Ultrasonic Sensors
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Operating Principle of Ultrasonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll learn about ultrasonic sensors. They work based on the time of flight of sound waves. Can anyone explain what this means?

Does that mean they send out sound waves and time how long it takes for them to come back?

Exactly! The time it takes for the sound to reflect back tells us the distance or if there's a crack. This is a fundamental concept in non-destructive testing.

So, it's like using sonar for underwater detection?

That's a great analogy! Both use sound waves to gather information. In construction, this helps ensure safety without damaging the material.
Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss practical applications. Can anyone name specific uses of ultrasonic sensors in civil engineering?

They're used for crack detection, right?

Correct! Ultrasonic sensors are critical for inspecting concrete structures for cracks or voids. This helps us maintain structural integrity.

Are there other areas they could be applied to?

Yes, they can also be used for thickness gauging and evaluating welds in construction materials.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think are some advantages of using ultrasonic sensors?

They don't damage materials since they're non-destructive!

Exactly! Their non-invasive nature is a huge advantage. Also, they can provide real-time data for monitoring.

What about accuracy?

Good question! Ultrasonic sensors can be very accurate when calibrated properly. They are also relatively cost-effective for what they achieve.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses ultrasonic sensors, detailing their operating principle based on the time of flight of sound waves. It emphasizes their applications, particularly in crack detection and non-destructive testing (NDT), highlighting their significance in civil engineering for assessing structural integrity.
Detailed
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors, as discussed in this section, operate on the principle of the time of flight of sound waves. These sensors are particularly useful in non-destructive testing (NDT) processes within civil engineering applications. They help detect cracks in concrete, which is vital for maintaining the safety and integrity of structures. By sending out ultrasonic sound waves and measuring the time it takes for the waves to reflect back after hitting an object, these sensors can determine distances or identify anomalies in materials, thus significantly enhancing monitoring and inspection capabilities in the field.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Principle of Ultrasonic Sensors
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Principle: Time of flight of sound waves
Detailed Explanation
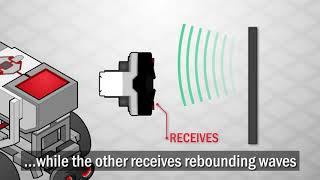
Ultrasonic sensors operate based on the principle of measuring the time it takes for sound waves to travel from the sensor to an object and back. When an ultrasonic sensor emits a sound wave, it travels through the air until it hits an object. The wave then bounces back to the sensor. By recording the time taken for this round trip, the sensor can calculate the distance to the object using the speed of sound in air, which is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like using an echo to gauge the distance to a wall. If you shout towards a wall, the time it takes for your voice to bounce back tells you how far away the wall is. Similarly, ultrasonic sensors 'listen' for the echo of the sound waves they send out.
Application of Ultrasonic Sensors
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Application: Crack detection in concrete, non-destructive testing (NDT)
Detailed Explanation
Ultrasonic sensors are widely used for various applications in civil engineering, particularly for detecting cracks in concrete structures. They perform non-destructive testing (NDT), which means that they evaluate the integrity of structures without causing any damage. The sensors emit sound waves that propagate through the material. If there is a crack or defect, the sound waves will behave differently than they would in undamaged material, leading to changes in the returned signal. This allows engineers to assess whether a structure is safe and identify any areas that may require repair.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sonar device used by submarines to detect objects underwater. Just like sonar, which sends out sound waves and listens for echoes to find objects, ultrasonic sensors in NDT send sound waves into concrete and check for echoes to find cracks or flaws.
Key Concepts
-
Operating Principle: Uses sound waves to measure distance or detect material properties.
-
Non-Destructive Testing: Allows examination without damaging the object.
-
Crack Detection: Essential for maintaining structural safety.
Examples & Applications
Ultrasonic sensors are often used in the field to monitor bridges for cracks, helping engineers assess safety before performing maintenance.
In manufacturing, ultrasonic testing can evaluate the integrity of welds in structural components.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
With sound waves swift and sound waves true, ultrasonic sensors measure all they do.
Stories
Imagine a bridge monitored day and night, ultrasonic sensors watch, ready for a fright. If cracks should form, they will show – safety first, they help us know!
Memory Tools
CRACK - C for Concrete, R for Reflection, A for Accuracy, C for Cost-efficient, K for Keep monitoring.
Acronyms
NDT - Non-Destructive Testing, that keeps our structures safe and undamaged while assessing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ultrasonic Sensor
A device that measures distance or detects changes in materials by emitting sound waves and measuring their time of flight.
- NonDestructive Testing (NDT)
A testing method used to evaluate the properties of a material, component, or assembly without causing damage.
- Crack Detection
The process of identifying fractures or voids in materials, crucial for structural integrity assessments.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
