Ultraviolet rays
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Ultraviolet Rays
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to look at ultraviolet rays. Who can tell me what we know about their position in the electromagnetic spectrum?

Are they part of the light spectrum we can see?

Great question! Ultraviolet rays occupy the wavelengths shorter than visible light, ranging from 400 nm down to 0.6 nm. Remember the acronym UV for Ultraviolet!

What are some sources of UV rays?

Primarily, UV rays arise from the sun! They can also come from specialized lamps, used in different applications. Now let's keep in mind that UV exposure is not always safe.
Effects of Ultraviolet Rays
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what UV rays are, let’s discuss their effects. Who can tell me why UV exposure is a concern for skin health?

Uh, because it can lead to tanning and burns?

Exactly! UV radiation induces melanin production in the skin which causes tanning. But excessive exposure can increase the risk of skin cancer. Remember: UV = Tanning but also = Cancer Risk!

What can we do to protect ourselves from UV rays?

Wearing sunscreen, sunglasses, and protective clothing are all effective measures. And it’s important to note that ordinary glass absorbs UV rays, providing a sort of shield indoors!
Practical Applications of Ultraviolet Rays
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about some practical applications. Can anyone think of where UV light is used beneficially?

Like in water purifiers?

Yes! UV lamps are used to kill germs in water purifiers. They effectively sterilize without chemicals. Another application is in LASIK eye surgery, utilizing UV for precision.

Why do welders need special goggles?

Great note! Welders are exposed to high amounts of UV radiation from welding arcs, necessitating protection to prevent eye damage. Always remember that safety equipment is critical when dealing with UV lights!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section details ultraviolet rays, their wavelengths, sources, and effects. UV radiation can cause skin tanning and has sterilizing properties, but it can be harmful in large quantities. Ozone layer plays a protective role by absorbing most of the UV radiation.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Ultraviolet Rays
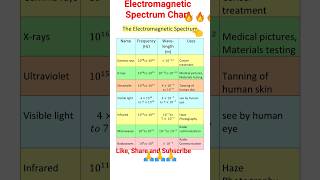
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum that covers wavelengths ranging from approximately 400 nm (4 × 10^-7 m) to 0.6 nm (6 × 10^-10 m). The sun serves as the primary natural source of these rays, which are also produced by specialized lamps. Most UV radiation is absorbed by the ozone layer in the earth's atmosphere, which lies about 40-50 km above the earth's surface, providing critical protection from overexposure.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation can lead to several detrimental effects on human health, such as skin tanning and an increased risk of skin cancer. The absorption properties of ordinary glass prevent UV rays from passing through, therefore shielding us from sunburn when indoors, even on sunny days.
In specific industries, such as welding, workers wear special protective goggles due to the large quantities of UV light produced by welding arcs, which can be harmful to the eyes. Additionally, the focused nature of UV radiation allows it to be utilized in applications like LASIK eye surgery and germicidal lamps in water purification systems. The ongoing concern regarding the depletion of the ozone layer due to chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) emphasizes the importance of maintaining our atmosphere's integrity.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Wavelength Range of Ultraviolet Rays
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It covers wavelengths ranging from about 4 × 10–7 m (400 nm) down to 6 × 10–10m (0.6 nm). Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is produced by special lamps and very hot bodies.
Detailed Explanation
Ultraviolet rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays. They span a range of approximately 400 nanometers (nm) to 0.6 nanometers. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy of the radiation. UV radiation can be emitted by specialized artificial sources like UV lamps, as well as natural sources like very hot objects, including the sun.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a rainbow; as we move from red to blue, the colors represent different wavelengths of light. UV rays are like the invisible colors beyond violet. Just as some plants can spring to life with the help of sunlight, certain lamps can artificially produce UV light to support processes like sterilization.
Sources of Ultraviolet Rays
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The sun is an important source of ultraviolet light. But fortunately, most of it is absorbed in the ozone layer in the atmosphere at an altitude of about 40 – 50 km.
Detailed Explanation
The sun emits a significant amount of ultraviolet radiation, which is why we have to be cautious to protect our skin from harmful effects like sunburn and skin cancer. However, much of this UV radiation is absorbed by the ozone layer, a protective layer in the earth's atmosphere located between 40 to 50 kilometers above the surface, which filters out the majority of harmful UV rays.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ozone layer as sunscreen for the Earth; just as we apply sunscreen to protect our skin from sunburns, the ozone layer serves a similar purpose by blocking out a lot of the intense UV radiation that would otherwise reach us.
Effects of Ultraviolet Rays on Humans
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
UV light in large quantities has harmful effects on humans. Exposure to UV radiation induces the production of more melanin, causing tanning of the skin.
Detailed Explanation
When humans are exposed to high levels of UV radiation, it can have harmful effects such as sunburn, premature aging of the skin, and increased risk of skin cancer. UV radiation interacts with the skin cells, prompting them to produce melanin, which causes the skin to darken as a protective response. This is how tanning occurs; the body is attempting to shield itself from further UV damage.
Examples & Analogies
Just as a plant grows taller and stretches towards the sunlight, our skin reacts to UV rays by producing more melanin for safety. However, prolonged exposure to sunlight without protection can lead to severe burns, similar to a plant wilting under excessively hot sun without water.
Protection from UV Rays
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
UV radiation is absorbed by ordinary glass. Hence, one cannot get tanned or sunburn through glass windows. Welders wear special glass goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from large amounts of UV produced by welding arcs.
Detailed Explanation
Ordinary glass can block much of the harmful UV radiation, meaning that if you are behind glass, such as in a car or a building, you are protected from getting sunburned, even on a sunny day. On the other hand, activities like welding release high levels of UV radiation, so welders must wear special goggles designed to block these harmful rays to protect their eyes.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of how a sunshade works in a car; it prevents most of the sun's rays from hitting you directly, just like glass shields you from UV light. However, welders need 'sunglasses' designed for extreme protection because the brightness and UV from welding arcs exceed typical sunlight.
Applications of Ultraviolet Rays
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Due to its shorter wavelengths, UV radiations can be focused into very narrow beams for high precision applications such as LASIK (Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis) eye surgery. UV lamps are used to kill germs in water purifiers.
Detailed Explanation
Ultraviolet radiation is beneficial in various applications beyond just health risks. For instance, in medical treatments like LASIK eye surgery, UV light is used to reshape the cornea with precision. Furthermore, UV lamps are essential in water purification systems where they effectively kill bacteria and viruses, ensuring safe drinking water.
Examples & Analogies
UV light used in LASIK is like a sculptor carefully carving a statue; it carefully reshapes the eye to improve sight. Similarly, think of how bacteria are like weeds in a garden; UV lamps ‘weed out’ harmful germs from water, making it clean and safe to drink.
Importance of Ozone Layer
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The ozone layer in the atmosphere plays a protective role, and hence its depletion by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) gas (such as freon) is a matter of international concern.
Detailed Explanation
The ozone layer is crucial for protecting all living organisms on Earth from the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays. Unfortunately, substances like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) have caused significant depletion of this protective layer, leading to increased UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface, which poses serious health risks.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the ozone layer as an umbrella that protects you from rain; if that umbrella has holes due to wear and tear (like CFC damage), you will get wet (exposed to UV rays). That's why protecting the ozone layer is like maintaining that umbrella in good condition.
Key Concepts
-
Ultraviolet Rays: Part of EM spectrum with wavelengths from 400 nm to 0.6 nm.
-
Sources: Primarily from the sun, also from specialized lamps.
-
Health Effects: Can cause tanning, skin damage, and increase skin cancer risk.
-
Protection: Ozone layer absorbs most harmful UV radiation.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: Exposure to UV rays leads to tanning and can result in skin burns if not protected.
Example 2: Ultraviolet lamps are widely used for sterilization purposes in water purification.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the sun's bright in the sky, wear sunscreen, oh my!
Stories
A young boy loved to play outside but learned that the stronger the sun's rays, the more he needed protection from skin damage.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym 'SAFE' to remember to Stay Aware of UV Exposure.
Acronyms
UV = Sun's Unseen Violence (for reminding about protection needs).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ultraviolet Rays
Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from 400 nm to 0.6 nm.
- Ozone Layer
A region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Melanin
A pigment produced by skin cells that helps protect the skin from UV damage.
- Lasik
A type of eye surgery that uses UV light to reshape the cornea.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
