Regional DAD Studies in India
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to DAD Studies in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss the role of Depth-Area-Duration studies in India. Can anyone tell me why these studies are conducted?

I think they help in managing water resources.

Exactly! These studies are crucial for managing water resources effectively and understanding rainfall distribution. What regions do you think might be important for these studies?

Maybe the flood-prone areas in the North-East?

Yes, the North-East India region is indeed vital due to its short-duration, high-intensity storms. Great point! Let's remember the acronym 'IMD' or 'Interactive Meteorological Data' to recall that the India Meteorological Department carries out these studies.

What about other regions in India?

Good question! Central India and the Western Ghats are also key regions for these studies. They help in analyzing storm characteristics and enhancing flood forecasting.

To summarize, DAD studies in India focus on crucial regions that face different storm patterns to manage water resources effectively.
Regions Analyzed in DAD Studies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve deeper into specific regions studied in these DAD analyses. Can someone name a few?

How about the Western Ghats?

Correct! The Western Ghats are significant due to their unique topographical challenges. What do you think studying this region could tell us?

It might show us how mountains affect rainfall distribution?

Exactly! The orographic effect can create varied rainfall patterns. Now, what about the Mahanadi Basin in Central India?

It could provide insights into how to manage dam inflows.

You've got it! Managing inflows is crucial for dam safety. Remember the mnemonic 'MHWN' or 'Maha Western North' to help recall Mahanadi, Western Ghats, and North-East India as vital study areas.

In summary, each region has its unique characteristics which are critical for understanding rainfall patterns and their impacts on water resource management.
Applications of DAD Studies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's discuss the applications of these DAD studies. How do you think they impact engineering?

They would help engineers design better drainage systems.

Absolutely! They inform the design of dams, urban infrastructures, and flood forecasting systems. Does anyone know why flood forecasting is important?

To prevent flooding and protect lives and property.

Exactly! Flood forecasting based on reliable DAD data plays a significant role in disaster management. To remember the importance, think of the acronym 'DURFL' for 'Design, Urban drainage, Risk management, Flood forecasting, and Lifesaving.'

In summary, DAD studies not only contribute to engineering but also enhance our ability to predict and manage flood risks effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
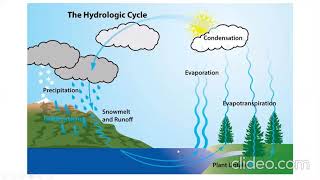
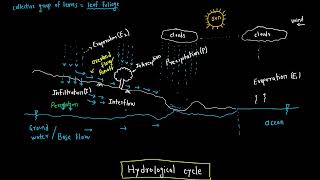
The section highlights essential DAD studies performed by India Meteorological Department (IMD) and Central Water Commission (CWC) across different meteorological subdivisions in India, such as Central India, the Western Ghats, and North-East India. These studies play a vital role in defining design storm characteristics pertinent to dam safety, urban drainage, and flood forecasting.
Detailed
Regional DAD Studies in India
In India, significant Depth-Area-Duration (DAD) analyses have been carried out by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the Central Water Commission (CWC) focusing on various meteorological subdivisions. These studies are crucial for understanding rainfall characteristics and aiding in the design of effective water resource management systems. The primary regions analyzed include:
- Central India: This region includes areas like the Mahanadi Basin where rainfall patterns are assessed to optimize stormwater management.
- Western Ghats: A significant geographical area where the effects of topography on rainfall distribution are studied.
- North-East India: Known for high-intensity, short-duration storms, particularly in Assam and Meghalaya, these regions require specific analyses due to extreme weather events.
- Peninsular India: Characterized by cyclonic rainfall that broadly covers areas, necessitating comprehensive DAD studies.
These investigations contribute valuable insights into designing storm characteristics essential for dam safety, urban drainage systems, and enhancing flood forecasting capabilities.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Regional DAD Studies
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some DAD analyses have been performed in India by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and Central Water Commission (CWC) for different meteorological subdivisions, such as:
Detailed Explanation
This introduces the concept that certain organizations, like the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the Central Water Commission (CWC), have performed studies focusing on Depth-Area-Duration (DAD) relationships in India. These studies aim to assess rainfall patterns and their impact on various geographical and climatic regions in the country. The studies are categorized based on different meteorological subdivisions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of scientists conducting research on how rainfall affects different areas of a country, similar to how a meteorologist might study weather variations in various regions, such as mountains versus flat plains.
Specific Regions Studied
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Central India (e.g., Mahanadi Basin)
- Western Ghats
- North-East India (Assam, Meghalaya – high intensity, short duration storms)
- Peninsular India (cyclonic rainfall, broad coverage)
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, specific regions of India where DAD studies have been conducted are highlighted. These include Central India, known for areas like the Mahanadi Basin, the Western Ghats, and the North-East region such as Assam and Meghalaya, which experience intense and brief storms. Additionally, Peninsular India is mentioned as a region affected by cyclonic rainfall that has a broader coverage. Each area’s unique rainfall characteristics influence the DAD analyses.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these regions like different ecosystems: a rainforest may experience short, heavy rains, while a plains area might have prolonged, gentle showers. Each ecosystem responds differently to rainfall, just like the various regions in India.
Purpose of DAD Studies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These studies help define design storm characteristics for dam safety, urban drainage, and flood forecasting.
Detailed Explanation
The purpose of conducting DAD studies in these regions is to gather data and insights that can be used for critical infrastructure planning and safety. The insights from these studies help in understanding how much rainfall can be expected in different areas over various durations. This information is crucial for designing safe dams, creating efficient urban drainage systems to manage stormwater, and accurately forecasting floods to protect communities.
Examples & Analogies
Just as city planners need to know the average expected traffic in order to design safe and adequate roads, engineers and hydrologists use DAD studies to predict rainfall and design structures that can handle potential floods, ensuring safety and functionality.
Key Concepts
-
IMD: The India Meteorological Department conducts crucial DAD studies across different regions in India.
-
Regional Analysis: Key areas studied include Central India, Western Ghats, North-East India, and Peninsular India.
-
Orographic Effects: Topography affects rainfall distribution, especially in areas like the Western Ghats.
Examples & Applications
The Mahanadi Basin is vital for understanding stormwater management in Central India.
In North-East India, short-duration storms can lead to significant floods, thus necessitating specific DAD analyses.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In India, rainfall's not the same, DAD studies help us name the game.
Stories
Once in India, scientists explored rainfall through depths, areas, and durations—gaining knowledge to protect lives.
Memory Tools
Remember 'MHWN' for Mahanadi, Himalayas, Western Ghats, and North-East, essential spots for DAD studies.
Acronyms
DURFL - Design, Urban drainage, Risk management, Flood forecasting, Lifesaving.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- DepthAreaDuration Relationship
A relationship that quantifies the relationship between precipitation depth, area over which it falls, and storm duration.
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
The principal agency responsible for weather forecasting and meteorological observations in India.
- Central Water Commission (CWC)
A governmental agency that oversees water resource management in India.
- Orographic Effect
The impact of topography on climate, particularly precipitation distribution.
- Hydrological Models
Computer simulations that model the movement, distribution, and quality of water in the environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
