Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to LVDT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the Linear Variable Differential Transformer, or LVDT, which is a crucial sensor in civil engineering. Can anyone tell me what principle it operates on?

Is it something related to electrical circuits?

Exactly! It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. This means that when an AC voltage is supplied, it creates a magnetic field that changes based on the position of a magnetic core.

So, does that mean the LVDT can measure how far something has moved?

Yes, precisely! It measures linear displacement. What's interesting is the accuracy it offers without any physical contact, which I'll explain later.
Applications of LVDT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to applications, can anyone think of where we might use an LVDT in civil engineering?

Maybe in monitoring bridges?

Great example! LVDTs are often deployed in bridge expansion monitoring. Can anyone elaborate?

I think they help detect how much a bridge expands or contracts with temperature changes.

Absolutely! They play a critical role in ensuring the structural health of bridges, providing data that informs maintenance decisions.
Advantages of LVDT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the advantages of LVDTs. What do you think makes them a preferred choice for displacement measurements?

Maybe because they are very accurate?

Correct! They provide high accuracy and repeatability. Another factor is that they don’t have physical contact, which reduces wear and increases lifespan.

So they can last longer without needing replacements?

Exactly! Their durability makes them cost-effective in the long run.
Displacement Measurement Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think precise displacement measurement is crucial for infrastructure like bridges?

It probably helps prevent structural failures?

Exactly! Monitoring displacement helps in early detection of potential issues. Can anyone think of other specific scenarios?

Like monitoring how much the ground settles after a new building is constructed?

Right! Settlement analysis is another key application. It helps engineers adjust designs based on real-time data.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
LVDTs utilize the principle of electromagnetic induction to measure linear displacements accurately. This sensor is widely used in civil engineering applications such as bridge expansion monitoring and settlement analysis, where precise displacement readings are crucial for structural health monitoring.
Detailed
Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)
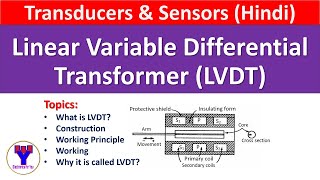
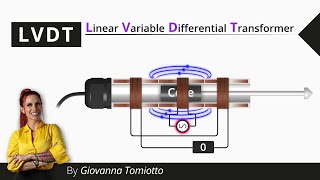
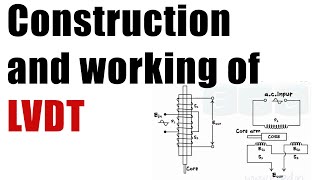
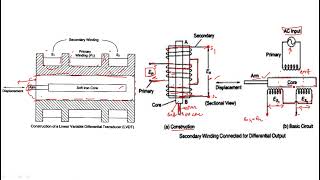
The Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) is a sophisticated electromechanical sensor that converts linear displacement into a corresponding electrical signal. The key principle behind its operation is electromagnetic induction, making it an effective tool for measuring very slight changes in position.
Key Points:
- Operating Principle: An LVDT comprises a primary coil and two secondary coils arranged symmetrically. When an AC voltage is supplied to the primary coil, a magnetic field is generated. As the core (the moving element) changes position, the induced voltage in the secondary coils alters according to the core's position, allowing accurate displacement measurement.
- Applications: LVDTs are highly valued in civil engineering for applications such as monitoring bridge expansion and conducting settlement analysis. These measurements are critical for ensuring safety and structural integrity in civil infrastructure.
- Advantages: The LVDT provides high accuracy, excellent linearity, and great repeatability without physical contact between components, which minimizes wear and tear.
In conclusion, LVDTs serve an essential role in real-time data acquisition in civil engineering projects, allowing engineers to monitor and analyze structural behavior under various conditions.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Principle of Operation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Principle: Electromagnetic induction
Detailed Explanation
The Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a primary coil, two secondary coils, and a movable core. When an alternating current passes through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field, inducing a voltage in the secondary coils. The amount of voltage induced is proportional to the position of the core within the coils, allowing for precise measurement of linear displacement.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of an LVDT like a piano with keys (the primary coil) and strings (the secondary coils). When you press a key (provide power), it vibrates the strings, creating sound (induced voltage). The further you press the key, the louder the sound, similar to how the core's position influences the induced voltage.
Applications of LVDT
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Application: Bridge expansion monitoring, settlement analysis
Detailed Explanation
LVDTs are widely used in civil engineering for monitoring purposes. For example, in bridge expansion monitoring, LVDTs can measure the changes in length as temperatures affect the materials, ensuring the bridge can expand and contract safely. Similarly, in settlement analysis, LVDTs help track vertical displacements of structures over time, providing vital data for maintaining structural integrity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bridge is like a rubber band that stretches and shrinks depending on the temperature. LVDTs act like your eyes watching the rubber band, measuring how much it stretches or shrinks to ensure it doesn’t snap. This monitoring helps engineers keep the bridge safe and functional.
Key Concepts
-
Electromagnetic Induction: The principle by which an LVDT operates, allowing it to sense displacement.
-
High Accuracy: LVDTs provide precise measurements, essential for structural health monitoring.
-
Non-contact Measurement: The LVDT's design allows for measurement without physical contact, reducing wear.
Examples & Applications
LVDTs are used in bridge expansion joints to measure changes accurately due to temperature fluctuations.
In settlement analysis, LVDTs are implemented to monitor ground movement after construction activities.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
LVDT steals the show, measures movements low and slow.
Stories
Imagine a bridge that stretches and bends. LVDT acts as its eyes, knowing just how much it extends.
Memory Tools
LVDT - Linear Value Determines Travel.
Acronyms
LVDT - Lightweight, Variable, Dependable Transformer.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)
A type of sensor used for measuring linear displacement through electromagnetic induction.
- Electromagnetic Induction
The process of generating electric current in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around it.
- Displacement
The distance moved in a specific direction from an initial position.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
