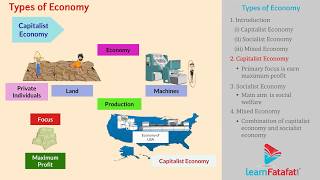
Socialist Economy
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Socialist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by defining a socialist economy. Who can tell me what it means?

Isn't it when the government controls everything?

Exactly! In a socialist economy, the government owns and controls the means of production. This aims to prioritize social welfare over individual profit.

So, there is no private property?

Correct! Public ownership means people do not own production resources privately. This leads to a system focused on equality.

What about how a socialist economy is planned?

Good question! In a socialist economy, economic activities are centrally planned by the government. They decide what to produce and how to distribute it to achieve societal goals.

What if the government makes poor decisions?

That's a concern. Central planning can lead to inefficiencies if the government fails to meet the people’s needs.

In summary, a socialist economy focuses on public control, planning, and equal distribution of resources.
Main Features of Socialist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the main features of a socialist economy. Can anyone name one?

Public ownership?

Correct! Public ownership is a key feature. This means resources are owned collectively rather than privately, ensuring that wealth is shared among citizens.

What about profit? Is there none?

Exactly! There's no profit motive. The primary goal is societal welfare, not making money.

Does that mean everyone earns the same?

Not necessarily the same, but the focus is on reducing income inequality through equal distribution efforts.

That sounds fair, but can it work?

It can lead to benefits like reduced poverty, but also risks like lack of innovation due to no competition. It's a complex balance.

In summary, the features of a socialist economy emphasize public control, welfare, equality, and central planning.
Examples of Socialist Economies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at some real-world examples of socialist economies. Can anyone name one?

Cuba?

Correct! Cuba is a well-known example where the government controls most production sectors.

What about North Korea?

Yes, North Korea is another example where the socialist framework leads to strict government control over resources and economic activities.

What happened to the Soviet Union?

The Soviet Union had a strong socialist economy until its collapse in 1991. It illustrates both the strengths and weaknesses of such a system.

So, is socialism a failure?

Not necessarily. It emphasizes social welfare. However, the lack of competition and government inefficiencies can pose significant challenges.

In summary, key examples include Cuba, North Korea, and the former Soviet Union, each showcasing different aspects of socialist economies.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In a socialist economy, the government owns and controls the means of production. It operates under principles of central planning, with no profit motive and an emphasis on the equitable distribution of wealth among citizens, contrasting strongly with capitalist systems. Countries like Cuba and North Korea serve as prominent examples.
Detailed
Socialist Economy
A socialist economy is characterized by public ownership of property and resources, directly controlled and managed by the government. In contrast to capitalist economies where the profit motive drives individual enterprise, socialist economies prioritize the welfare of society as a whole. Key features of a socialist economy include central planning, a lack of competition, and the goal of equal distribution of income and wealth among citizens.
Main Features of Socialist Economy:
- Public Ownership: The government owns and operates resources and means of production.
- Central Planning: Economic activities are planned and regulated by the government to ensure that community needs are met.
- No Profit Motive: Unlike capitalism, where profit drives enterprise, socialist economies focus on social welfare.
- Equal Distribution: Wealth and resources are distributed more equally among the population to mitigate class differences.
- No Competition: The government decides production and distribution, leading to the absence of competition.
Examples: Countries such as the former Soviet Union, North Korea, and Cuba exemplify socialist economies, focusing exclusively on government control over the economy.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Socialist Economy
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Definition: An economy where the means of production are owned and controlled by the government.
Detailed Explanation
In a socialist economy, the government directly owns and controls the resources and means of production. This means that industries, factories, and natural resources belong to the state rather than private individuals. The goal is to ensure that everyone has access to these resources and that they are used in a way that benefits society as a whole.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a large community garden where the community decides together what to plant and how to distribute the produce. In this setting, the produce is owned collectively, which is similar to how resources are managed in a socialist economy.
Main Features of Socialist Economy
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Main Features:
○ Public ownership of property and resources
○ Central planning by the government
○ No profit motive – welfare of society is the goal
○ Equal distribution of income and wealth
○ No competition; production decided by government plans
Detailed Explanation
The socialist economy has several distinct characteristics:
1. Public Ownership: All major resources and industries are owned by the government, which means profits are not the main concern; instead, resources are used for public welfare.
2. Central Planning: The government plays a significant role in planning the economy, making decisions about production and distribution to meet the needs of society.
3. Welfare Focus: Unlike capitalist economies that prioritize profit, socialist economies aim for the well-being of all citizens, ensuring everyone has access to basic needs.
4. Income Equality: The government works to reduce economic inequality by distributing wealth more evenly among the population.
5. Lack of Competition: Since production is governed by the plans made by the state, there is little room for competition among businesses, as the focus is on fulfilling social goals rather than competing for profits.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a school where all students share textbooks provided by the school. The textbooks are not sold for profit but are available to everyone equally, ensuring that all students, regardless of their background, have access to the same learning materials.
Examples of Socialist Economies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Examples: Former Soviet Union, North Korea, Cuba
Detailed Explanation
Several countries have implemented socialist principles within their economies. The former Soviet Union is one of the most notable examples, where the state controlled all aspects of economic life. North Korea follows a strict socialist model, focusing on state control over production and distribution. Similarly, Cuba has a socialist economy where the government owns most of the resources, and the aim is to provide for the citizens rather than generate profit.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a country as a big house where the government is the caretaker. In the former Soviet Union, this caretaker tried to manage every room (industry) and resource (natural wealth) to ensure all family members (citizens) had what they needed, prioritizing sharing over financial gain.
Key Concepts
-
Public Ownership: The government owns the production means.
-
Central Planning: Economic decisions are made by the government.
-
Welfare Orientation: Focus primarily on societal welfare instead of profit.
-
Equal Distribution: Aim to minimize income inequalities.
Examples & Applications
Cuba's economy is primarily controlled by the government.
The former Soviet Union implemented extensive central planning in production.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Socialism is great for sharing, with government caring, production's planned, so no need for daring!
Stories
Imagine a gardener (the government) that takes care of a community garden (society) where everyone shares fruits and vegetables, ensuring no one is left hungry. This gardener plans every planting to ensure each vegetable gets enough space.
Memory Tools
Remember 'P-C-W-E': Public ownership, Central planning, Welfare focus, and Equal distribution.
Acronyms
The acronym 'PCE' can be used to remember the core aspects
Public ownership
Central planning
and Economic equality.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Socialist Economy
An economic system where the means of production are owned and controlled by the government.
- Public Ownership
Ownership of production and resources by the government on behalf of the community.
- Central Planning
An economic system in which the government makes all decisions regarding the production and distribution of goods.
- Profit Motive
The drive for financial gain that motivates the operations of businesses in capitalist economies.
- Income Distribution
The way in which a nation’s total income is distributed among its population.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
