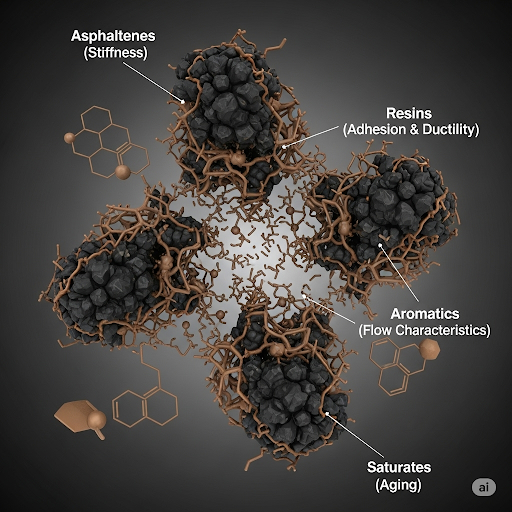
Understanding these components is vital, as the overall performance and durability of bituminous pavements hinge upon the quality and characteristics of the bitumen used.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Origin of Bitumen
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bitumen is produced from the fractional distillation of crude oil in refineries. It is the heaviest fraction left behind after the removal of lighter fuels like gasoline, diesel, and kerosene.
Detailed Explanation
Bitumen originates from crude oil, which is a natural resource derived from ancient organic materials subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years. In the refining process, crude oil is heated, and different components are separated based on their boiling points. During fractional distillation, the lighter fractions such as gasoline, diesel, and kerosene evaporate first, leaving the heavier fraction, which is bitumen. This makes bitumen one of the densest forms of hydrocarbons obtained from crude oil.
Examples & Analogies
Think of crude oil as a cake where different layers represent various oil products. When the cake (crude oil) is baked (refined), the lighter layers (like frosting) are removed first, and what remains at the bottom is the dense, heavy part (bitumen), which is thick and sticky, similar to the bottom layer of a cake that doesn't lift easily.
Chemical Composition of Bitumen
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bitumen is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons containing:
• Asphaltenes: High molecular weight compounds that contribute to the stiffness.
• Resins: Contribute to adhesion and ductility.
• Aromatics: Contribute to flow characteristics.
• Saturates: Paraffinic hydrocarbons that influence aging.
Detailed Explanation
The chemical composition of bitumen consists of various types of hydrocarbons that play different roles in its properties. Asphaltenes are large, complex molecules that make bitumen stiff and provide strength. Resins help the bitumen to stick to aggregates, while also enhancing its flexibility (ductility). Aromatics are smaller molecules that help bitumen flow better, especially under heat. Lastly, saturates are relatively simple hydrocarbons that can help determine how well bitumen ages over time. Together, these components make bitumen a versatile material for road construction.
Examples & Analogies
Consider bitumen like a recipe for a thick, rich sauce. Asphaltenes are the solid ingredients like vegetables, resins act like spices that enhance flavor (stickiness), aromatics are the lighter ingredients that help create a smooth texture (like cream), and saturates are the oils that ensure everything cooks well together and ages nicely without going bad.
Key Concepts
-
Bitumen Production: Derived from the fractional distillation of crude oil, creating a heavy residue.
-
Hydrocarbon Composition: Bitumen consists of Asphaltenes, Resins, Aromatics, and Saturates, each affecting its properties.
Examples & Applications
Bitumen is used as a binder in asphalt concrete for road paving projects.
The high viscosity of bitumen helps ensure strong adhesion to aggregates in pavement.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Asphaltenes make it tough, Resins keep it smooth enough, Aromatics aid the flow, Saturates help it not to slow.
Stories
Imagine a construction site where workers are busy mixing concrete. Each batch requires bitumen, but the mix needs to be just right. The workers rely on Asphaltenes to give strength, Resins to help it stick, Aromatics to ensure it flows properly, and Saturates to prevent aging. Each component tells a part of the story of how good roads are built!
Memory Tools
Remember 'A.R.S.' for Asphaltenes, Resins, Saturates in bitumen composition.
Acronyms
A.R.S. - Asphaltenes, Resins, Saturates to recall key components of bitumen.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Asphaltenes
High molecular weight compounds in bitumen that contribute to stiffness.
- Resins
Compounds in bitumen that enhance adhesion and ductility.
- Aromatics
Hydrocarbons in bitumen affecting flow characteristics.
- Saturates
Paraffinic hydrocarbons that influence the aging of bitumen.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
