Fork/Join Framework (Advanced Topic)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Fork/Join Framework
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the Fork/Join Framework, which is vital for effective multitasking in Java. Can anyone tell me what parallel processing means?

Does it mean performing multiple tasks at once?

Exactly! The Fork/Join Framework allows us to do just that by splitting tasks into smaller subtasks. This is especially useful for tasks that can be broken down. For example, when sorting large datasets.

How does it actually manage the subtasks?

Great question, Student_2! The tasks are managed by `ForkJoinPool`, which efficiently schedules and executes them. Remember, we can visualize this as a tree where each node represents a subtask.

Why do we need subtasks?

Subtasks allow for faster processing. They can be run in parallel on multi-core processors, significantly reducing execution time for large tasks. Think of it as teamwork—many hands make light work!
Using Fork/Join Framework in Java
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the basics, let's look at how to implement it. A key class here is `RecursiveTask` for tasks that return a result. Can someone summarize what 'recursive' means?

Isn't it when a function calls itself?

Correct! In our implementation, we will break down a task, call the function for each subtask, and eventually combine results. For example, when implementing a merge sort, we split the array until we have smaller arrays that can be merged.

How do we initiate this in Java?

Great point, Student_1! You create an instance of `ForkJoinPool` and use the `invoke()` method to begin processing your `RecursiveTask`. This manages all the subtasks and merges the results for you.

Can we use it for other types of problems?

Absolutely! It's versatile for any task that can be broken down into smaller chunks. This is particularly effective in processing large collections or data streams.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
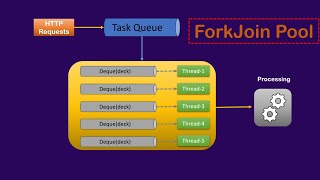
The Fork/Join Framework is designed for divide-and-conquer parallelism, effectively facilitating the execution of tasks by breaking them into smaller subtasks that can run in parallel. This framework, which utilizes the ForkJoinPool, optimizes resource usage and task management.
Detailed
Fork/Join Framework Overview
The Fork/Join Framework is an essential tool in Java for managing concurrent tasks through a divide-and-conquer strategy. Unlike single-threaded applications which handle tasks sequentially, this framework allows for complex problem-solving by dividing a large task into smaller independent subtasks that can be processed in parallel. This not only enhances performance but leverages modern multi-core processors effectively.
Key Features
The primary component of the Fork/Join Framework is the ForkJoinPool, which manages the execution of ForkJoinTask instances. The process generally follows these steps:
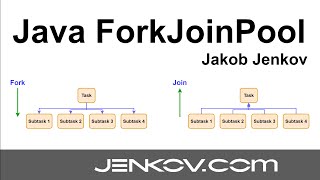
1. Fork: Split the main task into smaller subtasks.
2. Join: Execute the subtasks simultaneously and then combine the results once all are complete.
For example, an efficient implementation of the merge sort algorithm utilizes this framework by splitting the array into halves recursively, sorting each half in parallel, and merging the results.
This framework improves resource management, minimizes processing time, and is crucial for developing applications that require high performance and responsiveness.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Fork/Join Framework
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used for divide-and-conquer style parallelism.
Detailed Explanation
The Fork/Join framework is a specialized concurrency framework in Java designed to handle tasks that can be broken down into smaller sub-tasks. This approach is often referred to as 'divide-and-conquer' because it solves a problem by recursively dividing it into smaller tasks until they become simple enough to solve directly.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a large puzzle. Instead of tackling the entire puzzle at once, you can divide it into smaller sections (corners, edges, center pieces). Each person (or 'thread') can work on a specific section simultaneously, making it easier to complete the whole puzzle quickly.
Example of Divide-and-Conquer
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example: Breaking a task into smaller subtasks recursively (e.g., merge sort), running them in parallel using ForkJoinPool.
Detailed Explanation
In a typical divide-and-conquer example like merge sort, the large array to be sorted is divided into smaller arrays repeatedly until each array has a single element. At this stage, each array is inherently sorted, and then these smaller sorted arrays are merged back together in the correct order. The Fork/Join framework takes advantage of this process by allowing each division and merge to be handled in parallel, efficiently utilizing available CPU resources.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a team working on a large report. The project manager divides the report into sections and assigns them to different team members. Each person works on their section at the same time, and once all sections are complete, they’re combined into one complete report. This way, the project is completed faster than if one person did it all sequentially.
Using ForkJoinPool
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
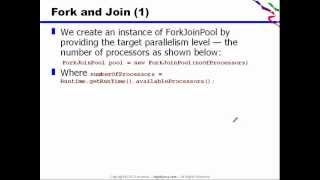
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.invoke(new RecursiveTaskImpl());
Detailed Explanation
The ForkJoinPool manages a pool of threads that executes tasks that extend the RecursiveTask or RecursiveAction classes. When a task is executed using the invoke() method, it automatically splits the task into smaller subtasks that can be processed in parallel. The pool manages task distribution and helps in balancing the workload among the available threads.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a kitchen in a restaurant where the chef prepares a large meal. Instead of cooking everything by themselves, the chef can delegate different parts of the meal to specialized cooks: one handles appetizers, another takes care of the main course, and a third prepares desserts. Each cook works on their station, and together they get the meal ready much quicker than if the chef did everything on their own.
Key Concepts
-
Divide-and-Conquer: A strategy to solve a problem by breaking it into smaller subproblems.
-
Concurrency: The execution of multiple tasks simultaneously or overlapping in time.
-
Tasks: Units of work that can be executed independently.
Examples & Applications
Using ForkJoinPool to implement Merge Sort by recursively dividing the array and sorting each half in parallel.
Computing Fibonacci numbers using the Fork/Join Framework by breaking down larger Fibonacci calculations into smaller branches.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When tasks are big and need a breach, Fork/Join will help them reach.
Stories
Imagine a chef who divides a big order into smaller meals. Each cook prepares their dish, and together they finish faster—a perfect parallel kitchen!
Memory Tools
DART: Divide tasks, Allocate resources, Run in parallel, Team up to finish.
Acronyms
FJP
Fork tasks
Join results
Parallel processing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fork/Join Framework
A Java framework designed for parallel processing that breaks tasks into smaller subtasks for concurrent execution.
- ForkJoinPool
The pool managing the execution of ForkJoinTask instances in the Fork/Join Framework.
- RecursiveTask
A type of ForkJoinTask that returns a result upon completion.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
