Gamma rays
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Gamma Rays
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Gamma rays lie at the high-frequency end of the electromagnetic spectrum. Can anyone tell me what we understand by 'high frequency'? It generally means shorter wavelengths.

So, it means that gamma rays have wavelengths less than 10^-10 meters?

Exactly! Gamma rays range from 10^-10 m to less than 10^-14 m. They are produced in nuclear reactions, but how do we detect them?

I think special detectors are needed since they can't be seen directly.

Correct! They are detected using instruments like Geiger counters and scintillation detectors. Now, let's summarize: gamma rays are extremely high-energy waves, produced by nuclear processes, and they can be detected with specialized equipment.
Applications of Gamma Rays
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

An essential application of gamma rays is in the treatment of cancer. Can anyone explain how this works?

Isn't it something to do with targeting the cancer cells directly?

Yes, gamma rays are used in radiotherapy to destroy cancerous cells. They penetrate bodily tissues and target malignant cells. Why is this important in medicine?

Because they can kill cancer cells with high precision, reducing damage to healthy cells!

Excellent point! Gamma rays deliver high doses of radiation to tumors while minimizing harm to surrounding healthy tissue. That's why they are incredibly valuable in oncology.
Gamma Rays vs Other Electromagnetic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's compare gamma rays with X-rays. What are the differences in their origins?

Gamma rays come from nuclear reactions, while X-rays are usually produced when charged particles decelerate.

Right! And what about their applications? While X-rays are commonly used for medical imaging, gamma rays are primarily used for treatment.

So both are important but serve different roles in healthcare.

Exactly! To encapsulate, gamma rays and X-rays are both forms of electromagnetic radiation but differ in their origins, properties, and applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
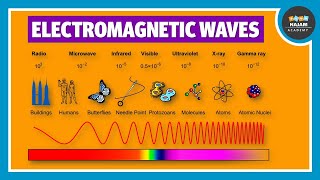
Gamma rays occupy the upper frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum, characterized by wavelengths from about 10^-10 m to less than 10^-14 m. They are emitted during nuclear reactions and by radioactive materials, and are critical in medical treatments, especially in oncology, to target and destroy cancer cells.
Detailed
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation with the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced during nuclear reactions and as a result of radioactive decay.
Key Characteristics:
- Wavelength Range: Gamma rays have wavelengths between 10^-10 m (0.1 nm) to 10^-14 m (0.0001 nm).
- Production: They are generated in high-energy processes such as nuclear reactions, nuclear decay, and are also emitted by certain radioactive materials.
- Applications in Medicine: Gamma rays are primarily used in medicine to destroy cancer cells through a process called radiotherapy, where targeted gamma radiation kills malignant cells without significantly harming surrounding healthy tissues.
Understanding gamma rays is crucial not only in nuclear physics but also in medical science, illustrating their dual role in generating profound knowledge and contributing to health.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition and Characteristics of Gamma Rays
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
They lie in the upper frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum and have wavelengths of from about 10–10m to less than 10–14m.
Detailed Explanation
Gamma rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation found at the high-energy end of the spectrum. Their wavelengths range from about 10 to the power of -10 meters (10 nm) to less than 10 to the power of -14m (0.1 nm). This places them at higher frequencies compared to other types of electromagnetic waves, like X-rays or visible light. The high frequency means they carry more energy, which can be significant in various applications, especially in medicine.
Examples & Analogies
Think of gamma rays as tiny, super-fast cars racing on a highway—the closer they get to the finish line (or upper frequency range), the faster and more powerful they become. Just as these fast cars can have a larger impact than slower ones, gamma rays, with their high energy, can interact with matter in powerful ways.
Production of Gamma Rays
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This high frequency radiation is produced in nuclear reactions and also emitted by radioactive nuclei.
Detailed Explanation
Gamma rays are produced during nuclear reactions, such as fission or fusion, or when radioactive nuclei decay. During these processes, energy is released, and some of it takes the form of gamma radiation. Unlike other types of radiation, gamma rays do not involve particle movement but rather are a form of electromagnetic energy released from the nucleus of an atom.
- Chunk Title: Applications of Gamma Rays
- Chunk Text: They are used in medicine to destroy cancer cells.
- Detailed Explanation: In medicine, gamma rays are utilized in radiation therapy, where high-energy radiation is directed at cancer cells to destroy them. This process exploits the ability of gamma rays to penetrate tissues effectively and target rapidly dividing cells, which are indicative of tumors. While cancer cells are often more sensitive to radiation than normal cells, care must be taken to minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sculptor chiseling away at a block of marble. The goal is to remove unwanted portions to reveal a beautiful statue. Similarly, gamma rays help 'chisel away' at cancerous cells, aiming to eliminate them while trying to preserve the healthy surrounding cells, just as a sculptor tries to leave the desired parts intact.
Key Concepts
-
Gamma rays: Electromagnetic radiation with very high frequency and energy.
-
Production: Result from nuclear reactions and radioactive decay.
-
Medical application: Used primarily in cancer treatment through radiotherapy.
Examples & Applications
Gamma rays produced during nuclear fission in a reactor.
Using gamma rays in PET scans to visualize and diagnose tumors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Gamma rays so bright and bold, / Cancer cells they will unfold. / Nuclear bursts send them on their way, / Healing wounds and saving the day.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a kingdom where sickness reigned, a mighty warrior, Gamma Ray, embarked on a quest to vanquish the dark forces of Cancer that plagued the land. With every step, he unleashed powerful bursts of energy, penetrating the defenses of his foes to bring healing and light.
Memory Tools
Remember 'GReat CAncer KIller' (G.R.C.A.K) to recall that Gamma Rays are a great cancer-killing treatment.
Acronyms
Gamma Rays = G.R.A.Y (Gamma Rays Against Yonder cells - symbolizing their role in fighting cancer).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Gamma rays
High-frequency electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from 10^-10 to less than 10^-14 meters, produced from nuclear reactions.
- Electromagnetic spectrum
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, ordered by frequency and wavelength.
- Radiotherapy
A medical treatment that uses gamma rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
