Oxidation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Oxidation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss oxidation and its impact on bituminous materials. Can anyone tell me what oxidation means in general?

Isn't it a chemical reaction where a substance combines with oxygen?

Correct! In the context of bituminous materials, oxidation happens when bitumen reacts with atmospheric oxygen. This reaction leads to an increase in stiffness and a reduction in ductility. Why do you think these changes are concerning for flexible pavements?

Because increased stiffness means it could crack more easily, right?

Exactly! Reducing ductility makes the material less flexible, which can lead to premature failure. Remember, we can use the acronym 'S&D' for Stiffness and Ductility to recall the effects of oxidation.

So, oxidation is basically bad for pavements?

Definitely! Now, let's summarize: oxidation increases stiffness and reduces ductility, which are not ideal for the longevity of pavements.
Consequences of Oxidation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've established what oxidation is. Now, what do you think are the long-term effects of this reaction on pavement materials?

It could probably make the pavement crack and degrade faster.

Correct! Oxidation leads to hardening of the surface, making it brittle, and if water gets in, it can cause further damage. This combination accelerates the deterioration process. Can anyone think of an additional factor that influences oxidation?

Maybe temperature changes? Hot weather could accelerate the reaction?

Spot on! Elevated temperatures can indeed speed up oxidation. So now we have various factors—temperature and exposure to atmospheric conditions—as influencers of this reaction. Let's summarize: oxidation not only hardens the bitumen but also increases its vulnerability to environmental degradation.
Preventing Oxidation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about prevention. What could we possibly do to protect our pavements from oxidation?

Using additives or modifiers in the bituminous mix?

Exactly! For instance, polymer-modified bitumen can enhance resistance to oxidation. Additionally, having proper drainage can prevent moisture penetration, which is often exacerbated by oxidation. Let's remember the acronym 'P.D.' for Prevention Measures — what can we do to combat oxidation?

Preventive measures like using additives and ensuring good drainage!

Right! So remember, employing the right strategies can significantly enhance the durability of our bituminous materials against oxidation. Let's recap: using additives and ensuring proper drainage can help mitigate oxidation effects.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
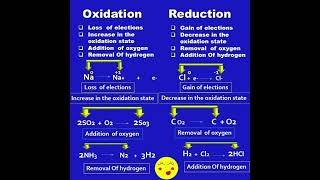
In this section, we explore the mechanism of oxidation in bituminous materials, which occurs when bitumen reacts with atmospheric oxygen. This reaction leads to undesirable changes such as increased stiffness and decreased ductility, affecting the overall durability and performance of flexible pavements.
Detailed
Oxidation in Bituminous Materials
Oxidation refers to the chemical reaction between bitumen and atmospheric oxygen. This process is a notable factor in the weathering of bituminous materials, especially under varying environmental conditions. The reaction results in significant changes to the properties of bitumen: it increases stiffness while diminishing ductility, making the pavements more susceptible to cracking and other forms of damage. This section delves into the technical aspects of oxidation, its implications for the durability of flexible pavements, and the necessity of addressing this phenomenon in material design and maintenance.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Oxidation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Oxidation is the reaction of bitumen with atmospheric oxygen.
Detailed Explanation
Oxidation occurs when bitumen, which is a viscous petroleum product, comes into contact with oxygen in the atmosphere. This reaction alters the chemical structure of the bitumen, which leads to changes in its properties. It can affect everything from how sticky the bitumen is to how well it can withstand mechanical stress. In essence, it involves the bitumen 'aging' prematurely due to exposure to an oxidizing environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of oxidation like how an apple turns brown when exposed to air. Just as oxygen reacts with the cells of the apple and changes its color and texture, oxygen reacts with bitumen, changing its properties.
Effects of Oxidation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Oxidation increases stiffness and reduces ductility.
Detailed Explanation
As oxidation occurs, the molecules in the bitumen form new bonds that make the material stiffer. While some degree of stiffness is desirable in a pavement, excessive stiffness means that the bitumen becomes less flexible. This reduction in flexibility, known as ductility, means the bitumen can no longer absorb tensile stresses effectively. As a result, the pavement can crack more easily under loads from traffic or environmental changes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the difference between fresh play-dough and hardened play-dough. Fresh play-dough can be stretched and molded easily (high ductility), while hardened play-dough breaks easily when you try to bend it (low ductility).
Key Concepts
-
Oxidation: A chemical reaction with oxygen that affects bitumen's properties.
-
Stiffness: Resistance to deformation that increases due to oxidation.
-
Ductility: Flexibility that decreases due to the same oxidation process.
Examples & Applications
Oxidation can lead to hardening in asphalt pavements, making them prone to cracking.
Bitumen's reaction with oxygen increases stiffness, which can reduce pavement lifespan.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When bitumen reacts with air, it gets hard and cannot bear.
Stories
Imagine a stretchy rubber band that hardens over time and can’t stretch anymore; that's what happens to bitumen when it oxidizes.
Memory Tools
Think 'S & D' - Stiffness increases, Ductility decreases due to oxidation.
Acronyms
O.R.D. - Oxidation Reduces Ductility.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Oxidation
A chemical reaction where bitumen reacts with atmospheric oxygen, leading to increased stiffness and reduced ductility.
- Stiffness
The ability of a material to resist deformation under applied forces.
- Ductility
The capacity of a material to undergo significant plastic deformation before rupture.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
