Temperature Susceptibility
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Temperature Susceptibility
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to discuss temperature susceptibility. Can someone tell me why it might be important for bitumen to maintain consistent stiffness with temperature changes?

I think it helps prevent cracks in the pavement when it's cold.

That's correct! Keeping a consistent stiffness means that bitumen can accommodate changes in temperature without becoming too hard or too soft. This quality is vital for the pavement's longevity.

So, if it becomes too soft in heat, doesn't that mean the pavement could wear out faster?

Exactly! Excessive softness in high temperatures leads to deformation, which impacts the pavement's durability. Remember, we're aiming for minimal temperature susceptibility to maintain stability.

How do we test for temperature susceptibility then?

Great question! We can determine this through various tests like the softening point test, which indicates how well the bitumen can resist softening at elevated temperatures.

What happens if the bitumen doesn't pass that test?

If the bitumen fails the softening point test, it might not be suitable for warm climates. It could lead to early pavement failures. Let's recap: temperature susceptibility is crucial for performance, we talk about stiffness, and tests like the softening point can confirm suitability.
Effects of Temperature on Bitumen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s elaborate on the effects of temperature on bitumen's characteristics. Why is understanding this critical for road construction?

Because if we understand how it behaves, we can choose the right type of bitumen for our climate!

Exactly! Different regions require bitumen with specific temperature susceptibility to avoid issues throughout the year. Can anyone think of an example?

In places with extreme winter, we need bitumen that stays flexible even when it’s freezing.

Correct! And in hot climates, we need a bitumen that won't melt or deform. It’s all about matching the right material to environmental conditions.

And this ties back to the importance of the tests we discussed!

Absolutely! Testing helps ensure that we use materials that won’t fail under temperature extremes. Let’s conclude with the key point: understanding temperature susceptibility is essential for choosing appropriate bitumen.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses temperature susceptibility in bitumen, emphasizing the importance of maintaining consistent stiffness across varying temperatures to ensure the durability and integrity of asphalt pavements.
Detailed
Temperature Susceptibility
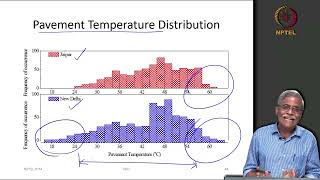
Temperature susceptibility is an essential property of bitumen that indicates how its stiffness varies with temperature changes. Ideally, good quality bitumen should exhibit minimal variation in stiffness with temperature fluctuations. This attribute is crucial for the performance of road pavements, as extreme temperatures can affect elasticity and, consequently, the pavement's ability to withstand various loading conditions. Ensuring that bitumen is temperature-resistant helps in preventing issues such as cracking in cold weather and softening in high temperatures. The performance and longevity of bitumen-based pavements depend significantly on its temperature susceptibility.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Temperature Susceptibility
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It should exhibit minimal variation in stiffness with changes in temperature.
Detailed Explanation
Temperature susceptibility refers to how much the stiffness of bitumen changes in response to temperature variations. Ideally, we want bitumen to maintain its properties when temperatures rise (like in hot weather) or drop (like in cold weather). This ensures that the bitumen used in pavements does not become too soft on hot days or too hard and brittle on cold days, which can lead to pavement failure or cracking.
Examples & Analogies
Think of temperature susceptibility like a rubber band. If you pull a rubber band and warm it, it becomes more flexible. However, if you put the same rubber band in the freezer, it becomes stiff and may snap easily if you try to stretch it. Similarly, bitumen should remain pliable and reliable regardless of whether it's hot or cold outside.
Importance of Temperature Susceptibility
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Temperature susceptibility is critical for the performance and durability of bituminous pavements, ensuring they withstand varying climatic conditions without deforming.
Detailed Explanation
Understanding temperature susceptibility is crucial because it affects not only how the pavement feels and performs under traffic but also how long it lasts. If the bitumen is too susceptible to temperature changes, it might lead to premature surface deformations, cracking, or other failures, which can be costly to repair. Thus, engineers must choose bitumen that can handle local temperature extremes without losing its functional properties.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a highway in a region that experiences extreme temperatures, like hot summers and cold winters. If the bitumen used in the pavement is not temperature-susceptible, it might soften and create ruts in the summertime while becoming too hard and cracking in the winter. Therefore, selecting the right bitumen helps prolong the life of the road and reduces maintenance costs in the long run.
Assessment of Temperature Susceptibility
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Tests, such as the Softening Point Test, are used to evaluate the temperature susceptibility of bitumen.
Detailed Explanation
To determine how a bitumen sample will perform with temperature changes, standardized tests are conducted. One common test is the Softening Point Test, where bitumen is heated until it reaches a specific point of softness. The temperature at which this occurs helps predict how the material will respond to actual service conditions on the road. The lower the softening point, the more susceptible the bitumen is to temperature-related changes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine testing a chocolate bar in different temperatures. On a hot day, the chocolate melts and loses its form, while on a cold day, it stays hard and can break easily. The Softening Point Test helps scientists understand the 'melting' behavior of bitumen so they can choose the right type for different weather conditions, similar to selecting chocolate that won't melt too quickly on a hot day.
Key Concepts
-
Temperature Susceptibility: The quality of bitumen to resist changes in stiffness with temperature fluctuations.
-
Testing Methods: Specific laboratory methods like softening point tests that gauge how temperature affects bitumen.
Examples & Applications
Bitumen graded for cold climates must maintain flexibility at low temperatures.
In hot climates, bitumen should resist softening to avoid deformation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If the summer heat arrives, keep your bitumen rigid and wise.
Stories
Once upon a time, a paved road faced hot summer days and cold winters. Only the bitumen that retained its strength through all conditions kept the road intact.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym STAY: S for Stiffness, T for Temperature, A for Assessment, Y for Yielding. To remember how to assess bitumen's temperature susceptibility.
Acronyms
BIT
for Bitumen
for Integrity
for Temperature – ensuring pavement integrity in varying temperatures.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Temperature Susceptibility
The ability of bitumen to maintain its stiffness despite changes in temperature.
- Stiffness
The resistance of bitumen to deformation under stress.
- Softening Point Test
A laboratory test used to determine the temperature at which bitumen becomes soft.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
