Challenges and Solutions - 5.4.2
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Power Density Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the challenges posed by power density in data centers. Can anyone explain what we mean by 'power density'?

I think it’s the amount of power generated in a given area?

Correct! High power density means more heat is generated per unit area. This can lead to overheating if not managed properly. What are some solutions we have?

Liquid cooling is one of them, right?

Exactly! Liquid cooling is effective because it absorbs heat better than air. It’s essential to handle high heat flux situations. What do you think is a critical advantage of using liquid cooling?

Maybe it minimizes the risk of thermal failure?

Yes! Along with that, it’s more efficient in removing heat. Let’s summarize: high power density increases cooling demands and liquid cooling effectively addresses these needs.
Space Efficiency in Cooling Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about space efficiency. Why is space a concern for cooling systems in data centers?

Because data centers are becoming more compact, right?

Exactly! Traditional cooling systems, like air cooling, require significant space for ducts and fans. How does immersion cooling help solve this problem?

It allows for a more compact arrangement by using the same space for cooling and housing components?

Correct! This space-saving strategy enhances efficiency. Let’s recap the importance of optimizing space for advanced cooling solutions.
Overview of Cooling Strategies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s review the cooling strategies we talked about. Can you name them?

We discussed liquid cooling and immersion cooling.

Correct! What makes immersion cooling unique?

It uses dielectric fluids to absorb heat directly from the components.

Exactly! Both methods are crucial for efficient thermal management as workloads increase. To summarize, advanced cooling methods are essential for maintaining system reliability and performance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
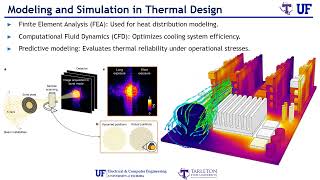
The section discusses the significant challenges faced in managing heat dissipation in data centers and high-performance computing systems. Key solutions such as liquid and immersion cooling are explored, emphasizing their effectiveness in handling increased power density and space efficiency.
Detailed
Challenges and Solutions
In this section, we analyze the thermal management challenges faced in data centers and high-performance computing (HPC) environments. As the demand for processing power increases, the heat generated by servers and processors also rises significantly, presenting considerable challenges in maintaining optimal operating conditions. Key issues include:
- Power Density: Modern processors and GPUs generate high heat flux, necessitating efficient cooling solutions to prevent overheating.
- Space Efficiency: Traditional air cooling methods require extensive space, which can be a limiting factor in densely packed server environments.
To tackle these challenges, the section outlines innovative cooling strategies:
- Liquid Cooling: Particularly effective for high power density applications, liquid cooling involves circulating a coolant through systems to absorb heat more effectively. This method significantly enhances thermal management performance compared to air cooling.
- Immersion Cooling: This advanced method submerges servers in dielectric fluids, allowing for direct heat absorption and offering a more compact layout.
The implementation of these solutions not only prevents thermal failure but also enhances energy efficiency, ensuring that data centers can meet the demands of modern workloads while maintaining optimal performance.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Power Density Challenge
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Power Density: With increasingly powerful processors and GPUs, the heat generated per unit area in data centers continues to rise. Liquid cooling solutions, particularly immersion cooling, are designed to address the high heat flux generated by modern chips.
Detailed Explanation
As processors become more powerful, they generate more heat in a smaller area. This increase in power density means that traditional cooling methods, like air cooling, may not be sufficient. To combat this, newer liquid cooling solutions, especially immersion cooling, have emerged. In immersion cooling, components are submerged in a cooling liquid that efficiently absorbs and dissipates heat, ensuring that temperatures remain within safe limits.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a sponge in a sink filled with water. The sponge absorbs water (heat), and the liquid helps to keep the sponge from getting too soggy (overheated). Just as a sponge can manage excess water more effectively when fully immersed, components can manage heat more effectively in liquid environments.
Space Efficiency Challenge
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Space Efficiency: Traditional air cooling methods require large physical spaces to house fans, ducts, and heat exchangers. Immersion cooling allows for more compact layouts and greater cooling efficiency by using the same space for both heat removal and component housing.
Detailed Explanation
Traditional cooling systems using fans and ducts take up considerable space, making it challenging to fit all the necessary equipment into cramped data center environments. In contrast, immersion cooling systems are more space-efficient because they eliminate the need for bulky air flow structures. By integrating cooling directly into the layout of components, data centers can maximize their space while maintaining effective heat management.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to cool down a room by placing a giant fan in the middle; it takes up a lot of space and may block pathways. Now, consider a small, efficient radiator that fits neatly along the wall providing the same level of cooling without taking up extra room. That's how immersion cooling systems work in comparison to traditional methods.
Key Concepts
-
Power Density: The heat generated per unit area from processors.
-
Liquid Cooling: A cooling method using liquid for efficient heat dissipation.
-
Immersion Cooling: A technique that involves submerging components in dielectric fluids.
Examples & Applications
Data centers using both air cooling and liquid cooling to manage heat from densely packed processors.
The use of immersion cooling in servers to achieve better space efficiency and cooling performance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a data center, heat's a real threat, liquid's the cooler you won't forget!
Stories
Imagine a crowded server room—it's hot and frantic. Then, the liquid cooling system arrives like a hero, bringing a chill and keeping everyone cool under pressure!
Memory Tools
Remember 'LIM': Liquid cooling, Immersion cooling, Manage heat effectively!
Acronyms
P.E.A.C.E
Power
Efficiency
Air (less)
Compact (layout)
Effective cooling.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Power Density
Refers to the amount of power generated in a specific area, affecting heat generation.
- Liquid Cooling
A thermal management technique that uses a liquid coolant to absorb and transfer heat away from components.
- Immersion Cooling
A cooling method where components are submerged in dielectric fluids that absorb heat.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
