Ranging Sensor Overview
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Ultrasonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore ultrasonic sensors, focusing on the HC-SR04, which can measure distances. Can anyone tell me how sound waves might help in measuring distances?

I think it sends sound and measures how long it takes for the echo to return.

Exactly! This principle is essential in ranging applications. We can use the formula Distance = (Time * Speed of Sound) / 2. What does each component represent?

Time is how long it takes for the echo to come back, and the speed of sound is how fast the sound moves.

Great insight! The speed of sound is about 343 meters per second at room temperature. Let's keep that in mind as we move forward.

The HC-SR04 uses two pins. Can anyone name them and what they do?

There's the Trigger pin that starts the measurement and the Echo pin that receives the signal.

Correct! Keep this in mind; the interaction with these pins will be crucial when we write our kernel module.
Distance Measurement Mechanics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into how the measurement works. Who can explain what happens when we trigger the sensor?

When we send a signal to the Trigger pin, it sends out a sound pulse, right?

Yes! And after that, what takes place when the sound pulse hits an object?

It bounces back, and the Echo pin detects it.

Right! The time measured during this process allows us to compute the distance. If we know the speed of sound, calculating distance becomes straightforward. Can anyone apply this formula practically?

If it takes 10 milliseconds for the echo to return, we can calculate: Distance = (10 ms * 343 m/s) / 2.

Exactly! Make sure you convert milliseconds to seconds when using the formula.
Practical Application of Ranging Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone think of real-life applications where ranging sensors like the HC-SR04 could be effectively used?

They could be used in robotics for obstacle detection!

You could also use them in automated parking systems.

Excellent examples! Ultrasonic sensors are indeed essential in many automated systems. Remember that understanding how these sensors work helps us interface them efficiently in programming.

What might be challenges when using these sensors?

I think they might struggle with measuring distances in windy conditions since the sound can be disturbed.

Great point! Environmental factors can affect measurements. Keeping these aspects in mind is crucial for practical applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, detailing its operational pins (Trigger and Echo) and how it measures distance using sound waves. The section presents the fundamental formula for calculating distance based on the speed of sound and the echo time.
Detailed
Ranging Sensor Overview
In this section, we will discuss the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, which is commonly used for ranging applications in embedded systems. The sensor functions by emitting sound waves and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return, allowing it to calculate the distance to an object.
Key Components of the Sensor:
- Trigger Pin: This pin sends a pulse to initiate a distance measurement.
- Echo Pin: This pin receives the return signal (echo) and helps determine the time of flight for the sound wave.
Distance Calculation:
The distance measurement is calculated using the formula:
Distance = (Time * Speed of Sound) / 2
Where:
- Time: The duration for which the echo pulse is received.
- Speed of Sound: Approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature (20°C).
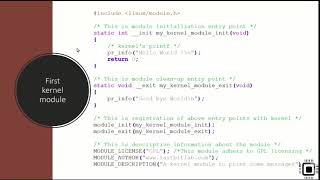
This formula is significant as it provides the means to convert the time measured back into a physical distance. The kernel module we will be developing will interact with the sensor’s GPIO pins to trigger the sensor, measure the echo pulse duration, and ultimately calculate the distance, which is accessible from user space. This overview lays the groundwork for developing the kernel module that we will explore in the following sections.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Ultrasonic Sensors
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For this example, we'll assume that we're working with a commonly used ultrasonic sensor, such as the HC-SR04 sensor, which has:
● Trigger Pin: Sends a pulse to start the measurement.
● Echo Pin: Receives the echo signal and measures the time taken.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, which is commonly used to measure distances. It consists of two primary components: the Trigger Pin and the Echo Pin. The Trigger Pin is responsible for initiating the distance measurement by sending a signal, while the Echo Pin listens for the signal that bounces back after hitting an obstacle. Understanding these pins is crucial as they are fundamental to how the ultrasonic sensor operates.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the Trigger Pin as someone shouting 'Hello!' into a canyon, which is an echo-producing environment. The Echo Pin is like the person waiting to hear their voice bounce back. Just like they need to shout to start the echo, the sensor needs to send a pulse to measure distance.
Distance Calculation Formula
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The formula to calculate the distance is based on the speed of sound:
Distance = (Time * Speed of Sound) / 2
Where:
● Time is the duration for which the echo pulse is received.
● Speed of Sound is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk describes how the distance is calculated using the formula. The distance measurement relies on the time it takes for the sound wave to travel from the sensor to an object and back. Since the time captured includes the journey to the object and the return, the formula divides by 2 to obtain the distance to the object alone. The speed of sound is an important factor, and at room temperature, it is roughly 343 meters per second. This context establishes the mathematical basis for the sensor's operation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a flashlight beam. When you point it at a wall and turn it on, the light travels to the wall and then back to you. If you could measure how long it takes for the light to return, you could calculate how far away the wall is. The same principle applies here with sound instead of light, and that’s how this distance formula works.
Interacting with the Sensor
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this demo, the kernel module will interact with the sensor's GPIO pins, measure the time for the echo to return, and calculate the distance. The user can then retrieve this data from user space.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains how the kernel module is designed to interact with the ultrasonic sensor. It emphasizes the role of the General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) pins in facilitating communication between the module and the sensor. The module will control the Trigger Pin to initiate the measurement and use the Echo Pin to listen for the response, calculating the distance based on the echo time. Finally, the chunk mentions that this data will be accessible from user space, making it usable in applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cooking popcorn in a microwave. You have to set the time (similar to triggering the measurement) and then listen for the popping noise (the echo). Once popped, you can open the microwave and enjoy your snack (retrieving data from user space). The kernel module operates in a similar manner, controlling the sensor and processing the results for you to use.
Key Concepts
-
Ultrasonic Sensor: A device that uses sound waves to measure distances.
-
HC-SR04: A specific model of ultrasonic sensor used commonly in projects.
-
Trigger and Echo Pins: The two main operational pins of the HC-SR04.
-
Distance Calculation: The method to determine the distance based on echo timing.
-
Speed of Sound: An important constant for calculating distance in air.
Examples & Applications
When calculating distance, if the echo time is 20 ms, the distance can be calculated as: Distance = (20 ms * 343 m/s) / 2 = 3.43 meters.
A robot equipped with an HC-SR04 can measure the distance to nearby objects and avoid collisions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To measure distance, just take a sound, the time and speed, then it’s found!
Stories
Imagine a robot that speaks to walls. It shouts loudly and waits for a call. By timing the echo, it knows when to stop, avoiding collisions as it hops and pops!
Memory Tools
To remember the formula, think 'Time and speed, distance you need.'
Acronyms
D = T * S / 2 - Just think of D for Distance, T for Time, and S for Speed!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- HCSR04
A popular ultrasonic sensor used for measuring distances by emitting sound waves and measuring echoes.
- Trigger Pin
The pin on the HC-SR04 that sends a pulse to initiate the distance measurement.
- Echo Pin
The pin on the HC-SR04 that receives the echo signal, allowing duration measurement of the sound wave's return.
- Distance
The physical space between the sensor and an object, calculated using the time it takes for the echo to return.
- Time of Flight
The duration of time it takes for the sound pulse to travel to the object and back.
- Speed of Sound
The speed at which sound travels in air, approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
