Chemical Reactions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Chemical Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss the fundamental types of changes that substances undergo. Can anyone tell me what a physical change is?

A physical change is like when ice melts into water, right? It changes form, but it's still water.

Exactly! That's a great example. Now, what about a chemical change? Anyone?

Isn't it when substances react with each other and form new substances?

Correct! Chemical reactions involve breaking and forming of bonds. For instance, the reaction of muriatic acid with sodium bicarbonate says, 'a chemical equation can represent this: NaHCO₃ + HCl → NaCl + H₂O + CO₂.' Can anyone explain what indicates a chemical change?

There might be gas production, color change, or formation of a precipitate!

Right! So, remember: changes involving breaking chemical bonds signify a chemical reaction.
Enzymes as Catalysts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's pivot a bit to enzymes. Who can tell me what an enzyme does?

Enzymes speed up chemical reactions, don’t they?

Exactly! They lower the activation energy of a reaction. Can anyone explain how they accomplish this?

By providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to proceed more easily?

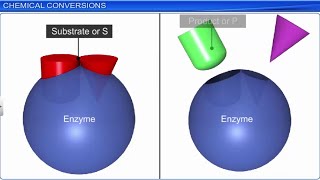
Great job! They form a complex with the substrate, which stabilizes the transition state, leading to the product formation. Here's a fun term: "E + S → ES → E + P." Does anyone remember what 'S' and 'P' stand for?

'S' is the substrate, and 'P' is the product!

That's right! So, enzymes are crucial for metabolism, enabling reactions that would otherwise be too slow.
Factors Influencing Rate of Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the factors affecting reaction rates. What do you think happens when we increase the temperature?

I think the reaction rates would increase. Molecules move faster, so they collide more!

Correct! There's a rule that states the rate doubles for every 10°C increase. What about substrate concentrations?

The reaction will initially increase with substrate concentration, but it'll level off once all enzymes are occupied, right?

Exactly! That maximum rate is called V max. So now, let’s recap: Reaction rates are influenced primarily by temperature and substrate concentration.
Understanding Chemical Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss the fundamental types of changes that substances undergo. Can anyone tell me what a physical change is?

A physical change is like when ice melts into water, right? It changes form, but it's still water.

Exactly! That's a great example. Now, what about a chemical change? Anyone?

Isn't it when substances react with each other and form new substances?

Correct! Chemical reactions involve breaking and forming of bonds. For instance, the reaction of muriatic acid with sodium bicarbonate says, 'a chemical equation can represent this: NaHCO₃ + HCl → NaCl + H₂O + CO₂.' Can anyone explain what indicates a chemical change?

There might be gas production, color change, or formation of a precipitate!

Right! So, remember: changes involving breaking chemical bonds signify a chemical reaction.
Enzymes as Catalysts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's pivot a bit to enzymes. Who can tell me what an enzyme does?

Enzymes speed up chemical reactions, don’t they?

Exactly! They lower the activation energy of a reaction. Can anyone explain how they accomplish this?

By providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to proceed more easily?

Great job! They form a complex with the substrate, which stabilizes the transition state, leading to the product formation. Here's a fun term: "E + S → ES → E + P." Does anyone remember what 'S' and 'P' stand for?

'S' is the substrate, and 'P' is the product!

That's right! So, enzymes are crucial for metabolism, enabling reactions that would otherwise be too slow.
Factors Influencing Rate of Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the factors affecting reaction rates. What do you think happens when we increase the temperature?

I think the reaction rates would increase. Molecules move faster, so they collide more!

Correct! There's a rule that states the rate doubles for every 10°C increase. What about substrate concentrations?

The reaction will initially increase with substrate concentration, but it'll level off once all enzymes are occupied, right?

Exactly! That maximum rate is called V max. So now, let’s recap: Reaction rates are influenced primarily by temperature and substrate concentration.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the nature of chemical reactions, explaining the difference between physical changes and chemical changes. We delve into how enzymes facilitate chemical reactions by lowering activation energy, leading to significantly increased reaction rates.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve the transformation of substances through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. These reactions can be categorized into two types: physical changes, which involve alterations in state or shape without bond breaking (e.g., melting ice), and chemical changes, where new substances are formed from reactants (e.g., the reaction between barium hydroxide and sulfuric acid).
The rate of any reaction can be expressed mathematically, and several factors can influence this rate, including temperature. A notable aspect of chemical reactions in biological systems is the role of enzymes. Enzymes are biological catalysts that significantly speed up reaction rates—sometimes by millions of times—by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed.
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions follow specific pathways and can be influenced by various external conditions, such as substrate concentration, temperature, and pH levels. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial in the study of metabolism and biochemical processes.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Chemical Reactions
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
How do we understand these enzymes? Let us first understand a chemical reaction. Chemical compounds undergo two types of changes. A physical change simply refers to a change in shape without breaking of bonds. This is a physical process. Another physical process is a change in state of matter: when ice melts into water, or when water becomes a vapour. These are also physical processes. However, when bonds are broken and new bonds are formed during transformation, this will be called a chemical reaction.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we learn about chemical reactions and how they differ from physical changes. A chemical reaction involves breaking and forming bonds, transforming substances into different chemical entities—this is not just a change in form but a fundamental change in the composition of matter. For example, when ice melts, it changes from solid to liquid, but its molecular structure (water, H2O) remains the same. In contrast, when hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to form water, new bonds form and the original gases are converted into a different substance (water).
Examples & Analogies
Think of a chemical reaction like baking a cake. You take different ingredients (flour, sugar, eggs) which remain unchanged before mixing, but once you mix and bake them, they chemically transform into cake, a new substance, just like how chemical reactions change substances into new forms.
The Role of Rate in Reactions
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Rate of a physical or chemical process refers to the amount of product formed per unit time. It can be expressed as: δP / δt. Rate can also be called velocity if the direction is specified. Rates of physical and chemical processes are influenced by temperature among other factors. A general rule of thumb is that rate doubles or decreases by half for every 10°C change in either direction.
Detailed Explanation
Here, the focus is on the rate of reactions, which is a measure of how quickly products are formed. This rate is influenced by factors such as temperature; for most reactions, an increase in temperature generally speeds up the reaction. The equation δP / δt gives the rate at which a product (P) is formed over a time period (t). Understanding the rate helps scientists predict how fast a reaction will occur, which is crucial in many scientific and industrial processes.
Examples & Analogies
An analogy for this concept is the speed of a car. Just like a car moves faster when pressing on the gas pedal harder (analogous to increasing temperature), reactions speed up at higher temperatures. For instance, a cold soda will fizz less than a warm soda because the warmer temperature increases the reaction rate of carbon dioxide escaping.
Enzymes as Catalysts
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Catalysed reactions proceed at rates vastly higher than that of uncatalysed ones. When enzyme catalysed reactions are observed, the rate would be vastly higher than the same but uncatalysed reaction. For example, Carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme in the cytoplasm, dramatically speeds up the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains the role of enzymes as catalysts. Enzymes are special proteins that speed up chemical reactions significantly without being consumed in the process. For instance, carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and water, allowing millions of molecules of carbonic acid to form every second, compared to a slow conversion without the enzyme. Understanding enzymes is crucial as they play significant roles in biological processes, enabling reactions that would not happen at a significant rate otherwise.
Examples & Analogies
Consider enzymes as the ‘accelerators’ of chemical reactions. Imagine a sports game where players are moving slowly. If a referee (the enzyme) helps by setting rules for faster plays, the game proceeds much quicker. In a similar way, enzymes help chemical reactions occur more quickly and efficiently.
Metabolic Pathways
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A multistep chemical reaction, when each of the steps is catalysed by the same enzyme complex or different enzymes, is called a metabolic pathway. For example, Glucose → 2 Pyruvic acid is a metabolic pathway in which glucose becomes pyruvic acid through ten different enzyme catalysed metabolic reactions.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, the concept of metabolic pathways in biology is introduced. Metabolic pathways consist of a series of linked chemical reactions where the product of one reaction is the substrate for the next, all catalyzed by enzymes. Understanding these pathways is essential as they play significant roles in energy production, metabolism, and overall biological functions. For example, glucose breakdown into pyruvate occurs in several steps, each regulated by a specific enzyme, and is essential for cellular energy production.
Examples & Analogies
Think of metabolic pathways like an assembly line in a factory. Each station represents an enzyme that adds or modifies a product (the substrate) as it moves along. Just as it would be impossible for the factory to run smoothly without each station doing its job, energy production in our cells relies on each enzyme functioning correctly in metabolic pathways.
Key Concepts
-
Chemical Changes: Involve bond breaking and forming, resulting in new substances.
-
Enzymes: Biological catalysts that lower activation energy and speed up reactions.
-
Rate of Reaction: Influenced by temperature, concentration of substrate, and the presence of enzymes.
Examples & Applications
Example of a physical change includes ice melting into water.
Example of a chemical reaction is the combustion of glucose in cellular respiration.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Enzymes lower that energy bar, making reactions go so far!
Stories
Once upon a time, in the world of chemistry, there was a magical catalyst called an enzyme, who could speed up any reaction, turning slow dances into fast-paced ballrooms of molecules.
Memory Tools
Remember CRISP: Chemical bonds change, Reaction rate increases, Enzymes lower activation energy, Substrates bind, Products form.
Acronyms
Use the acronym STEP
Substrate
Transition state
Enzyme
Product to remember the flow of enzyme activity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Chemical Reaction
A process where bonds are broken in reactants and new bonds are formed in products.
- Physical Change
A change that does not alter the substance's chemical composition.
- Enzyme
A biological catalyst that accelerates chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.
- Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
- Substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme acts.
- Product
The substance produced as a result of a chemical reaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
