Examples - 2.3.3
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Capitalist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with the capitalist economy. Can anyone tell me what a capitalist economy is?

Is it where private individuals own the means of production?

Exactly! In a capitalist economy, the means of production and resources are privately owned. What do you think is the main driving force behind this system?

The profit motive?

That's correct! The profit motive drives innovation and efficiency. A quick way to remember this could be 'P for Profit, O for Ownership'—this emphasizes the roles of profit and ownership in capitalism.

Can you give us examples of capitalist economies?

Sure! Examples include the United States, Australia, and Japan. Each of these countries exemplifies the principles of a capitalist economy. Can anyone share what they think could be a disadvantage of capitalism?

Maybe income inequality?

Yes! That's a significant point, as wealth can become concentrated in the hands of a few.
Exploring Socialist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to the socialist economy. Who can explain what this economy entails?

It's where the government owns and controls the means of production, right?

Correct! In socialism, the government plays a central role. What’s the main goal of this type of economy?

Ensuring the welfare of society rather than making profits?

Exactly! Imagine the acronym 'Welfare First', which summarizes socialism's focus on societal welfare. Can you name some examples of socialist economies?

North Korea and Cuba?

That's right! Both are known for their government-controlled economies. But, what challenges do you think these systems face?

Lack of competition?

Absolutely! This can lead to inefficiencies in production.
Mixed Economy Insights
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the mixed economy next. Can someone explain what a mixed economy is?

It's a combination of both private and public sector?

Yes! It mixes ownership to leverage the advantages of both systems. How does the government interact in a mixed economy?

It regulates and controls key industries?

Exactly! This regulation allows for both economic growth and social welfare. What countries can you think of that follow this mixed model?

India and the UK?

Correct! Both utilize a mixed economy to balance efficiency and equitable distribution of resources. Would anyone like to share potential pros or cons of this system?

It might promote equality but could also reduce efficiency?

Definitely! Balancing those aspects is key in mixed economies.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Through specific examples, this section explores how capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies function in practice. These examples provide a clearer understanding of the theoretical concepts previously discussed in the chapter.
Detailed
In this section, we delve into real-world instances of capitalism, socialism, and mixed economies to illustrate these economic systems' characteristics and functionalities. Examples such as the United States, known for its capitalist economy, highlight features like private ownership and market-driven prices. Socialist economies like the former Soviet Union showcase the government's control over production and the absence of a profit motive, emphasizing public welfare. Additionally, mixed economies like India represent a blend of public and private sectors, demonstrating how different economic models coexist in practice. These examples serve to reinforce the theoretical understanding of each economy type and their implications for societal welfare.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
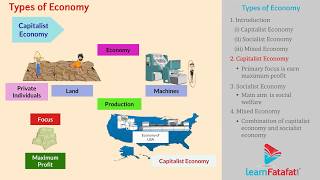
Definition of a Capitalist Economy
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An economy where the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals.
Detailed Explanation
In a capitalist economy, private individuals, rather than the government, own the resources and industries that produce goods and services. This means that people are free to use their property as they wish, leading to innovation and entrepreneurial activities.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine an artist who creates paintings. In a capitalist economy, the artist has the freedom to sell their work as they please. They decide how much their paintings cost, whom to sell to, and how to promote their art, illustrating personal ownership and control.
Main Features of a Capitalist Economy
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Main Features:
- Private ownership of property and resources
- Freedom of choice and enterprise
- Profit motive is the driving force
- Minimal government interference
- Prices determined by market forces (demand and supply)
Detailed Explanation
The main features of a capitalist economy emphasize individual rights and autonomous decision-making. For example, individuals can own businesses, choose what to produce, and set prices based on what consumers are willing to pay. The goal is to generate profits, which is a key motivation for entrepreneurs. Additionally, the market is largely self-regulating, with minimal involvement from government authorities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a farmer selling crops at a local market. The farmer decides how many crops to grow based on demand and sets his prices. If he grows apples, and the demand is high, he might increase prices. This situation illustrates how prices are determined through supply and demand, a core principle of capitalism.
Examples of Capitalist Economies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Examples: United States, Australia, Japan
Detailed Explanation
Countries like the United States, Australia, and Japan are prime examples of capitalist economies. In these nations, businesses operate with relative freedom from government control, and individuals have significant rights to own and operate property. Each of these countries has developed robust markets supported by a framework of laws that protect property rights and promote business.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the tech companies in the United States, such as Apple and Google. They were started by individuals who had innovative ideas and capital, reflecting the entrepreneurial spirit of capitalism. These companies thrive in an environment that encourages innovation and profit-maximization.
Key Concepts
-
Private Ownership: Refers to resources being owned by individuals rather than the government.
-
Public Ownership: Refers to resources being owned by the government or society as a whole.
-
Profit Motive: The drive for financial gain and profit magnifying entrepreneurship in a capitalist economy.
-
Welfare of Society: A primary goal of socialist economies aimed at improving the living standards of all citizens.
Examples & Applications
The United States operates as a capitalist economy where private enterprises thrive.
Cuba exemplifies a socialist economy where the government controls production and distribution.
India represents a mixed economy with both private businesses and government enterprises coexisting.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a capitalist land, the profit stands, while in socialism, welfare expands.
Stories
Imagine a village where everyone shares resources equally—this is socialism. Now picture a bustling market where every stall is privately owned, selling goods for profit—this is capitalism.
Memory Tools
For economies: C for Capitalism, P for Profit; S for Socialism, S for Society; M for Mixed, M for Manage.
Acronyms
PWS
Private Wealth in Socialism.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where production means are privately owned and operated for profit.
- Socialist Economy
An economic system where production means are owned and controlled by the government to ensure societal welfare.
- Mixed Economy
An economic system combining elements of both capitalism and socialism, allowing for both private and public sector engagement.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
