Fundamental Natural Period (T)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Importance of T
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to talk about the Fundamental Natural Period, or T, in earthquake-resistant design. Why do you think it's important?

I think it might relate to how structures respond to earthquakes.

Exactly! The natural period is crucial as it influences how a building will react to seismic forces. The longer the period, the more sway the building can have.

How do we actually calculate T?

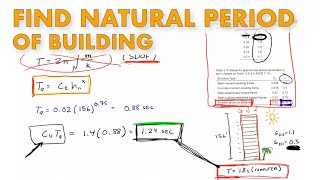
Good question! For moment-resisting frames, use the formula T = 0.075 × h^0.75. Can anyone tell me what 'h' represents?

Isn't 'h' the height of the building?

That's correct! And for other structures, the formula is T = 0.09 × √d, where 'd' is the base dimension. Understanding these formulas helps us calculate the base shear effectively.

Can we remember 'T' by thinking of it as 'Time to sway'?

That's a great mnemonic! Let’s summarize today: T helps determine how buildings will sway during an earthquake, calculated based on height or base dimensions.
Application of T in Design Base Shear
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How does calculating T influence our design base shear, or Vb? Why is this important?

Base shear is like the first line of defense against seismic forces, right?

Correct! Vb is derived from the formulas where T is a fundamental variable. It's critical in establishing how much force a structure must resist.

So, if we miscalculate T, we might under-design the structure?

Absolutely! An incorrect T could lead to inadequate design for seismic forces. Let's remember that safe design must account for T.

Can I summarize? T affects how we estimate base shear, which is essential for safety!

Great summary! Always keep in mind that T is not just a number, but it underpins the structure's earthquake safety.
Concrete and Steel Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Does T apply the same way to all structures, like concrete and steel?

I think it might differ since they have different properties.

Exactly. Moment-resisting frames have specific calculations using T = 0.075 × h^0.75, while other structures use another approach. Why is that?

Because they react differently to lateral forces?

That's right! Concrete frames might behave differently compared to steel frames. It's important to tailor our calculations accordingly.

If we think of different 'characters' of structures, that could help decide which formula to use!

Great analogy! Remember the character of the structure can suggest how it should respond during seismic events.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Fundamental Natural Period (T) is essential for determining the base shear in seismic design. For moment-resisting frames, T can be calculated using the formula T = 0.075 × h^0.75, while for other structures, it is determined using T = 0.09 × √d.
Detailed
Fundamental Natural Period (T)
The Fundamental Natural Period (T) is a crucial parameter in the seismic design of structures as it directly influences the calculation of design base shear. The period is defined based on the building's height (h) and, for moment-resisting frames, is calculated using the formula:
- T = 0.075 × h^0.75
For other structures, the formula is: - T = 0.09 × √d,
where 'd' represents the base dimension of the building in the direction of lateral force.
Understanding the natural period is vital for engineers to ensure that their designs can effectively withstand seismic forces without collapsing. It helps in establishing the dynamic response of the structure during an earthquake, leading to better risk mitigation and safety.
Youtube Videos
![[BCT2025 Webinar] Long Period Ground Motion in Earthquake – its Impacts, Measures and Effects 1](https://img.youtube.com/vi/0lGZlFHEbS4/mqdefault.jpg)






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Required for Design Base Shear Calculation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Required to calculate design base shear.
Detailed Explanation
This point emphasizes that the fundamental natural period (T) is critical for calculating the design base shear, which is the force that a building must resist during an earthquake. The base shear helps determine how structures should be designed to withstand seismic activity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a swing. The time it takes for the swing to go back and forth is similar to the fundamental natural period of a building. Just as the swing’s motion can be affected by how high you push it, a building's response to an earthquake is influenced by its natural period.
Calculation for Moment-Resisting Frames
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• For moment-resisting frames:
T = 0.075 × h^0.75
Detailed Explanation
For moment-resisting frames, the formula T = 0.075 × h^0.75 defines how to calculate the fundamental natural period based on the height (h) of the building. This formula shows that as the height of a building increases, the natural period becomes longer, indicating a slower response to seismic forces.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a tall tree swaying in the wind versus a short shrub. The taller the tree, the slower it sways (has a longer natural period), just like a taller building will have a longer fundamental natural period.
Calculation for Other Structures
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• For other structures:
h
T = 0.09 × √d
Where, h = height of the building (m) d = base dimension of building (m) in the direction of lateral force
Detailed Explanation
For structures that are not moment-resisting frames, the formula T = 0.09 × √d calculates the fundamental natural period using the base dimension (d) in the direction of lateral force. This shows that both the height and base dimensions are important for understanding how structures will respond to seismic forces.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a wide flat table versus a tall narrow one. The flat table (wider base) is likely to be more stable and requires different considerations compared to the tall one during an earthquake, highlighting how the base dimension affects stability.
Key Concepts
-
Fundamental Natural Period (T): A crucial parameter in determining how a structure will respond during an earthquake based on its height or base dimension.
-
Base Shear (Vb): The total lateral force acting on a building during seismic events, influenced significantly by T.
Examples & Applications
Example of a 30m tall moment-resisting frame: Calculating T using T = 0.075 × 30^0.75 results in a specific value of the natural period.
For a rectangular building with a base dimension of 10m using T = 0.09 × √10, allows engineers to determine different responses to lateral forces.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When T is low, the sway is tight; but when it’s high, it’s a different sight.
Stories
Imagine a tall tree in a gentle breeze. As it sways, the height of the tree determines how much it bends and moves, just like buildings during a quake.
Memory Tools
Remember T as 'Time to Sway'; T helps to plan and brace for seismic day.
Acronyms
T = Time to respond
Height helps us correspond.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fundamental Natural Period (T)
The time taken for a building to complete one full cycle of motion during an earthquake; crucial in determining how structures will sway.
- Base shear (Vb)
The total lateral force that results from seismic acceleration acting on the building's mass.
- Height (h)
The vertical measurement of a building from its base to its highest point.
- Base dimension (d)
The horizontal measurement of a building in the direction of lateral force affecting the structure.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
