Executors and Thread Pools
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is an Executor?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

An Executor in Java is an interface that defines a method for executing tasks. Can anyone tell me why using an Executor is beneficial compared to managing threads directly?

I think it might be simpler to use, but I'm not sure how it actually helps with performance.

Great point! Executors help us to manage thread execution more efficiently by reusing threads from a pool instead of constantly creating new ones, thereby minimizing resource consumption and overhead.

How do we create an Executor in Java? Is there a specific syntax?

Yes, you can create an ExecutorService using the Executors factory method. For example, with a fixed thread pool, you can write: `Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);` which creates a pool of 5 threads.

Does that mean all 5 threads are used at the same time?

Exactly! When you submit tasks, they will be executed by any of the available threads in the pool. This way, you are maximizing resource utilization.

What happens if all threads are busy?

If all threads are occupied and a new task comes in, it will be queued until a thread becomes available, allowing for organized task handling.

To summarize, Executors manage task execution and provide us with efficient thread reuse, with an easy syntax for implementation.
Types of Executors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the different types of Executors we can use. Can anyone remind me what a FixedThreadPool is?

It's the type where we specify a fixed number of threads, right?

Exactly! FixedThreadPool has a predefined number of threads that can handle multiple tasks. Now, can someone explain what a CachedThreadPool does?

I think it creates threads as needed, and if there are threads in the pool that are idle, it will reuse them.

Correct! It's really useful for tasks with varying workloads. How about SingleThreadExecutor? What does that provide?

That executes tasks sequentially with just one thread.

Right! Useful when task ordering is essential. Finally, can anyone summarize why these different types of executors are beneficial?

They each serve different use cases depending on how much task concurrency we need and resource management!

Excellent summary! To recap: FixedThreadPool is for fixed tasks, CachedThreadPool is for variable tasks, SingleThreadExecutor is for sequential tasks, and ScheduledThreadPool is used for timed tasks.
Advantages of Executors and Thread Pools
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed Executors, but let's now focus on why we prefer them over manual thread management. What advantages do they offer?

They help with resource management?

Yes! They reuse threads, which reduces the overhead that comes from creating and destroying threads frequently. What else?

They prevent thread exhaustion?

That's correct! By limiting the number of concurrent threads executing, Executors help prevent resource depletion. What about latency?

Using them reduces latency because we are not creating new threads for every task?

Exactly! This leads to better performance. Remember the acronym **REE**: Resource management, Avoiding exhaustion, and Reducing latency. Can we all repeat that?

REE - Resource management, Avoiding exhaustion, Reducing latency!

Great! Just to summarize, Executors provide efficient resource utilization, prevent thread exhaustion, and help reduce latency.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains how the Executor framework provides a design pattern for managing and reusing threads via thread pools. It outlines the various types of executors and their advantages such as better resource management and reduced latency in thread handling.
Detailed
Executors and Thread Pools
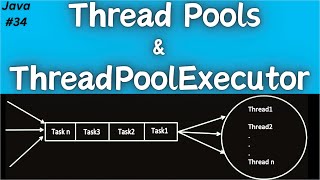
The Executor framework in Java provides a powerful and flexible way to manage threads and execute tasks. By utilizing thread pools, developers can improve the efficiency of thread management and enhance application performance. The primary components of this framework include:
Executors
Executors are responsible for executing submitted tasks. They manage a pool of threads that can be reused, rather than creating and destroying threads for each task. The creation of an executor instance can be done through methods such as:
Types of Executors
There are several types of executors available:
- FixedThreadPool: A fixed size pool where a predefined number of threads are created.
- CachedThreadPool: Creates new threads as needed and reuses previously constructed threads when they are available.
- SingleThreadExecutor: Ensures that tasks are executed sequentially using a single worker thread.
- ScheduledThreadPool: Allows scheduling of tasks to execute after a given delay or periodically.
Advantages of Using Executors
Utilizing the Executor framework offers multiple advantages:
- Better Resource Management: Reusing threads reduces the overhead of thread creation.
- Avoids Thread Exhaustion: Limits the number of concurrent threads, preventing system resource depletion.
- Reduces Latency: By managing thread lifecycles, it reduces latency associated with frequent thread creation and destruction.
In summary, the Executor framework and thread pools enable developers to build efficient, scalable applications while minimizing the complexity associated with thread management.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Executors
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Executors:
Provide a flexible way to manage and reuse threads via thread pools.
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
executor.execute(new Task());
executor.shutdown();
Detailed Explanation
Executors are utility classes in Java that help manage worker threads. Instead of creating a new thread for each task, you can create a pool of threads. This way, when a task needs to run, it can use a thread from the pool. For example, by using Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5), you create a pool with 5 threads that can handle tasks. The method executor.execute(new Task()) submits a new task to the executor, where 'Task' is a task that implements Runnable. Finally, executor.shutdown() is called to cleanly shut down the executor when you're done with it.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant kitchen where several chefs (threads) are waiting to prepare various dishes (tasks). Instead of hiring a new chef for every order, the restaurant keeps a fixed number of chefs. When an order comes in, one chef from this pool takes the task, prepares the meal, and once done, is ready to take the next order. This approach increases efficiency and reduces the stress of constantly hiring and firing chefs.
Types of Executors
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Types:
• FixedThreadPool
• CachedThreadPool
• SingleThreadExecutor
• ScheduledThreadPool
Detailed Explanation
There are several types of executors in Java, each serving different needs. A FixedThreadPool maintains a constant number of threads, a CachedThreadPool creates new threads as needed but will reuse previously constructed threads, a SingleThreadExecutor ensures that all commands are executed sequentially in a single thread, and a ScheduledThreadPool can schedule tasks to run after a given delay or periodically. Choosing the right executor type depends on the specific requirements of your application.
Examples & Analogies
Think of different types of service counters at a bank. A FixedThreadPool is like a bank with a specific number of tellers available at all times to assist customers. A CachedThreadPool is like a drive-thru that opens additional lanes whenever there's a traffic spike but doesn't keep them open when not needed. A SingleThreadExecutor is like a personal banker who handles all your queries one at a time, while a ScheduledThreadPool is like an appointment system that allows customers to set specific times to meet their banker.
Advantages of Using Executors
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advantages:
• Better resource management
• Avoids thread exhaustion
• Reduces latency from frequent thread creation/destruction
Detailed Explanation
Using executors provides multiple advantages. Firstly, they help manage system resources better by reusing threads instead of creating new ones frequently, which can be costly in terms of performance. Secondly, a limited pool of threads ensures that we do not run out of threads, which can lead to resource exhaustion. Finally, because threads are reused and not created and destroyed repeatedly, the overhead associated with these operations is significantly reduced, resulting in lower latency and faster application performance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider your favorite coffee shop where baristas are always ready at the counter. When it’s busy, they handle multiple orders efficiently, avoiding a rush of customers waiting for new baristas to start working. This is similar to how executors manage threads efficiently, allowing your application to process tasks quickly without running out of available resources.
Key Concepts
-
Executor: Simplifies the management of task execution in Java.
-
Thread Pool: Collection of threads that allows task concurrent execution.
-
FixedThreadPool: An executor with a fixed number of threads.
-
CachedThreadPool: An executor that creates threads as needed.
-
SingleThreadExecutor: A sequentially executing single-threaded executor.
-
ScheduledThreadPool: An executor for scheduling tasks.
Examples & Applications
Using FixedThreadPool: ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); creates a thread pool of 5 threads that can execute tasks concurrently.
Using CachedThreadPool: ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); creates threads as needed and reuses them when available, ideal for tasks with unpredictable execution time.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When threads come and go in a flowing pool, Executors keep them in control and cool.
Stories
Imagine a library where books (tasks) are only checked out by librarians (threads) when needed. Once the librarians finish with the books, they return them to avoid waiting lines (queues).
Memory Tools
Remember REE for Executors' benefits: Resource management, Exhaustion prevention, and Efficiency in execution.
Acronyms
FCS for types of Executors
FixedThreadPool
CachedThreadPool
SingleThreadExecutor.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Executor
An interface in Java that defines a method for executing tasks, simplifying thread management.
- Thread Pool
A collection of threads used to execute multiple tasks concurrently to manage resources efficiently.
- FixedThreadPool
An executor that maintains a fixed number of threads for executing tasks.
- CachedThreadPool
An executor that creates new threads as needed and reuses previously constructed threads.
- SingleThreadExecutor
An executor that uses a single thread to execute tasks sequentially.
- ScheduledThreadPool
An executor that can schedule tasks to execute after a given delay or periodically.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
