Nucleic Acids
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Structure of Nucleic Acids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the structure of nucleic acids. Can anyone tell me what nucleic acids are?

Aren't they the genetic materials in our cells?

Exactly! Nucleic acids, mainly DNA and RNA, are vital for storing and transmitting genetic information. They consist of smaller units called nucleotides.

What do nucleotides consist of?

Great question! Each nucleotide is made up of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group — think of it as a treasured triple combo.

What kind of sugar do DNA and RNA have?

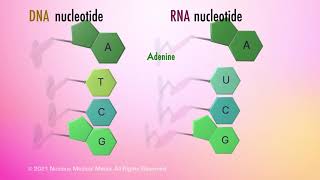
Good catch! DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, while RNA has ribose sugar. Remember, D for DNA and Deoxyribose!

Why is it important to know the structure?

Understanding the structure helps us grasp how nucleic acids function in genetics and protein synthesis. Let's summarize: nucleotides make up nucleic acids, which are essential for genetic material.
Types of Nucleic Acids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, we mentioned DNA and RNA. Who can explain the difference between the two?

DNA is double-stranded and holds the genetic blueprint, right?

Exactly! DNA is double-helix shaped, which provides stability, while RNA is usually single-stranded. What about their functions?

DNA directs protein synthesis. But, what does RNA do?

Correct! RNA plays a key role in translating the genetic information from DNA into proteins. We have different types of RNA too, like mRNA and tRNA.

Can we summarize the major functions?

Of course! DNA is for storage and transmission of genetic information. RNA is involved in protein synthesis. They work closely to orchestrate cellular functions.
Importance of Nucleic Acids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know the types of nucleic acids, why are they essential for life?

Is it because they contain the instructions for forming proteins?

Exactly! They provide the templates for protein synthesis and are crucial in heredity. Anyone can recall how they influence traits?

Genes encoded in DNA determine traits and characteristics.

Correct! Genes are segments of DNA that encode proteins, affecting everything from eye color to enzyme activity. Let's summarize: nucleic acids are pivotal for genetic information, protein synthesis, and inheritance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores nucleic acids, focusing on their structure and function. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, which include a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA and RNA play vital roles in storing and transmitting genetic information.
Detailed
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules necessary for all known forms of life, primarily represented by DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). They are classified as polynucleotides, which are long chains of nucleotides linked together by phosphodiester bonds. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (either a purine - adenine or guanine, or a pyrimidine - cytosine, uracil, or thymine), a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA is double-stranded and acts as the genetic blueprint, responsible for storing genetic information, while RNA is typically single-stranded and plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and gene expression. The fundamental relationship between nucleic acids and proteins underscores their role in heredity and the biochemical activity of all living organisms.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The other type of macromolecule that one would find in the acid insoluble fraction of any living tissue is the nucleic acid. These are polynucleotides. Together with polysaccharides and polypeptides these comprise the true macromolecular fraction of any living tissue or cell.
Detailed Explanation
Nucleic acids are one of the main categories of macromolecules found in cells, alongside polysaccharides and proteins. They are classified as polynucleotides, which means they are large molecules composed of repeating units called nucleotides. These nucleotides form long chains that are essential for various functions in the cell.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a long train where each car represents a nucleotide. Just like a train connects different stations, nucleotides connect to form nucleic acids, which play crucial roles in the functioning of living organisms.
Components of Nucleotides
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For nucleic acids, the building block is a nucleotide. A nucleotide has three chemically distinct components. One is a heterocyclic compound, the second is a monosaccharide, and the third a phosphoric acid or phosphate.
Detailed Explanation
Nucleotides, the building blocks of nucleic acids, consist of three parts: a nitrogenous base (the heterocyclic compound), a sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous base can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, or thymine, each playing a different role within DNA and RNA structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a nucleotide like a sandwich: the bread represents the sugar, the lettuce and tomato represent the phosphate group, and the protein filling represents the nitrogenous base. Each part is essential to create a complete, functional sandwich (nucleotide).
Types of Nitrogenous Bases
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As you notice in Figure 9.1, the heterocyclic compounds in nucleic acids are the nitrogenous bases named adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine. Adenine and Guanine are substituted purines while the rest are substituted pyrimidines. The skeletal heterocyclic ring is called purine and pyrimidine respectively.
Detailed Explanation
Nucleotides contain specific nitrogenous bases categorized into two types: purines (which include adenine and guanine) that have a double-ring structure, and pyrimidines (which include cytosine, uracil, and thymine) that have a single-ring structure. These bases pair in specific ways, forming the structure of DNA and RNA.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a game of musical chairs where adenine and thymine are a pair, just like cytosine and guanine. Each pairing follows specific rules, akin to how they must match perfectly to maintain stability in the molecular structure.
Difference Between DNA and RNA
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The sugar found in polynucleotides is either ribose (a monosaccharide pentose) or 2’ deoxyribose. A nucleic acid containing deoxyribose is called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) while that which contains ribose is called ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Detailed Explanation
The difference between DNA and RNA lies in their sugar component: DNA contains deoxyribose, and RNA contains ribose. This small change significantly impacts the structure and function of these nucleic acids, with DNA serving primarily in genetic information storage, while RNA is crucial for protein synthesis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of DNA as a hard drive that stores all the information of a computer, while RNA acts like a messenger that carries instructions from the hard drive to different parts of the computer to execute tasks.
Key Concepts
-
Nucleotides: The building blocks of nucleic acids, consisting of a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base.
-
Types of Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA have distinct structures and functions, crucial for genetic information and protein synthesis.
-
Gene: A segment of DNA that encodes proteins, determining traits and characteristics.
Examples & Applications
DNA serves as the genetic blueprint in all living organisms, while RNA participates in protein synthesis.
Mutations in DNA can lead to genetic disorders or influence traits.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Nucleotides are quite the feat, with sugar, base, and phosphate neat.
Stories
Imagine a tree, with DNA roots extending deep, creating branches of RNA that produce proteins — the fruit of genetic inheritance.
Memory Tools
For remembering the nitrogenous bases: 'A Good Cat Takes Urgent Action' — Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil.
Acronyms
DAN = DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) as the genetic duo.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Nucleotide
The basic building block of nucleic acids, consisting of a nitrogenous base, sugar, and phosphate group.
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, a double-stranded nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions for living organisms.
- RNA
Ribonucleic acid, a single-stranded nucleic acid involved in the synthesis of proteins.
- Nitrogenous Base
A component of nucleotides that can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine (found in DNA), or uracil (found in RNA).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
