Concurrency and Parallelism
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Concurrency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing concurrency. Can anyone tell me what they think concurrency means?

I think it means running multiple tasks at the same time.

Great guess! Actually, concurrency allows tasks to be in progress at the same time but doesn't necessarily mean they are executed simultaneously. It's about managing multiple tasks effectively. You can remember it as 'coordinated progress.'

So, it’s like when one task is waiting, the system can switch to another task, right?

Exactly! This technique is called context switching. Can anyone think of an example where we might need concurrency?

Like when a web browser loads a page while also running scripts?

Exactly! That's a perfect example of concurrency in action.

To summarize, concurrency allows us to bunch tasks together in progress optimally.
Exploring Parallelism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about parallelism now. Who can explain how parallelism is different from concurrency?

Isn't it about doing multiple tasks at the same exact time, like using multiple CPU cores?

Exactly! Parallelism involves executing tasks literally at the same time using separate processors or cores. Think of it like a production line where different workers handle different tasks simultaneously.

So, could we say all parallel processing is concurrent, but not all concurrency is parallel?

Perfectly put! That distinction is crucial for understanding how to leverage both in programming. Parallelism can significantly improve performance, especially for tasks that can be divided into smaller sub-tasks.

To summarize, while concurrency is about structure and management of tasks, parallelism leverages multiple resources for actual simultaneous execution.
Real-World Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can someone give an example of applications that benefit from both concurrency and parallelism?

Gaming applications! They need to manage graphics, input, and sound all at the same time.

Exactly! In gaming, concurrency helps manage these elements together, while parallelism can help process complex graphics calculations across multiple cores.

What about web servers? They need to handle many requests!

Absolutely! A web server can manage concurrent requests from different users while leveraging parallelism to process them more efficiently.

So, both concepts are essential in designing responsive and efficient applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
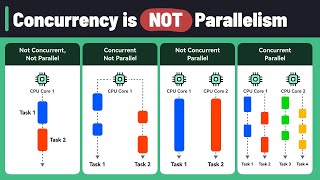
This section distinguishes between concurrency and parallelism, noting that concurrency allows multiple tasks to progress without necessarily executing simultaneously, while parallelism leverages multiple CPU cores to execute tasks truly at the same time. Understanding the difference is crucial for implementing efficient multithreaded applications.
Detailed
Concurrency and Parallelism
Concurrency and parallelism are two fundamental concepts in the realm of multithreading and programming that enhance the efficiency of modern applications.
Concurrency
Concurrency refers to the ability of a system to handle multiple tasks at once, even though these tasks may not actually be running simultaneously. This is often facilitated through context switching, where the CPU switches between tasks based on their status and priorities. Concurrency allows a program to be responsive and efficiently utilize resources, particularly in single-core systems where tasks are interleaved.
Parallelism
On the other hand, parallelism involves executing multiple tasks literally at the same time across multiple CPU cores. This means that tasks can be divided into smaller sub-tasks that are processed simultaneously, significantly speeding up execution time for compute-intensive operations. Unlike concurrency, which may involve waiting for resources to become available, parallelism uses multiple threads or processes to maximize throughput.
In summary, concurrency and parallelism can coexist, but they are not the same. While concurrency allows for multitasking and responsiveness in applications, parallelism maximizes performance by taking advantage of modern multi-core processors. Understanding these concepts is key for developers looking to create efficient, high-performance applications.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Concurrency
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Concurrency:
Multiple tasks are in progress at the same time (context switching). It may run on a single CPU core.
Detailed Explanation
Concurrency allows multiple tasks to progress simultaneously, meaning that even if not running simultaneously, they can be processed in overlapping periods. This is often achieved through context switching, where the CPU rapidly switches between tasks to give the illusion that they are running at the same time. Even a single-core CPU can handle multiple tasks this way, which may lead to more efficient use of resources.
Examples & Analogies
Think of concurrency like a juggler who handles several balls at once. Although it seems they are juggling all balls continuously, at any given moment, they only have one ball in hand while the others are in the air, creating the appearance that they are all being handled simultaneously.
Understanding Parallelism
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Parallelism:
Tasks are literally executed at the same time using multiple CPU cores.
Detailed Explanation
Parallelism is when tasks are run simultaneously, utilizing multiple CPU cores or processors. This allows for true simultaneous execution of tasks, which can significantly speed up processing time. Unlike concurrency, where tasks might share time on a single core, parallelism divides the workload among multiple cores, so each core processes a different task at the same instant.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of chefs preparing different components of a meal in parallel. Instead of one chef working sequentially on each dish component (like in concurrency), each chef simultaneously works on their respective dish, cooking veggies, boiling pasta, and grilling meat all at once, leading to a faster meal preparation.
Concurrency vs. Parallelism
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
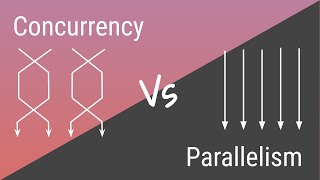
Concurrency ≠ Parallelism, but they can coexist.
Detailed Explanation
While concurrency and parallelism both involve multiple tasks, they are not the same. Concurrency is about managing multiple tasks at once, potentially on a single processor through context switching. In contrast, parallelism is about executing tasks simultaneously across multiple processors. Despite these differences, they can coexist in applications—concurrent programs can leverage parallel processing for performance improvements.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a busy restaurant. At peak hours, multiple waitstaff (concurrency) are taking orders from and serving customers, even if only one chef (parallelism) is preparing dishes for several tables. So, while orders are being taken concurrently, the cooking might be truly parallel if the chef has multiple tasks that he can manage at once.
Key Concepts
-
Concurrency: Managing multiple tasks at the same time without simultaneous execution.
-
Parallelism: Actual simultaneous execution of multiple tasks across CPU cores.
Examples & Applications
A web browser loading multiple elements of a webpage concurrently while rendering.
A video game processing user inputs, rendering graphics, and playing audio in parallel.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In concurrency, tasks interact, each waits for its turn, that's a fact.
Stories
Think of a busy restaurant kitchen where chefs are preparing different meals at the same time - that's concurrency. Now visualize all the chefs working together on the same dish simultaneously for a faster service - that's parallelism.
Memory Tools
C for Concurrency means 'Cohesion of tasks', P for Parallelism means 'Performance through Parallel action'.
Acronyms
C-P
- Concurrency
- Parallelism - manage tasks vs. execute tasks.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Concurrency
The ability to manage multiple tasks at the same time, emphasizing task progress rather than simultaneous execution.
- Parallelism
The simultaneous execution of multiple tasks on different processors or cores, enhancing performance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
