Capitalist Economy
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Capitalist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the capitalist economy. Can anyone tell me what a capitalist economy is?

Is it where everything is owned by private companies?

Great start! Yes, a capitalist economy is characterized by private ownership of the means of production. This means individuals or corporations own resources and make economic decisions.

What’s the main goal in a capitalist economy?

The main goal is profit! This profit motive is a driving force in such economies, encouraging efficiency and innovation. Remember: P.E.P. — Profit, Efficiency, and Profitability.

What about government involvement?

In a capitalist economy, government involvement is minimal. The market largely dictates prices based on supply and demand. This is important for free market dynamics.

Can you give us examples of countries with capitalist economies?

Sure! Examples include the United States, Australia, and Japan. These nations represent the diverse applications of capitalist principles.

To summarize, a capitalist economy allows private ownership, prioritizes profit, maintains minimal government interference, and lets market forces determine prices. Keep this in mind!
Main Features of a Capitalist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into the main features of a capitalist economy. Who can name one?

Private ownership!

Correct! The first feature we should highlight is private ownership of property and resources. In capitalism, individuals own means of production, unlike socialist economies.

What does 'freedom of choice' mean?

Freedom of choice allows consumers to select what they wish to buy and entrepreneurs to decide what to sell. This drives competition and diversity in the market. It’s vital — think of it as choosing your favorite ice cream flavor!

Is competition also a part of it?

Absolutely! Competition ensures that businesses strive to improve, leading to better products and prices, ultimately benefiting consumers.

And government interference is minimal, right?

Yes! Minimal government interference means that businesses operate freely with few regulations. Just remember: G.M.P. — Government Minimal Presence!

In summary, a capitalist economy features private ownership, freedom of choice, competition, profit motives, and minimal government interference, all essential for market dynamics.
Market Forces in a Capitalist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss how prices are determined in a capitalist economy. Can anyone tell me how this works?

Is it based on how much people want something?

Exactly! Prices are determined by supply and demand. When demand exceeds supply, prices typically rise. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices generally fall.

So, it's all about balancing, right?

Yep! This balance is what drives the market. It’s an essential component of capitalism, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently.

What happens if a company sets prices too high?

Good question! If prices are set too high and consumers don’t buy, companies may have to lower their prices to clear stock. This self-regulating feature is crucial in a capitalist system.

So, demand and supply create a cycle?

Precisely! It's a continuous cycle where the market adapts. Remember the cycle as S.D.S. — Supply, Demand, Supply!

To summarize, prices are determined by market forces of supply and demand, allowing a capitalist economy to thrive on competition and efficiency.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
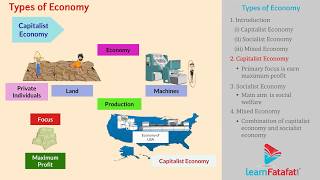
In a capitalist economy, the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals, with key features including private property, profit motivation, and minimal government involvement, as seen in countries like the United States, Australia, and Japan.
Detailed
Capitalist Economy
A capitalist economy is defined as an economic system where the means of production are privately owned and controlled by individuals or corporations. The essential characteristics of this economic system include:
- Private Ownership: Individuals and businesses own property and resources, which allows them to make decisions based on personal or corporate interest.
- Freedom of Choice: Consumers have the freedom to choose what to purchase, and entrepreneurs can decide what to produce.
- Profit Motive: The primary goal of businesses in a capitalist economy is to generate profit, motivating innovation and efficiency.
- Minimal Government Interference: The government plays a limited role in the economic activities of individuals, primarily to maintain order and protect property rights rather than control the economy.
- Market-Determined Prices: Prices for goods and services are established through the forces of supply and demand, allowing markets to self-regulate.
Countries such as the United States, Australia, and Japan exemplify capitalist economies, showcasing varying degrees of government involvement while supporting free-market principles. This system aims to foster competition and economic growth, driving innovations that enhance living standards.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Capitalist Economy
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An economy where the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals.
Detailed Explanation
A capitalist economy is defined by the ownership of production resources—such as factories, land, and capital—by private individuals or businesses. Unlike in government-controlled systems, decisions about production and distribution of goods and services are made by individuals rather than by the state. This allows people to make choices based on their interests, potentially leading to innovation and competition.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a local bakery. The owner, a private individual, decides the types of bread to bake based on what customers like and what they are willing to pay. This decision is driven by personal insight and demand, not government mandates.
Main Features of Capitalist Economy
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Private ownership of property and resources
● Freedom of choice and enterprise
● Profit motive is the driving force
● Minimal government interference
● Prices determined by market forces (demand and supply)
Detailed Explanation
There are several key features of a capitalist economy. First, property and resources are privately owned, meaning individuals have the right to buy, sell, and manage them as they see fit. Second, individuals have the freedom to make choices about their work and investments, fostering entrepreneurship. Third, the profit motive drives individuals and companies to innovate and improve efficiency, as they aim to maximize their earnings. Additionally, government interference is minimal, which allows market forces to dictate prices based on demand and supply—if a product is in high demand, its price will rise, encouraging more production.
Examples & Analogies
Think of technology companies like Apple or Samsung. They decide what products to develop based on consumer demand, seeking to maximize profits, and they do so with limited government control over their business decisions.
Examples of Capitalist Economies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Examples: United States, Australia, Japan
Detailed Explanation
Several countries operate under a capitalist economic system. The United States is often viewed as the archetypal capitalist country due to its strong emphasis on free markets and minimal government intervention. Australia and Japan also highlight the principles of capitalism through their systems, with private ownership of businesses being central to their economies. These countries showcase a wide range of products and services that are developed based on market demands.
Examples & Analogies
When you think about shopping in the United States, you'll find numerous brands and products competing for your attention. This competition—driven by the need to attract consumers—efficiently meets the diverse needs of the population.
Key Concepts
-
Private Ownership: Individuals or corporations own the means of production.
-
Profit Motive: Businesses operate primarily to generate profit.
-
Minimal Government Interference: Limited regulatory role of government in economic activities.
-
Market Forces: Prices are determined by the dynamics of supply and demand.
Examples & Applications
The United States operates a capitalist economy where businesses set prices based on competition and consumer demand.
In Japan, the government supports private enterprises while maintaining minimal regulations, exemplifying a capitalist approach.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a land where owners thrive, Capitalist dreams come alive. Freedom of choice, profit in sight, Market forces make it all right.
Stories
Once in a bustling town, there were shops run by folks named Joe, Sally, and Fred. Each sold their unique treats, and prices changed with what people wanted. This was a world of choices, driven by the wish to earn profits.
Memory Tools
P.E.G.S. — Profit, Efficiency, Government Minimal, Supply & Demand make up capital's grand plan.
Acronyms
C.P.M.S. — Capitalism, Private ownership, Market Forces, Supply & Demand.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals.
- Private Ownership
Ownership of resources and production by private individuals or businesses.
- Profit Motive
The intention to gain financial profit as the primary goal of business activities.
- Market Forces
The supply and demand dynamics that determine the price of goods and services.
- Minimal Government Interference
Limited involvement of the government in regulating economic activities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
