Microwaves
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Microwaves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore microwaves, a fascinating part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Does anyone know what defines microwaves?

I think it has to do with their frequency, right?

Exactly! Microwaves have frequencies in the gigahertz range. This makes their wavelengths much shorter than those of radio waves. Can anyone tell me how this property is useful?

I remember they are used in radar systems!

Right! Their shorter wavelengths allow them to be used effectively in radar systems, which are crucial for aircraft navigation.
Production of Microwaves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about how microwaves are produced. They are generated by devices like klystrons and magnetrons. Have any of you heard of these devices?

Klystrons sound familiar. Are they like vacuum tubes?

That's correct! Klystrons and magnetrons use vacuum technology to produce microwaves efficiently. Magnetrons are particularly well-known for their role in microwave ovens.

How do they work in microwave ovens?

Great question! The microwaves resonate with water molecules in food, converting energy from the microwaves into kinetic energy and heating the food.
Applications of Microwaves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Microwaves have many applications. Besides being used in cooking, can anyone think of other uses?

Um, radar systems for speed detection in sports like baseball?

Exactly! Microwaves are also used in radar for detecting speed in athletics and for aircraft navigation.

What about communication?

Yes! Microwaves are utilized in some communication technologies as well. Their ability to penetrate clouds and rain makes them very effective.
Scientifically Understanding Microwave Effects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore how microwaves heat food. Why do you think they are effective in doing so?

Because they match the frequency of water molecules and excite them?

Exactly! This efficient transfer of energy from microwaves to water molecules is what makes microwave ovens so effective.

So, do they heat food evenly?

Good observation! Microwaves can lead to uneven heating, which is why it's important to stir food or rotate it for even cooking.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Microwaves, which are short-wavelength radio waves with frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range, are generated by devices such as klystrons and magnetrons. Their short wavelengths make them ideal for uses in radar systems for aircraft navigation and in domestic microwave ovens, where they efficiently heat food by exciting water molecules.
Detailed
Microwaves are a critical subset of the electromagnetic spectrum characterized by short wavelengths and high frequencies, typically in the gigahertz range. They are generated by specialized devices such as klystrons, magnetrons, and Gunn diodes. Their unique properties make them suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in radar systems, which are instrumental for aircraft navigation and speed detection in sports like baseball and tennis. Moreover, microwave ovens are a popular household application where the frequency of microwaves is tuned to resonate with water molecules, facilitating effective energy transfer to heat food. This concept not only highlights the practical uses of microwaves but also emphasizes their scientific principles linked to electromagnetic wave behavior.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Microwaves Overview
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Microwaves (short-wavelength radio waves), with frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range, are produced by special vacuum tubes (called klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn diodes).
Detailed Explanation
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic wave that have very short wavelengths, typically ranging from 1 millimeter to 1 meter. They operate in the gigahertz frequency range, which means they are produced and can oscillate at extremely high frequencies, usually by devices like klystrons, magnetrons, and Gunn diodes. These devices are designed to convert electrical energy into microwave radiation that can then be used in various applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of microwaves like a fast-paced game of ping pong. Just as the balls bounce quickly back and forth between players, microwaves oscillate rapidly and can transfer energy efficiently. This rapid oscillation is useful in many technologies, including microwave ovens where they heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate quickly.
Radar Systems Using Microwaves
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
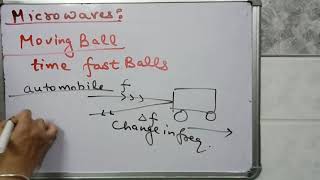
Due to their short wavelengths, they are suitable for the radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Radar also provides the basis for the speed guns used to time fast balls, tennis-serves, and automobiles.
Detailed Explanation
Microwaves are particularly advantageous in radar applications due to their short wavelengths. These short wavelengths allow them to bounce off of objects, which provides details about the distance and speed of moving objects, such as cars or aircraft. Radar systems emit microwave signals that, upon hitting an object, reflect back and are analyzed to determine the object's position and velocity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine playing a game of dodgeball in the dark. If you throw a ball and it hits a player, you can estimate how far away they are by listening to how long it takes for the ball to come back to you. That’s similar to how radar works – it sends out microwaves and measures how long it takes for them to bounce back to calculate the distance to an aircraft or speeding car.
Microwave Ovens
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Microwave ovens are an interesting domestic application of these waves. In such ovens, the frequency of the microwaves is selected to match the resonant frequency of water molecules so that energy from the waves is transferred efficiently to the kinetic energy of the molecules. This raises the temperature of any food containing water.
Detailed Explanation
Microwave ovens utilize microwaves to heat food by exciting water molecules within the food items. The microwaves are tuned to a specific frequency that aligns with the natural frequency at which water molecules vibrate. This resonance allows the microwaves to effectively transfer energy to the molecules, causing them to vibrate more rapidly, which increases the temperature and cooks the food. This technology allows for rapid heating compared to traditional cooking methods.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a dance party in which everyone needs to move to the same beat to enjoy the party. If all the dancers (water molecules) are moving together in sync with the music (microwaves), they can dance more energetically and have a great time. In a microwave oven, water molecules resonate with the microwaves, making them 'dance' and thus heat the food quickly.
Key Concepts
-
Microwaves: Short-wavelength electromagnetic waves in the GHz range.
-
Klystrons: Vacuum tubes used to generate microwaves.
-
Magnetrons: Devices that produce microwaves for applications like cooking and radar.
-
Radar: Microwaves are vital for detecting the speed and position of objects.
Examples & Applications
Microwave ovens use microwaves to heat food by exciting water molecules within the food.
Radar systems utilize microwaves to track aircraft navigation and measure speed.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Micro-waves, fast and neat, cooking food is their treat.
Stories
Imagine a chef who only cooks with magic waves that dance around food, making it hot and ready in minutes!
Memory Tools
Killy Max, the radar champ, generates waves that help you camp.
Acronyms
MIR
Microwaves
Interactions
Radiance – to recall how microwaves interact and produce heat.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Microwaves
Electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from gigahertz (GHz) to microwave frequencies, characterized by short wavelengths.
- Klystron
A specialized vacuum tube used to generate microwaves by controlling the flow of electrons.
- Magnetron
A type of vacuum tube that generates microwaves and is commonly used in microwave ovens.
- Radar
A system that uses microwaves to detect the position and speed of objects.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
