Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Economic Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're wrapping up our exploration of the three primary types of economies: capitalist, socialist, and mixed. Let's dive into how each type contributes to the economy.

What are the main strengths of having a mixed economy?

Great question! A mixed economy combines the efficiency of the market found in capitalist economies with the equity considerations of socialist economies. This blend aims to harness the best of both worlds.

What would be some challenges of a capitalist economy?

In a capitalist system, while there’s high efficiency and innovation, it can lead to issues like inequality and lack of access to basic services. Remember, capitalist economies prioritize profit, which can sometimes overlook social welfare.

Can you give us an example of a country that uses a mixed economy?

Of course! India is an excellent example of a mixed economy, where both public and private sectors play significant roles in the economic landscape.

So, is the mixed economy the best option for every country?

It often depends on a country's specific needs, resources, and political climate. However, most nations are currently leaning towards this model to achieve a balance between economic growth and social equity.

In summary, understanding these economic types equips us to engage with current economic debates and policies more thoughtfully.
Impacts of Economic Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve deeper into how economic systems affect societal dynamics. For example, how does socialism promote equity?

I think it’s because resources are shared more equally.

Exactly! Socialism aims for a fair distribution of wealth, which can reduce income gaps among the population. However, can anyone point out a potential downside?

There might be less incentive for individuals to work harder since the profit isn't a motivator.

Spot on! While aiming for equality, sometimes these systems can dampen individual motivation and innovation. Now, how does a capitalist system encourage growth?

By incentivizing businesses to create more and improve services or products.

Correct! The profit motive in capitalism drives innovation and efficiency, but it’s important to strike a balance, especially when disparities arise.

That’s where the mixed economy comes in again!

Right! By blending elements, a mixed economy can promote growth while ensuring fairness. Always remember, understanding these systems helps us evaluate real-world economies.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In conclusion, each type of economy, whether capitalist, socialist, or mixed, has unique strengths and weaknesses. The contemporary trend is toward mixed economies, which seek to leverage the efficiency of markets while ensuring social equity through government intervention.
Detailed
Conclusion
In the realm of economic systems, each type of economy presents its own set of merits and challenges. Capitalist economies emphasize private ownership and market-driven approaches, while socialist economies focus on public ownership and centrally planned distribution of resources. The mixed economy model, which incorporates elements from both systems, has become prevalent in today's world. This approach aims to optimize market efficiency while promoting social welfare, illustrating a balanced strategy to address the diverse economic needs of nations. Understanding these fundamental economies enables one to appreciate the broader implications of economic policies and their societal impacts.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Merits and Limitations of Economies
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Each type of economy has its own merits and limitations.
Detailed Explanation
This statement means that every economic system comes with its strengths and weaknesses. For instance, a capitalist economy promotes innovation and individual success due to the profit motive, but can also lead to inequality. On the other hand, a socialist economy aims to distribute wealth more equally but may lack the same level of efficiency and innovation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of different types of schools: a private school might offer excellent resources but be expensive, while a public school aims to be inclusive for everyone but may have limited funding. Similarly, different economic systems prioritize various goals and outcomes.
Adoption of Mixed Economy Model
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Most countries today follow the mixed economy model to combine the efficiency of the market with the equity of government control.
Detailed Explanation
The mixed economy model includes aspects of both capitalism and socialism. This means that governments intervene in certain areas like healthcare and education to promote fairness and welfare, while still allowing free market principles to operate in others, like consumer goods. This approach aims to balance the positives of both systems, leveraging the strengths of a market-driven environment while ensuring that basic needs are met.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bakery that makes both artisanal bread (market-driven) and provides subsidized bread for low-income families (government control). This way, the bakery can thrive while also serving the community's needs.
Key Concepts
-
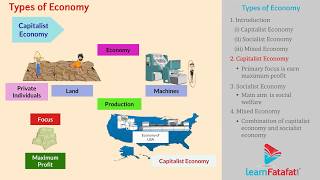
Capitalist Economy: An economy emphasizing private ownership and market-driven profits.
-
Socialist Economy: An economy where the government controls production for societal welfare.
-
Mixed Economy: A combination of public and private sectors aiming for balance.
-
Market Efficiency: The idea of optimizing output through free-market principles.
Examples & Applications
The United States exemplifies a capitalist economy, characterized by minimal government intervention.
North Korea represents a socialist economy, where the government controls all economic activities.
India is a mixed economy, where agriculture and key industries are often managed by the government.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the land of market drive, capitalist economies thrive.
Stories
Imagine a town where the baker shares equally with all; that's the spirit of socialism, where none feel small.
Memory Tools
MIX for Mixed Economy: Market efficiency, Inclusion, and eXtraction of social equity.
Acronyms
PES for types of economies
Private (Capitalist)
Equal (Socialist)
Shared (Mixed).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where private individuals own and control the means of production.
- Socialist Economy
An economic system where the government owns and controls the means of production.
- Mixed Economy
An economic system combining both private and public enterprises.
- Market Forces
Economic factors that affect the price of goods and services through supply and demand.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
