Thermal Management Strategy - 5.4.1
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thermal Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss thermal management strategies, specifically in data centers and high-performance computing systems. Can anyone tell me why thermal management is crucial in these environments?

I think it’s because the processors generate a lot of heat!

Exactly! High-performance processors generate substantial heat that can affect performance and reliability if not managed properly. Remember this: Good thermal management equals better performance. Let's explore how this is achieved.

What methods do data centers use for cooling?

Great question! Data centers use both air and liquid cooling systems. Can anyone guess which is more efficient?

I think liquid cooling would be more efficient, right?

Correct! Liquid cooling is particularly effective for high-performance systems. Now, let’s summarize: thermal management helps processors run reliably by managing heat through air and liquid cooling.
Air Cooling Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s begin by discussing air cooling. Air cooling typically involves large fans circulating air. Who can tell me what components this airflow cools?

It cools the heat sinks attached to the processors.

Exactly! The heat sinks are critical as they help dissipate heat from the processors into the air. Now, what is a common challenge with air cooling?

I think it needs a lot of space for all the fans and ducts.

Precisely! Space efficiency is an issue. To overcome this, many data centers are adopting liquid cooling solutions. Can anyone explain how these systems work?

I think they involve liquid that absorbs heat from the processors?

That's right! Liquid cooling systems use a coolant that circulates to absorb heat. Let’s summarize: Air cooling is effective but requires more space, while liquid cooling offers enhanced efficiency.
Liquid Cooling Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's focus on liquid cooling, particularly immersion cooling. Who can tell me what immersion cooling involves?

It’s when servers are immersed in liquids, right?

Yes! This method is extremely efficient at heat absorption. Why do you think this is beneficial for high-performance systems?

Because it can handle higher power densities without overheating?

Correct! Immersion cooling also allows for space efficiency, reducing the area needed for cooling setups. Let's wrap up: Liquid cooling is more efficient and reduces space compared to traditional air cooling.
Challenges in Thermal Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we look at the challenges in thermal management, power density is significant. Can anyone explain why higher power density poses a challenge?

Because it generates more heat in a smaller area!

Exactly! This makes cooling even more critical. So, how do we address these increasing power densities?

By using more efficient liquid cooling systems?

That’s right! Advanced cooling methods like immersion cooling help manage this effectively. Summarizing today’s discussion: Power density and space efficiency are challenges, but we can overcome them with innovative thermal management strategies.
Conclusion and Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we conclude our sessions on thermal management, let’s recap what we learned. What are the two primary cooling methods in data centers?

Air cooling and liquid cooling!

Correct! And why is liquid cooling often favored?

It’s more efficient and requires less space!

Exactly! Remember, efficient thermal management ensures the performance and reliability of high-performance processors. Great job today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
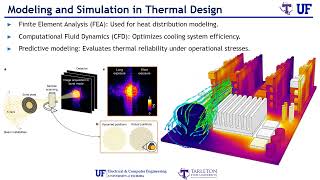
The section outlines the thermal management strategies utilized in data centers and HPC systems. It emphasizes the integration of air and liquid cooling systems to combat challenges such as power density and spatial constraints, ensuring efficient operation and reliability of high-performance processors.
Detailed
Thermal Management Strategy
This section focuses on the thermal management strategies employed in data centers and high-performance computing (HPC) systems, where high-performance processors generate significant heat. Effective thermal management is crucial to ensure optimal operation, reliability, and performance of these systems.
Key Strategies:
- Air Cooling: The conventional method involves the use of forced air cooling systems, where large fans circulate air to pass over heat sinks attached to individual processors, facilitating heat dissipation.
- Liquid Cooling: For more efficient cooling, particularly in high-performance environments, liquid cooling methods such as immersion cooling are implemented. In immersion cooling, servers or chips are immersed in dielectric fluids to extract heat directly from components.
Challenges Addressed:
- Power Density: The increasing power density of modern processors necessitates advanced cooling solutions to handle the heat flux generated.
- Space Efficiency: Traditional cooling systems require significant space, while liquid cooling solutions, especially immersion cooling, can reduce the required physical footprint.
Outcome:
The combined approach of utilizing both air cooling and liquid cooling systems allows data centers to effectively manage heat, ensuring that processors operate within safe temperature limits, thereby maximizing performance and efficiency.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Thermal Management in Data Centers
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Data centers employ both air cooling and liquid cooling systems to manage the heat generated by the numerous processors:
Detailed Explanation
In data centers, managing heat is crucial due to the large number of processors that generate heat during their operation. To keep these systems cool, two primary methods are used: air cooling and liquid cooling. Air cooling involves using large fans to circulate air, while liquid cooling utilizes coolant fluids to absorb and carry heat away from components.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a busy kitchen where multiple burners are on, creating lots of heat. Just like a chef needs fans to circulate air or a cooling system to maintain a comfortable temperature, data centers need to prevent their processors from overheating using these cooling techniques.
Air Cooling Method
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Air Cooling: The most common method is forced air cooling, where large fans circulate air through the racks of servers, passing over heat sinks attached to each processor.
Detailed Explanation
The air cooling method relies on large fans that push air over heat sinks attached to processors. Heat sinks are designed to absorb heat from the processors and then increase the surface area for the air to flow over, effectively dissipating the heat into the surrounding air. This way, the processors can stay at optimal temperatures and perform efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine blowing on hot soup to cool it down. Just like your breath helps lower the soup temperature, the fans in a data center blow air over the heated processors to keep them cool.
Liquid Cooling Method
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Liquid Cooling (Immersion Cooling): For high-performance systems, immersion cooling is increasingly used. In this method, servers or chips are immersed in dielectric fluids, which absorb heat directly from the components. The heated fluid is then pumped through heat exchangers to dissipate the heat.
Detailed Explanation
Liquid cooling, especially immersion cooling, is a method where servers or chips are placed directly into special liquids that can absorb heat. As the components heat up, the liquid transfers this heat away efficiently. The heated liquid is moderated and sent to a heat exchanger, where the heat is expelled, allowing for continued cooling. This method provides effective heat management, especially in high-performance environments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a hot bath where immersing yourself in water can help regulate your body temperature. Similarly, immersion cooling uses fluids to manage heat in electronic components, ensuring they cool down effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Thermal Management: Involves techniques to manage heat in electronic systems for optimal performance.
-
Air Cooling: A common method employed using fans for circulating air over components.
-
Liquid Cooling: More efficient cooling solution where liquids absorb and carry heat away.
-
Immersion Cooling: Innovative method of cooling by submerging components in dielectric fluids.
-
Power Density: A crucial consideration as it relates to the heat generated per unit area.
Examples & Applications
Data centers use air cooling systems with large fans circulating cool air around servers.
High-performance computing systems adopt liquid cooling solutions to efficiently manage heat in densely packed environments.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When processors heat up, cooling is the key, air or liquid, that's how it should be.
Stories
Imagine two friends: Air Cooling and Liquid Cooling. Air is always blowing, trying to cool as best as it can. Liquid, on the other hand, immerses electronics to keep them fresh and efficient. Together, they conquer heat!
Memory Tools
Remember A-L-I for cooling: A stands for Air, L for Liquid, and I for Immersion.
Acronyms
Use A.C.E. - Air Cooling Efficiently, to remember air cooling's efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thermal Management
The practice of managing heat generated by electronic systems to ensure optimal operating conditions.
- Air Cooling
A method of heat dissipation using fans to circulate air over heat sinks.
- Liquid Cooling
Cooling technique where liquids absorb heat from components and carry it away to heat exchangers.
- Immersion Cooling
A cooling technique wherein electronic components are submerged in dielectric fluids to enhance heat dispersion.
- Power Density
The amount of power consumed per unit area, which can affect heat generation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
