Thread Priorities and Scheduling
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thread Priorities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss thread priorities in Java. Can anyone tell me what a thread priority is?

I think it's like how important a thread is compared to others when they are executed.

Exactly! Each thread can be assigned a priority that can influence how the JVM schedules it relative to other threads. The method used is `setPriority()`. Can you guess what the normal priority level is?

Is it 5?

Correct! The priority levels are defined as MIN_PRIORITY (1), NORM_PRIORITY (5), and MAX_PRIORITY (10). Remember this with the acronym 'M-N-M' for Minimum-Normal-Maximum.

So does this mean that a higher priority thread gets executed first?

Typically yes, but remember that the actual behavior can vary based on the OS scheduler's implementation.

I see! Do some operating systems ignore thread priorities?

Good question! Some OSs might not consider priorities strictly, so it’s crucial to test how your application behaves across different platforms.

To summarize, thread priorities can help us manage execution but bear in mind the OS role in scheduling.
Thread Scheduling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about thread priorities, let’s discuss scheduling. Can anyone explain what thread scheduling means?

It must refer to how threads are given CPU time for execution.

That's correct! Mostly, the CPU executes multiple threads based on the scheduling policy, which can be preemptive or non-preemptive. What do you think preemptive scheduling means?

I think it means higher priority threads can interrupt lower priority ones.

Exactly! In a preemptive system, the OS can suspend a currently running thread to run a higher priority thread. This leads to more responsive applications. However, in non-preemptive systems, a running thread must yield control voluntarily.

So, if my application uses high priority threads, can they always expect to run first?

Not necessarily. Even high priority threads can get delayed based on synchronization and the OS scheduler. Always test and monitor your applications.

In summary, thread scheduling determines how and when each thread runs. This can be affected by their assigned priorities and the operating system’s scheduling strategy.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore thread priorities and how they influence the scheduling of threads within the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM allows setting thread priorities using the setPriority() method, and while it schedules threads based on these priorities, the actual behavior depends on the operating system’s scheduler.
Detailed
Thread Priorities and Scheduling
This section introduces the concept of thread priorities in Java, which can be assigned using the setPriority() method. Threads in Java can have a priority level defined by constants: MIN_PRIORITY (1), NORM_PRIORITY (5), and MAX_PRIORITY (10). While the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) attempts to schedule threads according to these priorities, it's essential to understand that the real scheduling is largely influenced by the underlying operating system. Consequently, the way threads get executed can differ based on the OS's scheduling policies. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for developing efficient multi-threaded applications.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Thread Priorities
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Threads can be assigned priorities using setPriority().
• JVM schedules threads based on priority but exact behavior depends on the OS scheduler.
Detailed Explanation
In Java, threads are assigned priorities that can be adjusted using the setPriority() method. This priority level indicates the importance of a thread relative to others. Higher priority threads are more likely to be scheduled to run before lower priority ones. However, it's essential to understand that while the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) uses these priorities to schedule threads, the actual scheduling can differ depending on the operating system's thread scheduler, which can have its own algorithms for managing CPU time among threads.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a teacher who has to assign homework to a group of students. Some students need to complete their projects sooner than others due to upcoming deadlines. By labeling students based on urgency (high priority for urgent projects, lower for those due later), the teacher can ensure that the more pressing assignments are addressed first. However, the effectiveness of this strategy might change depending on how the students (representing the CPU) handle their time and workload.
Understanding Thread Priorities
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Priorities: MIN_PRIORITY (1), NORM_PRIORITY (5), MAX_PRIORITY (10).
Detailed Explanation
Java allows you to set thread priorities using three predefined constants: MIN_PRIORITY (which has the lowest value of 1), NORM_PRIORITY (assigned a value of 5, which is the default for newly created threads), and MAX_PRIORITY (the highest priority with a value of 10). These constants help in categorizing threads based on their importance and urgency. By manipulating these priorities, developers can influence which threads get executed more frequently, but the actual impact on performance will depend heavily on the system's thread scheduling policies.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a restaurant where some orders are prioritized over others. A regular meal (NORM_PRIORITY) might take a standard amount of time to prepare, while a VIP order (MAX_PRIORITY) is rushed through, and a simple snack (MIN_PRIORITY) might be prepared last. Although the waiter tries to prioritize the VIP order, unforeseen circumstances (like kitchen issues) might affect how efficiently each item is served, similar to how an operating system may handle thread scheduling irrespective of priority.
Key Concepts
-
Thread Priority: Integer values assigned to threads affecting their execution order.
-
setPriority(): A method to set thread priority that influences thread scheduling.
-
Preemptive Scheduling: Higher priority threads can interrupt lower priority threads.
Examples & Applications
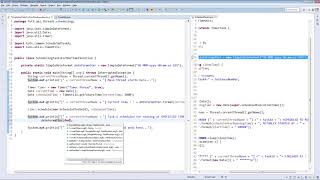
Example of setting thread priority:
Thread t = new Thread();
t.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
In a sample application, a GUI thread can be set to a lower priority while background calculations are at a higher priority to ensure smooth responsiveness.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When threads compete for a fair slice and set priority nice!
Stories
Imagine three friends playing a game, the one with the loudest voice gets the first turn, just as threads with higher priority get executed first in the JVM.
Memory Tools
'M-N-M' for Minimum, Normal, Maximum priorities — clear and precise!
Acronyms
P-H-L
Priority
Higher
Lower to remember how scheduling functions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thread Priority
An integer value assigned to each thread that affects the scheduling of threads in the JVM.
- setPriority()
A method used to set the priority of a thread in the Java programming language.
- Preemptive Scheduling
A scheduling method where higher priority threads can interrupt lower priority threads.
- Operating System Scheduler
The system that manages the execution of threads by determining which thread to run at any given time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
