Thread Methods
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thread Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today, we're going to discuss some important methods in the Thread class that help us manage multithreading in Java. Can anyone remind me why we use multithreading?

To perform multiple tasks at the same time!

Exactly! Now, let's dive into some common thread methods. First up is the `start()` method. Who can tell me what that does?

It starts the thread and calls its `run()` method!

Right! This is important because it initiates the threading process. Remember, `start()` is often used first to create new threads. Now, what about the `sleep(ms)` method? What can it do?

It pauses the thread for a specified amount of time!

Yes, and this can help in various scenarios, like waiting for a resource to become available. How do you feel about using this method creatively?

We could use it to avoid busy-waiting, right?

Absolutely! Great connection. To recap, we discussed `start()` and `sleep()`, two foundational methods for thread management.
Advanced Thread Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our last session, we covered the basics of `start()` and `sleep()`. Now, let’s explore `join()`. What do you think happens when we call `join()` on a thread?

The current thread waits until the called thread finishes?

Exactly! This method is essential for coordinating thread execution. Now, what about `yield()`? Can someone explain its purpose?

It tells the scheduler to give other threads a chance to run.

Spot on! It’s like saying, ‘I’m done for now, let’s see what others can do.’ Now, let's look at `interrupt()`. Why would we want to interrupt a thread?

To stop it or to tell it to clean up and finish its work?

Exactly! It's a way to stop operations gracefully. In summary, these methods make managing threads much more effective.
Best Practices with Thread Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've learned about thread methods, it’s crucial to follow best practices. When should we use `sleep()` wisely?

Only when necessary to avoid freezing up the thread unnecessarily!

Great point! Overusing it can lead to performance issues. Also, using `join()` can prevent problems with data consistency. What have you learned about the importance of these methods?

They help ensure that threads communicate and work together without conflicts.

Exactly! Safe threading leads to efficient applications. Let’s wrap up. Why are these methods foundational to multithreading in Java?

Because they provide control over thread execution and improve performance!

Right again! Excellent understanding, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore several key methods of the Thread class, including start(), run(), sleep(), join(), yield(), and interrupt(). These methods play crucial roles in controlling thread behavior, enabling multitasking and resource management in Java applications.
Detailed
Thread Methods in Java
In this section, we discuss important methods available in the Java Thread class that facilitate the control and management of thread execution. These methods are critical for implementing multithreading in Java applications, allowing developers to create efficient and responsive programs that can perform multiple tasks concurrently. The methods covered include:
- start(): Initiates a new thread and calls its run() method, enabling asynchronous execution of code.
- run(): Contains the code that defines what the thread will execute.
- sleep(ms): Temporarily pauses the current thread's execution for a specified time in milliseconds, which is useful when a thread needs to wait before continuing its operation.
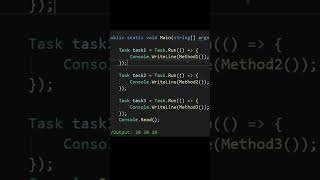
- join(): Causes the current thread to wait until the thread on which join() is called has completed execution. This is useful for ensuring that certain operations complete before proceeding.
- yield(): Suggests to the thread scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield its current use of the CPU, allowing other threads to execute.
- interrupt(): Interrupts a thread, which can be used to signal a thread that it should stop what it's doing and handle the interrupt.
Understanding these methods enhances a programmer's ability to manage threading, leading to more efficient applications capable of multitasking effectively.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Thread Methods
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Commonly used methods in the Thread class:
• start() – Starts the thread.
• run() – Contains the code executed by the thread.
• sleep(ms) – Pauses the thread for specified milliseconds.
• join() – Waits for the thread to finish.
• yield() – Suggests the thread scheduler to pause current thread and allow others to execute.
• interrupt() – Interrupts the thread.
Detailed Explanation
The Thread class in Java provides several methods to manage thread execution. Each method has a specific purpose:
- start(): This method initiates the thread, changing its state from 'New' to 'Runnable'.
- run(): It contains the code that will be executed by the thread. When the thread finally starts running, this method is invoked.
- sleep(ms): This method pauses the thread for a specified time in milliseconds. It puts the thread to sleep, freeing up the CPU for other threads.
- join(): This method makes one thread wait for another to complete. It’s useful when you need a thread to finish before continuing.
- yield(): A hint to the thread scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield its current use of the CPU. This can help prevent one thread from monopolizing CPU time.
- interrupt(): This method is used to interrupt a thread. When a thread is interrupted, it can stop what it's doing or check if it should stop, allowing it to respond to interruptions gracefully.
Examples & Analogies
Think of thread methods like a conductor of an orchestra. Just as a conductor manages the musicians to ensure they play their parts in harmony, thread methods manage how threads operate. For instance, calling start() is like the conductor giving the signal to begin. sleep(ms) is akin to giving the musicians a break before continuing. Similarly, join() could be likened to waiting for a particular musician to finish their solo before the orchestra plays together again.
start() and run()
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• start() – Starts the thread.
• run() – Contains the code executed by the thread.
Detailed Explanation
The start() method is crucial as it transitions the thread from the 'New' state to the 'Runnable' state. This is when the thread is ready to run and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) schedules it for execution. The run() method is a placeholder for the code that will run in the thread. It should define the task you want the thread to perform. Importantly, you never call run() directly on the thread; instead, it’s invoked by the JVM when the thread is executed.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're directing a play. start() is like calling 'Action!' to indicate it's time to start performing. Once the actors begin, they follow their script in the run() method, which represents what they will say and do during the performance. Each actor (or thread) can perform their own lines in parallel to give a dynamic experience.
sleep() and join()
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• sleep(ms) – Pauses the thread for specified milliseconds.
• join() – Waits for the thread to finish.
Detailed Explanation
The sleep(ms) method is used to temporarily halt the execution of a thread, which can be useful for controlling timing and resource use. By specifying how long to sleep, you allow other threads to run or to synchronize actions between them. On the other hand, join() is when one thread needs to wait for another thread to complete before proceeding. This is particularly helpful in scenarios where the outcome of one thread determines what happens in another.
Examples & Analogies
Think of sleep() like taking a break during a workout. You pause to catch your breath (allowing other threads to work), then you get back to the exercise. join() is similar to waiting for a friend to finish their task before you both what you planned to do next. It ensures that you don't start the next activity until they are ready.
yield() and interrupt()
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• yield() – Suggests the thread scheduler to pause current thread and allow others to execute.
• interrupt() – Interrupts the thread.
Detailed Explanation
The yield() method serves as a suggestion to the thread scheduler that the current thread is willing to pause and let other threads take their turn. It's a way of promoting fairness among threads. The interrupt() method, however, can signal a thread that it should stop what it's doing and potentially handle the interruption. This is particularly valuable for threads that are performing time-consuming tasks and may need to respond promptly to interruptions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider yield() as being in a queue at a coffee shop. If you see a new customer behind you who looks more hurried, you might decide to step aside for a moment (yielding your turn) to let them go ahead. interrupt() is like a friend texting you urgently while you're busy. Their message prompts you to drop what you're doing and check in on them, regardless of your prior engagement.
Key Concepts
-
start(): Method to begin thread execution.
-
run(): Code executed by the thread.
-
sleep(ms): Pauses execution for a specific duration.
-
join(): Waits for the thread to finish.
-
yield(): Suggests thread scheduler to pause current thread.
-
interrupt(): Stops a thread's execution.
Examples & Applications
Using start(), a new thread begins and can execute its run() method asynchronously.
Calling join() on a thread ensures that the current thread waits for its completion before continuing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When a thread starts, it's ready to run,
Stories
Imagine a relay race where one runner (thread) passes the baton (control) to the next, but first, they need to take a short break (sleep) before they can continue.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'SURJI' for thread methods: Start, Unwind (yield), Run, Join, Interrupt.
Acronyms
The acronym 'SJIY' can help recall `start`, `join`, and `yield`.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- start()
A method that begins the execution of a thread in Java.
- run()
The method containing the code that the thread executes.
- sleep(ms)
Pauses the thread for a specified time in milliseconds.
- join()
Makes the current thread wait until the thread on which join() is called finishes.
- yield()
Suggests that the current thread is willing to yield its use of the CPU.
- interrupt()
Interrupts the execution of a thread, signaling it to stop.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
