Proctor’s needle consists of a point, attached to graduated needle shank and spring loaded plunger.
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Proctor’s Needle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today we are discussing the Proctor’s needle. Can anyone tell me what the Proctor’s needle is used for?

Is it used to measure soil properties?

Exactly! It's primarily used for rapid determination of the water content of soil in the field. This is important for compaction. Can anyone think of why knowing water content would be crucial during compaction?

If the moisture content is too high or too low, it could affect how well the soil compacts.

Great point! When we compact soil, we want to do it at what's called optimum moisture content. What might be a practical use of the needle?

It could help ensure that construction sites are properly compacted before building.

Yes, that's correct! Maintaining proper compaction ensures the stability of structures. Don’t forget that the Proctor’s needle must be calibrated for specific soil types before use.
Calibration of Proctor’s Needle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into how we calibrate the needle. Why do you think calibrating it is essential?

If we don't calibrate it, we might get incorrect water content readings.

Exactly! Calibration establishes a reference curve for specific soil types, making field measurements reliable. What do you think happens if we use it without calibration?

We could end up either over- or under-compacting the soil.

That's right, which could compromise the integrity of the construction. Remember, each different soil type may require a unique calibration curve!
Variations of Proctor’s Needle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, who can tell me about the variations of the Proctor’s needle?

There are different cross-sectional shapes for the needles, right?

Correct! Each shape is designed to work effectively with various soil types. Can anyone see how this might be beneficial?

Different shapes might penetrate soil differently, giving us a more accurate measure.

Exactly! This adaptability increases the accuracy and reliability of our moisture measurements in the field.
Importance of Proctor’s Needle in Construction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's talk about the role of Proctor’s needle in the construction process. Why is it so vital?

It helps ensure the soil is properly compacted, which is essential for building stability.

Exactly! Proper compaction mitigates risks of settling and structural failure. What could happen if we ignore moisture content during compaction?

The building could experience foundation issues?

Exactly! Understanding the moisture content allows us to prevent such problems, ensuring safety and longevity in construction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Proctor’s needle facilitates quick assessments of water content in soil during construction and compaction processes. This device, calibrated for specific soil types, ensures that compaction is executed efficiently, contributing to optimal construction outcomes.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Proctor’s Needle Overview
Proctor’s needle is a vital instrument utilized for the rapid measurement of water content in soil, which is crucial when conducting field tests for compaction.
- Construction: The tool features a pointed needle connected to a graduated shank and incorporates a spring-loaded plunger mechanism.
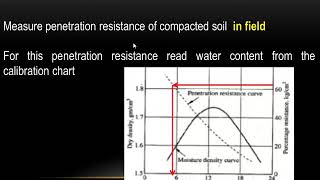
- Calibration: Prior to its field application, the Proctor’s needle must be calibrated based on the specific soil characteristics in a laboratory environment. The resultant calibration curve is essential for accurately determining the placement water content in situ.
- Needle Variants: Different cross-sectional shapes of the needle point are available to cater to varying soil types and conditions.
Significance: Efficient use of the Proctor’s needle enhances the ability to monitor and control soil compaction processes, thereby influencing overall project success and integrity.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Purpose of Proctor's Needle
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Used for rapid determination of water content of soil in field.
Detailed Explanation
Proctor's needle is a specialized tool designed to quickly measure the water content in soil samples on-site. This rapid determination is crucial because the moisture level in soil can significantly affect its compaction and engineering properties.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're baking bread. If you add too much or too little water, the dough won't rise properly. Similarly, soil needs the right moisture level for optimal compaction during construction projects.
Alternative to Proctor's Needle
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Rapid moisture meter is used as an alternative.
Detailed Explanation
In addition to the Proctor's needle, there are rapid moisture meters available that can also quickly gauge the water content in soil. These alternatives might use different technologies but aim to provide similarly quick and effective moisture readings.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the rapid moisture meter like using a digital thermometer instead of a traditional one. Both give you the same information, but the digital option is often faster and easier to read.
Components of Proctor's Needle
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Proctor’s needle consists of a point, attached to graduated needle shank and spring loaded plunger.
Detailed Explanation
The Proctor's needle is constructed with a sharp point that penetrates the soil, a graduated shank to measure the depth of penetration, and a spring-loaded plunger that helps apply the necessary force for consistent measurements. This design allows for precise reading of soil conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a syringe used for injections. Just like the syringe has a needle to penetrate the skin and a plunger to push the medicine out, the Proctor's needle uses its parts to accurately assess soil moisture.
Variability in Needle Points
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Varying cross sections of needle points are available.
Detailed Explanation
Proctor's needles can come with different needle points that have varying cross-sections, which can influence how easily they penetrate different types of soil. The choice of needle point helps in obtaining accurate measurements based on specific soil characteristics.
Examples & Analogies
This is similar to using different types of screws for different materials. Just as a wood screw is designed to work well with wood, a particular needle point is tailored to be most effective for certain soil types.
Reading Penetration Force
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- The penetration force is read on stem at top.
Detailed Explanation
When using the Proctor's needle, the amount of force required to penetrate the soil is measured at the top of the needle shank. This reading helps determine the soil's water content based on pre-established calibration curves.
Examples & Analogies
Think about measuring your own weight with a scale. Just like you observe the reading on the scale to understand how much you weigh, the operator reads the force reading on the needle to assess soil moisture.
Calibration Process
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- To use the needle in field Calibration in done on the specific soil in lab and calibration curve is prepared and the curve is used in the field to determine placement water content.
Detailed Explanation
Before deploying the Proctor's needle in the field, it needs to be calibrated using the specific soil type being tested in a laboratory environment. This calibration involves creating a curve that links needle force readings to accurate moisture content values, which can then be referenced during field measurements.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine calibrating a set of scales to measure ingredients accurately when cooking. Once you know how much a cup of flour weighs on your scale, you can use that information repeatedly to ensure your recipes turn out perfectly every time.
Key Concepts
-
Proctor’s Needle: A tool for measuring soil moisture quickly in the field.
-
Calibration: Essential for accurate readings before field use.
-
Optimum Moisture Content: The ideal water content for effective soil compaction.
Examples & Applications
Using the Proctor’s needle on a construction site to determine moisture levels before beginning backfill operations.
Calibration of the needle in a laboratory setting with known soil samples to create a reference chart for field use.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Proctor’s needle sharp and bright, tells the soil’s moisture right.
Stories
Imagine a construction worker named Sam who always checks moisture first before compacting. He uses the Proctor's needle – it's his trusty tool that never fails.
Memory Tools
MOP - Measure, Optimize, and Perform. Remember to measure moisture, optimize compaction, and perform construction efficiently.
Acronyms
PWC - Proctor's Water Content. Think of this when using the Proctor’s needle.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Proctor’s Needle
A tool used for rapid determination of soil water content in the field.
- Calibration
The process of adjusting the Proctor’s needle to produce accurate measurements for specific soil types.
- Optimum Moisture Content (OMC)
The water content at which soil compacts most efficiently.
- Penetration Force
The force applied to the Proctor’s needle to measure soil resistance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
