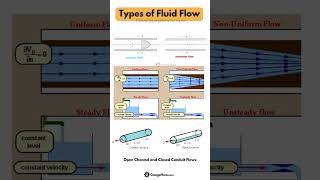
Understanding Streamlines
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Streamlines
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning everyone! Today, we’re diving into the concept of streamlines. Can anyone tell me what they understand by the term 'streamline'?

A streamline is a line that shows the direction a fluid particle will travel, right?

Exactly! Streamlines indicate the flow direction at every point in the fluid. They are crucial for visualizing fluid motion.

How do streamlines help in understanding fluid behavior?

Great question! Streamlines allow us to analyze flow patterns and identify regions of high and low velocity. They help in predicting the effects of different forces on fluid flow.

Can you give an example of where we might see these in real life?

Certainly! A common example is the flow of air around an aircraft. Streamlines help engineers design wings for optimal performance.

In summary, streamlines are essential for visualizing and analyzing fluid flows. They represent fluid motion and help reveal how changes in flow conditions affect performance.
Stream Functions and Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand streamlines, let’s talk about stream functions. Who can explain what a stream function is?

Isn't it a function that simplifies the analysis of fluid motion?

Correct! Stream functions help simplify two-dimensional flow analysis by reducing variables. The relationship between stream functions and velocities is critical.

How do you define the velocity components using stream functions?

Good point! The velocity in the x-direction (u) is the partial derivative of the stream function with respect to y, and the velocity in the y-direction (v) is the negative partial derivative with respect to x.

That sounds useful! Is there an equation we can remember for this?

Yes! You can remember: \( u = \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial y} \) and \( v = -\frac{\partial \psi}{\partial x} \). This relationship helps us analyze fluid flows effectively.

In summary, stream functions simplify the fluid flow analysis by relating velocity components, making it easier to solve complex fluid dynamics problems.
Applications in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to the application of streamlines in computational fluid dynamics, or CFD. Why do you think streamlines are important in CFD?

They help us visualize complex flow patterns, right? Like around different shapes or structures.

Exactly! For instance, in simulating airflow around an F-16 fighter jet, streamlines show where the airflow accelerates or decelerates.

What about the rotating cylinders mentioned? How do they demonstrate the use of streamlines?

Great observation! Rotating cylinders can be modeled in CFD to visualize unsteady streams of fluid using streamlines, which can reveal how air bubbles or other flow perturbations behave.

So, streamlines not only help in visualizing flows but also provide data for performance analysis?

Exactly! They allow engineers to optimize designs based on flow behaviors. Remember, understanding streamlines is fundamental to mastering fluid mechanics.

In conclusion, streamlines and stream functions are powerful tools in CFD, playing crucial roles in our understanding of complex fluid behaviors.
Real-World Examples and Problem Solving
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s put knowledge of streamlines and stream functions into practice. Can anyone provide an example of a problem we could solve using this knowledge?

What if we have fluid flowing around a building? How do we determine the streamline pattern?

Excellent example! For the flow around a building, we can visualize the streamlines using simulations, which would guide us on changes in velocity around the structure.

How can we quantify the flow rate through these streamlines?

To quantify flow rates, we can calculate the volumetric flux between two streamlines to understand the continuity and conservation of mass in fluid flow.

You mentioned using the difference in stream functions earlier. How does that help?

The difference in stream functions between points indicates the volume of fluid flowing between them – a key concept for practical fluid flow analysis.

In summary, being able to apply stream functions and streamline analysis to real-world scenarios is vital for predicting and managing fluid behaviors.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on streamlines as fundamental tools in fluid mechanics that help visualize flow patterns and velocity distributions. It highlights their application in computational fluid dynamics, particularly in complex scenarios like the flow around aircraft and rotating cylinders. The section also covers the definitions, equations, and various types of flow associated with stream functions.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Understanding Streamlines
This section delves into the fundamental concept of streamlines in fluid mechanics, critical for understanding how fluids behave in motion. Streamlines are imaginary lines representing the flow of fluid particles, indicating the direction of flow at any given point. When discussing computational fluid dynamics (CFD), the visualization of streamlines assists engineers and scientists in analyzing complex flows, such as those around aircraft (like an F-16 fighter jet) and rotating cylinders.
The section introduces stream functions, a mathematical tool that transforms complex two-dimensional flow problems into simpler forms by reducing the number of dependent variables. The relationships between velocity components and stream functions are outlined mathematically, where gradients of stream functions correspond to fluid velocities in different directions. Concepts like incompressible and compressible flow, continuity equations, and the critical nature of mass conservation are also integrated into the discussion.
Key principles include visualizing fluid motion, understanding the role of pressure gradients along streamlines, and applying Bernoulli's principle in regions of low friction. Through examples and exercises, students learn not just the theory but also practical applications of these concepts through simulations and problem-solving approaches.
Youtube Videos


![Streamline Equation: Example 1 [Fluid Mechanics #6]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/QiBL7b00Ezw/mqdefault.jpg)
![Streamline Animation [Fluid Mechanics]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/liNA14aPl2s/mqdefault.jpg)





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Streamlines
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Let us go very basic of the streamline and stream functions which is essential for undergraduate students that part what I will cover it. So today I will be very basic way we will talk about what is the stream functions okay and we will talk about that in a two-dimensional coordinate systems we can have the stream functions.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the concept of stream functions, emphasizing their importance in understanding fluid flow. Stream functions provide a way to visualize and analyze fluid motion in two-dimensional coordinate systems, allowing engineers and scientists to simplify complex fluid behaviors into manageable equations. The goal is to explore the meaning and utility of stream functions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to understand traffic flow on a busy highway. Just like you can predict how cars move based on lanes, speed limits, and intersections, stream functions help predict how fluid particles move in a given space.
Defining Stream Functions
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If I convert these two-dimensional equations to of u and v to dependent variables of scalar velocity component instead of two velocity components if I use only a single dependent variable then my problems will be sorted out.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains how stream functions simplify fluid dynamics by reducing the complexity of equations. Instead of dealing with two velocity components (u and v), we can use a single scalar stream function to describe the flow, which makes calculations much easier.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef baking a cake. Instead of dealing with separate measurements for flour, sugar, and eggs, the chef can use a recipe that gives them a combined measurement, such as '1 cup of dry ingredients.' It streamlines the process.
Physical Interpretation of Streamlines
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If you look at the streamlines, as you know it, let I take a very simple examples. There is a hump or you can say it is a buildings okay, there is a big buildings are there and you have a uniform stream flow, uniform stream flow. So if want to draw a streamlines will go like this, go like this, go like this. So these are the streamlines we can artistically draw.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk provides a visual and practical way to understand streamlines in a flow scenario. For instance, streamlines demonstrate how air would flow over a building, indicating areas of high and low velocity and helping predict how the building affects the airflow. This visualization aids engineers in designing buildings and structures with considerations of wind flow.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how wind moves around a mountain. The wind 'streamlines' can illuminate how it flows over and around the mountain, showing areas of turbulence and calmness. Understanding streamlines here helps meteorologists predict weather patterns better.
Mass Conservation Equation and Bernoulli's Principle
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So I can have a basic mass conservation equations and Bernoulli's equations to solve the problems. That is why the Bernoulli's equations is very famous because the regions where you have a very very less frictional force components.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk delves into the principles of mass conservation and Bernoulli's equation, highlighting their relevance to fluid mechanics. These equations describe how mass is conserved in a flowing fluid and how fluid pressure varies with speed, allowing for various applications in engineering design. Understanding these principles helps to predict fluid behavior in different scenarios.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a water slide. As the water flows down the slide, it speeds up (Bernoulli's principle) while also conserving the amount of water that moves downward (mass conservation). This understanding is key in designing efficient water parks!
Applications of Stream Functions
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So, we can also solve some examples. That is what is today plans after demonstrating you the CFD software, how it is showing the streamlines for a rotating cylinders, two rotating cylinders and F-16 flight airplane.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses the practical applications of stream functions in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), specifically in simulations involving complex flow around objects like rotating cylinders and aircraft. CFD tools allow for visualization and analysis of fluid flows, making it easier to solve real-world engineering problems.
Examples & Analogies
It’s like using a flight simulator to see how an airplane can maneuver through the air before it actually takes off. Engineers employ CFD simulations to visualize airflow patterns, which helps in designing better, safer aircraft.
Key Concepts
-
Streamlines: Lines indicating the direction of fluid flow.
-
Stream Function: A tool to simplify fluid dynamics equations by reducing dependent variables.
-
Velocity Components: Determined through the gradients of stream functions.
-
Continuity Equation: The principle governing mass conservation in fluid dynamics.
-
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): Numerical simulations to understand fluid flow behavior.
Examples & Applications
The flow of air around an airplane wing is visualized using streamlines to optimize performance.
In CFD simulations, the patterns of streamlines help engineers analyze complex flow behaviors around structures.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Streamlines help us see, how fluids like to be. Follow the lines, in flow they confine, gaining insights divine!
Stories
Imagine a river with many branches; each branch represents a streamline, guiding the flow of water. The water flows smoothly, illustrating the importance of streamlines in understanding movement.
Memory Tools
Remember: 'SFP' - Stream Function simplifies Flow analysis by defining relationships between velocity and flow direction.
Acronyms
SFM - Stream Functions Matter, because they simplify complex fluid dynamics!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Streamlines
Imaginary lines that represent the flow direction of fluid particles in a fluid flow.
- Stream Function
A mathematical function that simplifies fluid flow analysis by reducing the number of variables in two-dimensional flow.
- Velocity
The speed and direction of fluid flow at a given point.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
A field of study that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve fluid flow problems.
- Mass Conservation
The principle that mass cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
