Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to RTDs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will learn about Resistance Temperature Detectors or RTDs. They are used to measure temperature based on the resistance change of metal with temperature. Can anyone tell me what materials are typically used in RTDs?

I think platinum and copper are common materials used.

That's correct! Platinum, in particular, is favored for its stability. Remember this with the acronym 'PC' for Platinum and Copper. So, how does the operating principle of an RTD work?

I believe it's about measuring the resistance change.

Exactly! The resistance changes linearly with temperature, which makes RTDs highly accurate. This principle is crucial for their application in monitoring temperatures in civil engineering.
Applications of RTDs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's delve into the applications of RTDs in civil engineering. Can anyone give examples of where we might want to monitor temperature?

We could use them to monitor temperatures in concrete during curing.

Great point! Monitoring curing temperature ensures the concrete achieves its designed strength. How important do you think that is for structural integrity?

Very important! If the temperature isn’t controlled, it might lead to cracks or failures.

Exactly! Accurate temperature measurement is vital in avoiding structural issues, especially in large constructions like bridges.
Importance of RTDs in Structural Health Monitoring
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the importance of RTDs in structural health monitoring. Why do we need such accurate temperature measurements?

To ensure the materials perform well under different temperature conditions?

Exactly! Temperature can affect the mechanical properties of materials, and maintaining optimal conditions is essential. Can anyone think of another reason why RTDs are valuable?

They help in predictive maintenance of structures!

Right again! By monitoring temperature changes, engineers can predict when maintenance is needed, potentially preventing failures. Remember this connection for future discussions!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) use the change in electrical resistance in metals, typically platinum or copper, to measure temperature accurately. Their applications include monitoring temperatures in buildings and pavements, emphasizing their significance in civil engineering for maintaining structural integrity.
Detailed
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD)
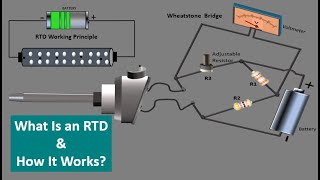
RTDs, or Resistance Temperature Detectors, are specialized sensors used primarily for temperature measurement in various applications, including civil engineering. They operate on the fundamental principle that a material’s electrical resistance varies with temperature.
Key Characteristics
- Material: The most common materials used for RTDs are platinum and copper due to their stable and predictable resistance-temperature relationship.
- Principle: The resistance changes with temperature following a nearly linear relationship, making RTDs highly accurate for a range of temperatures.
Applications in Engineering
RTDs are crucial in different civil engineering applications. They provide precise temperature monitoring in structures like buildings and pavements. For example, in concrete curing processes, accurate temperature data enables engineers to assess the quality and performance of the cured material, ensuring safety and durability.
In conclusion, the adoption of RTDs in temperature monitoring contributes significantly to structural health monitoring and overall civil engineering practices.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Principle of RTDs
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Principle: Resistance change of metal with temperature
Detailed Explanation
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) operate on the principle that the electrical resistance of certain metals changes with temperature. Specifically, as the temperature increases, the resistance of the metal also increases. This relationship is predictable and can be utilized to measure temperature accurately. Often, platinum is used as the sensing element due to its stable and known resistance characteristics across a wide temperature range.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a metal wire that expands slightly when heated; this expansion also affects how freely electricity can pass through it. In a similar way, an RTD uses changes in resistance to detect temperature variations, much like how a balloon expands with air—both provide clear indicators of changing conditions.
Materials Used in RTDs
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Material: Platinum, copper
Detailed Explanation
RTDs can be made from various metals, but platinum and copper are the most common. Platinum is favored for its stability, accuracy, and wide temperature range, making it ideal for industrial applications. Copper, while less stable than platinum, is often used for lower temperature measurements where cost may be a concern. Each material has benefits that make it suitable for specific applications but platinum is generally the gold standard in accuracy and performance.
Examples & Analogies
Think of platinum like the luxury sedan of temperature sensors—it’s high quality and reliable, perfect for precise needs in a laboratory setting. In contrast, copper is like a trusty pickup truck—perfect for flagging simple measurements but not ideal for situations requiring the highest precision.
Applications of RTDs
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Application: Temperature monitoring in buildings and pavements
Detailed Explanation
RTDs are widely used in various applications where accurate temperature measurement is critical. For instance, in civil engineering, they monitor the temperature of buildings, pavements, and other structures to ensure they are within safe limits during construction and their lifetime. Monitoring temperature helps prevent issues such as thermal expansion, which can damage materials over time if not properly managed.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef baking a cake; if the oven temperature isn’t just right, the cake may not rise or could even burn. Similarly, RTDs help engineers ensure that the temperature of concrete during curing is optimal, so that structures like bridges and buildings set correctly without compromising safety.
Key Concepts
-
RTD: A sensor that measures temperature through resistance changes in metals.
-
Principle of Operation: Resistance changes linearly with temperature.
-
Materials: Commonly made from platinum and copper for their stability.
-
Applications: Used in monitoring curing temperatures in civil engineering.
Examples & Applications
Using RTDs to monitor the temperature of concrete during its curing process to ensure structural integrity.
Implementing RTDs in pavements to measure temperature fluctuations and assess their effects on material strength.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Platinum and copper, sensors of heat, measuring resistance, can't be beat!
Stories
Imagine a construction site where workers use RTDs to monitor the temperature of concrete. 'Too hot or too cold?' they ask, ensuring a strong structure is built. The RTD, like a wise mentor, guides them to perfect conditions.
Memory Tools
Use the mnemonic 'PC' for Platinum and Copper to remember the primary materials for RTDs.
Acronyms
RTD
Resistance Tracking Device.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- RTD
Resistance Temperature Detector, a type of temperature sensor that measures temperature based on the resistance change of metals.
- Resistance
A measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current, which varies with temperature in metals.
- Curing
The process of maintaining adequate moisture, temperature, and time to allow the concrete to achieve its desired strength.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
